Molecular polymorphism of Abeta in Alzheimer's disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Molecular polymorphism of Abeta in Alzheimer's disease
Harry Levine 3rd et al. Neurobiol Aging. 2010 Apr.
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease is defined pathologically by the presence of senile plaques, which consist primarily of extracellular aggregates of fibrillar Abeta peptide, and neurofibrillary tangles, which are abnormal, intracellular bundles of fibrillar tau protein. The advent of amyloid binding agents as diagnostic imaging probes for Alzheimer's disease (AD) has made it imperative to understand at a molecular and disease level what these ligands are reporting. In addition to improving the accuracy of diagnosis, we argue that these selective ligands can serve as probes for molecular polymorphisms that may govern the pathogenicity of abnormal protein aggregates.
Copyright (c) 2008 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no actual or potential conflicts of interest for the views expressed in this manuscript
Figures
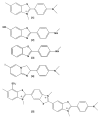
Figure 1
Amyloid-Binding Ligands
- [1]
Thioflavine T - [2]
PIB1 - [3]
BTA-1 - [4]
IMPY - [5]
Thioflavine S (mixture) - [6]
Congo Red - [7]
Chrysamine G - [8]
X-34 - [9]
BSB
Figure 1
Amyloid-Binding Ligands
- [1]
Thioflavine T - [2]
PIB1 - [3]
BTA-1 - [4]
IMPY - [5]
Thioflavine S (mixture) - [6]
Congo Red - [7]
Chrysamine G - [8]
X-34 - [9]
BSB
Similar articles
- Curcumin inhibits formation of amyloid beta oligomers and fibrils, binds plaques, and reduces amyloid in vivo.
Yang F, Lim GP, Begum AN, Ubeda OJ, Simmons MR, Ambegaokar SS, Chen PP, Kayed R, Glabe CG, Frautschy SA, Cole GM. Yang F, et al. J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 18;280(7):5892-901. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404751200. Epub 2004 Dec 7. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15590663 - Synthesis of Thiophene-Based Optical Ligands That Selectively Detect Tau Pathology in Alzheimer's Disease.
Shirani H, Appelqvist H, Bäck M, Klingstedt T, Cairns NJ, Nilsson KPR. Shirani H, et al. Chemistry. 2017 Dec 1;23(67):17127-17135. doi: 10.1002/chem.201703846. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Chemistry. 2017. PMID: 28926133 Free PMC article. - Synthesis of biphenyltrienes as probes for beta-amyloid plaques.
Zhuang ZP, Kung MP, Kung HF. Zhuang ZP, et al. J Med Chem. 2006 May 4;49(9):2841-4. doi: 10.1021/jm051020k. J Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16640346 Free PMC article. - [The pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease with special reference to "amyloid cascade hypothesis"].
Tamaoka A. Tamaoka A. Rinsho Byori. 2013 Nov;61(11):1060-9. Rinsho Byori. 2013. PMID: 24450113 Review. Japanese. - [Molecular imaging of beta-amyloid plaques in the brain].
Ono M. Ono M. Brain Nerve. 2007 Mar;59(3):233-40. Brain Nerve. 2007. PMID: 17370649 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
- In vivo PET imaging of beta-amyloid deposition in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease with a high specific activity PET imaging agent [(18)F]flutemetamol.
Snellman A, Rokka J, López-Picón FR, Eskola O, Salmona M, Forloni G, Scheinin M, Solin O, Rinne JO, Haaparanta-Solin M. Snellman A, et al. EJNMMI Res. 2014 Aug 1;4:37. doi: 10.1186/s13550-014-0037-3. eCollection 2014. EJNMMI Res. 2014. PMID: 25977876 Free PMC article. - Self-propagation of pathogenic protein aggregates in neurodegenerative diseases.
Jucker M, Walker LC. Jucker M, et al. Nature. 2013 Sep 5;501(7465):45-51. doi: 10.1038/nature12481. Nature. 2013. PMID: 24005412 Free PMC article. Review. - Context dependence of protein misfolding and structural strains in neurodegenerative diseases.
Mehta AK, Rosen RF, Childers WS, Gehman JD, Walker LC, Lynn DG. Mehta AK, et al. Biopolymers. 2013 Nov;100(6):722-30. doi: 10.1002/bip.22283. Biopolymers. 2013. PMID: 23893572 Free PMC article. - The existence of Aβ strains and their potential for driving phenotypic heterogeneity in Alzheimer's disease.
Lau HHC, Ingelsson M, Watts JC. Lau HHC, et al. Acta Neuropathol. 2021 Jul;142(1):17-39. doi: 10.1007/s00401-020-02201-2. Epub 2020 Aug 2. Acta Neuropathol. 2021. PMID: 32743745 Review. - Deficient high-affinity binding of Pittsburgh compound B in a case of Alzheimer's disease.
Rosen RF, Ciliax BJ, Wingo TS, Gearing M, Dooyema J, Lah JJ, Ghiso JA, LeVine H 3rd, Walker LC. Rosen RF, et al. Acta Neuropathol. 2010 Feb;119(2):221-33. doi: 10.1007/s00401-009-0583-3. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Acta Neuropathol. 2010. PMID: 19690877 Free PMC article.
References
- Aguzzi A, Heikenwalder M, Polymenidou M. Insights into prion strains and neurotoxicity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(7):552–61. - PubMed
- Aslund A, Herland A, Hammarstrom P, Nilsson KP, Jonsson BH, Inganas O, Konradsson P. Studies of Luminescent Conjugated Polythiophene Derivatives: Enhanced Spectral Discrimination of Protein Conformational States. Bioconjug Chem. 2007 - PubMed
- Attems J, Lintner F, Jellinger KA. Amyloid beta peptide 1-42 highly correlates with capillary cerebral amyloid angiopathy and Alzheimer disease pathology. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 2004;107(4):283–91. - PubMed
- Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arvanitakis Z, Kelly JF, Aggarwal NT, Shah RC, Wilson RS. Neuropathology of older persons without cognitive impairment from two community-based studies. Neurology. 2006;66(12):1837–44. - PubMed
- Bierer LM, Hof PR, Purohit DP, Carlin L, Schmeidler J, Davis KL, Perl DP. Neocortical neurofibrillary tangles correlate with dementia severity in Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Neurol. 1995;52(1):81–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AG026423-01A2/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG005119/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000165/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG005119-20A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000165-47/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026423/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RR-00165/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical