Surveillance for neuraminidase inhibitor resistance among human influenza A and B viruses circulating worldwide from 2004 to 2008 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Surveillance for neuraminidase inhibitor resistance among human influenza A and B viruses circulating worldwide from 2004 to 2008
Tiffany G Sheu et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Sep.
Abstract
The surveillance of seasonal influenza virus susceptibility to neuraminidase (NA) inhibitors was conducted using an NA inhibition assay. The 50% inhibitory concentration values (IC(50)s) of 4,570 viruses collected globally from October 2004 to March 2008 were determined. Based on mean IC(50)s, A(H3N2) viruses (0.44 nM) were more sensitive to oseltamivir than A(H1N1) viruses (0.91 nM). The opposite trend was observed with zanamivir: 1.06 nM for A(H1N1) and 2.54 nM for A(H3N2). Influenza B viruses exhibited the least susceptibility to oseltamivir (3.42 nM) and to zanamivir (3.87 nM). To identify potentially resistant viruses (outliers), a threshold of a mean IC(50) value + 3 standard deviations was defined for type/subtype and drug. Sequence analysis of outliers was performed to identify NA changes that might be associated with reduced susceptibility. Molecular markers of oseltamivir resistance were found in six A(H1N1) viruses (H274Y) and one A(H3N2) virus (E119V) collected between 2004 and 2007. Some outliers contained previously reported mutations (e.g., I222T in the B viruses), while other mutations [e.g., R371K and H274Y in B viruses and H274N in A(H3N2) viruses) were novel. The R371K B virus outlier exhibited high levels of resistance to both inhibitors (>100 nM). A substantial variance at residue D151 was observed among A(H3N2) zanamivir-resistant outliers. The clinical relevance of newly identified NA mutations is unknown. A rise in the incidence of oseltamivir resistance in A(H1N1) viruses carrying the H274Y mutation was detected in the United States and in other countries in the ongoing 2007 to 2008 season. As of March 2008, the frequency of resistance among A(H1N1) viruses in the United States was 8.6% (50/579 isolates). The recent increase in oseltamivir resistance among A(H1N1) viruses isolated from untreated patients raises public health concerns and necessitates close monitoring of resistance to NA inhibitors.
Figures
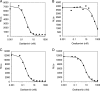
FIG. 1.
Assessment of the IC50s for oseltamivir, using the chemiluminescent NAI assay. (A) Oseltamivir-sensitive A/Massachusetts/6/2006 (H1N1) virus; (B) oseltamivir-resistant A/Massachusetts/5/2007 (H1N1) virus with the mutation H274Y; (C) oseltamivir-sensitive A/Washington/1/2007 (H3N2) virus; (D) oseltamivir-resistant A/Texas/12/2007(H3N2) virus with the E119V mutation. x axis, NA activity in relative light units (RLUs). y axis, oseltamivir concentrations (nM) on a logarithmic scale. Data points indicate actual activity measured at a single time point using a plate reader, Victor 3V. The data line represents the best-fit curve generated using Robosage software.
Similar articles
- Neuraminidase inhibitor susceptibility profile of pandemic and seasonal influenza viruses during the 2009-2010 and 2010-2011 influenza seasons in Japan.
Dapat C, Kondo H, Dapat IC, Baranovich T, Suzuki Y, Shobugawa Y, Saito K, Saito R, Suzuki H. Dapat C, et al. Antiviral Res. 2013 Sep;99(3):261-9. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.003. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Antiviral Res. 2013. PMID: 23791870 - Neuraminidase inhibitor susceptibility surveillance of influenza viruses circulating worldwide during the 2011 Southern Hemisphere season.
Okomo-Adhiambo M, Sleeman K, Lysén C, Nguyen HT, Xu X, Li Y, Klimov AI, Gubareva LV. Okomo-Adhiambo M, et al. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2013 Sep;7(5):645-58. doi: 10.1111/irv.12113. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23575174 Free PMC article. - Evolution of the neuraminidase gene of seasonal influenza A and B viruses in Thailand between 2010 and 2015.
Tewawong N, Vichiwattana P, Korkong S, Klinfueng S, Suntronwong N, Thongmee T, Theamboonlers A, Vongpunsawad S, Poovorawan Y. Tewawong N, et al. PLoS One. 2017 Apr 14;12(4):e0175655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175655. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28410396 Free PMC article. - Influenza neuraminidase inhibitors: antiviral action and mechanisms of resistance.
McKimm-Breschkin JL. McKimm-Breschkin JL. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2013 Jan;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):25-36. doi: 10.1111/irv.12047. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23279894 Free PMC article. Review. - Laninamivir octanoate: a new long-acting neuraminidase inhibitor for the treatment of influenza.
Ikematsu H, Kawai N. Ikematsu H, et al. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2011 Oct;9(10):851-7. doi: 10.1586/eri.11.112. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2011. PMID: 21973296 Review.
Cited by
- Genetic characterization of influenza B virus and oseltamivir resistance in pediatric patients with acute respiratory infections: a cross-sectional study.
Alizadeh S, Edalat F, Letafati A, Pirbonyeh N, Tabibzadeh A, Mousavizadeh L, Moattari A, Karbalaie Niya MH. Alizadeh S, et al. Virus Genes. 2024 Nov 5. doi: 10.1007/s11262-024-02119-x. Online ahead of print. Virus Genes. 2024. PMID: 39499431 - A Novel Prodrug Strategy Based on Reversibly Degradable Guanidine Imides for High Oral Bioavailability and Prolonged Pharmacokinetics of Broad-Spectrum Anti-influenza Agents.
Jung Y, Ahn SB, An T, Cha HM, Kim M, Cheon H, Jang Y, Lee H, Kim B, Kim M, Lee Y. Jung Y, et al. ACS Cent Sci. 2024 Jul 4;10(8):1573-1584. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c00548. eCollection 2024 Aug 28. ACS Cent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39220698 Free PMC article. - Impact of the H274Y Substitution on N1, N4, N5, and N8 Neuraminidase Enzymatic Properties and Expression in Reverse Genetic Influenza A Viruses.
Gaymard A, Picard C, Vazzoler G, Massin P, Frobert E, Sabatier M, Barthelemy M, Valette M, Ottmann M, Casalegno JS, Lina B, Escuret V. Gaymard A, et al. Viruses. 2024 Mar 1;16(3):388. doi: 10.3390/v16030388. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543754 Free PMC article. - Molecular Determinants of Drug Resistance and Mutation Patterns in Influenza Viruses Circulating in Poland Across Multiple Epidemic Seasons: Implications for Vaccination Strategies.
Hallmann E, Masny A, Poznańska A, Pozo F, Casas I, Brydak LB. Hallmann E, et al. Med Sci Monit. 2024 Mar 6;30:e942125. doi: 10.12659/MSM.942125. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 38446736 Free PMC article. - Genomic Analyses Uncover Evolutionary Features of Influenza A/H3N2 Viruses in Yunnan Province, China, from 2017 to 2022.
Zhang M, Zhou J, Ni R, Zhao X, Chen Y, Sun Y, Liu Z, Han X, Luo C, Fu X, Shao Y. Zhang M, et al. Viruses. 2024 Jan 18;16(1):138. doi: 10.3390/v16010138. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38257838 Free PMC article.
References
- Baum, E. Z., P. C. Wagaman, L. Ly, I. Turchi, J. Le, D. Bucher, and K. Bush. 2003. A point mutation in influenza B neuraminidase confers resistance to peramivir and loss of slow binding. Antivir. Res. 59:13-22. - PubMed
- Baz, M., Y. Abed, J. McDonald, and G. Boivin. 2006. Characterization of multidrug-resistant influenza A/H3N2 viruses shed during 1 year by an immunocompromised child. Clin. Infect. Dis. 43:1555-1561. - PubMed
- Bright, R. A., M. J. Medina, X. Xu, G. Perez-Oronoz, T. R. Wallis, X. M. Davis, L. Povinelli, L. Cox, and A. I. Klimov. 2005. Incidence of adamantane resistance among influenza A (H3N2) viruses isolated worldwide from 1994 to 2005: a cause for concern. Lancet 366:1175-1181. - PubMed
- Bright, R. A., D. Shay, J. Bresee, A. Klimov, N. Cox, and J. Ortiz. 2006. High levels of adamantane resistance among influenza A(H3N2) viruses and interim guidelines for use of antiviral agents: United States, 2005-06 influenza season. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 55:44-46. - PubMed
- Bright, R. A., D. K. Shay, B. Shu, N. J. Cox, and A. I. Klimov. 2006. Adamantane resistance among influenza A viruses isolated early during the 2005-2006 influenza season in the United States. JAMA 295:891-894. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials