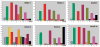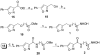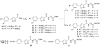Use of the nitrile oxide cycloaddition (NOC) reaction for molecular probe generation: a new class of enzyme selective histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) showing picomolar activity at HDAC6 - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2008 Aug 14;51(15):4370-3.
doi: 10.1021/jm8002894. Epub 2008 Jul 22.
Affiliations
- PMID: 18642892
- PMCID: PMC3913184
- DOI: 10.1021/jm8002894
Use of the nitrile oxide cycloaddition (NOC) reaction for molecular probe generation: a new class of enzyme selective histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) showing picomolar activity at HDAC6
Alan P Kozikowski et al. J Med Chem. 2008.
Abstract
A series of hydroxamate based HDAC inhibitors containing a phenylisoxazole as the CAP group has been synthesized using nitrile oxide cycloaddition chemistry. An HDAC6 selective inhibitor having a potency of approximately 2 picomolar was identified. Some of the compounds were examined for their ability to block pancreatic cancer cell growth and found to be about 10-fold more potent than SAHA. This research provides valuable, new molecular probes for use in exploring HDAC biology.
Figures
Figure 1
General structural features of compounds 1–11.
Figure 2
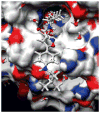
Compound 7 docked into the binding site of the current HDAC6 homology model.
Chart 1. Comparison of IC50 (nM) Values of Compounds 1–11 and SAHA against Class I and Class II HDACs
Scheme 1. Synthesis of Compounds 15–17a
a Reactions and conditions: (a) ethyl chlorooximidoacetate, triethylamine, THF, rt, 16 h; (b) (Boc)2O, THF, reflux, 16 h.
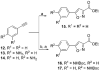
Scheme 2. Synthesis of Compounds 1 and 2a
a Reagents and conditions: (a) NaBH4, MeOH, rt, 30 min; (b) NaH (60%), DMF, 0 °C to rt, 1 h then methyl 5-bromovalerate, 0 to 70 °C, 12 h; (c) NH2OH·HCl, KOH, MeOH, rt, 15 min; (d) LiOH, THF, MeOH, H2O, 0 °C to rt, 1 h; (e) HCl·NH2(CH2)4COOMe, EDCI, HOBT, DIEA, DMF, 0 °C to rt, 12 h.
Scheme 3. Synthesis of Compounds 3–11a
a Reagents and conditions: (a) LiOH, THF, MeOH, H2O, 0 °C to rt, 1 h; (b) HCl·NH2(CH2)_n_COOMe, EDCI, HOBT, DIEA, DMF, 0 °C to rt, 12 h; (c) NH2OH·HCl, KOH, MeOH, rt, 15 min; (d) TFA, CH2Cl2, 0 °C to rt, 2 h; (e) Ac2O, pyridine, CH2Cl2, 0 °C to rt, 5 h.
Similar articles
- Optimization of activity-based probes for proteomic profiling of histone deacetylase complexes.
Salisbury CM, Cravatt BF. Salisbury CM, et al. J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Feb 20;130(7):2184-94. doi: 10.1021/ja074138u. Epub 2008 Jan 25. J Am Chem Soc. 2008. PMID: 18217751 - Design and synthesis of non-hydroxamate histone deacetylase inhibitors: identification of a selective histone acetylating agent.
Suzuki T, Matsuura A, Kouketsu A, Hisakawa S, Nakagawa H, Miyata N. Suzuki T, et al. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005 Jul 1;13(13):4332-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2005.04.002. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 15927839 - Design, synthesis, and evaluation of cyclic amide/imide-bearing hydroxamic acid derivatives as class-selective histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors.
Shinji C, Maeda S, Imai K, Yoshida M, Hashimoto Y, Miyachi H. Shinji C, et al. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006 Nov 15;14(22):7625-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2006.07.008. Epub 2006 Jul 31. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16877001 - Non-hydroxamate histone deacetylase inhibitors.
Suzuki T, Miyata N. Suzuki T, et al. Curr Med Chem. 2005;12(24):2867-80. doi: 10.2174/092986705774454706. Curr Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16305476 Review. - Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors with Anticancer Activity.
Ma N, Luo Y, Wang Y, Liao C, Ye WC, Jiang S. Ma N, et al. Curr Top Med Chem. 2016;16(4):415-26. doi: 10.2174/1568026615666150813145629. Curr Top Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26268343 Review.
Cited by
- Pharmacophore-based virtual screening of ZINC database, molecular modeling and designing new derivatives as potential HDAC6 inhibitors.
Poonia P, Sharma M, Jha P, Chopra M. Poonia P, et al. Mol Divers. 2023 Oct;27(5):2053-2071. doi: 10.1007/s11030-022-10540-3. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Mol Divers. 2023. PMID: 36214962 - Preclinical activity, pharmacodynamic, and pharmacokinetic properties of a selective HDAC6 inhibitor, ACY-1215, in combination with bortezomib in multiple myeloma.
Santo L, Hideshima T, Kung AL, Tseng JC, Tamang D, Yang M, Jarpe M, van Duzer JH, Mazitschek R, Ogier WC, Cirstea D, Rodig S, Eda H, Scullen T, Canavese M, Bradner J, Anderson KC, Jones SS, Raje N. Santo L, et al. Blood. 2012 Mar 15;119(11):2579-89. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-10-387365. Epub 2012 Jan 19. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22262760 Free PMC article. - New insights into the treatment of multiple myeloma with histone deacetylase inhibitors.
Cea M, Cagnetta A, Gobbi M, Patrone F, Richardson PG, Hideshima T, Anderson KC. Cea M, et al. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(4):734-44. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23016853 Free PMC article. Review. - Human ATP-binding cassette transporters ABCB1 and ABCG2 confer resistance to histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor ricolinostat (ACY-1215) in cancer cell lines.
Wu CP, Hsieh YJ, Murakami M, Vahedi S, Hsiao SH, Yeh N, Chou AW, Li YQ, Wu YS, Yu JS, Ambudkar SV. Wu CP, et al. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;155:316-325. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.07.018. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30028995 Free PMC article. - Direct effects of non-antifungal agents used in cancer chemotherapy and organ transplantation on the development and virulence of Candida and Aspergillus species.
Chen SC, Lewis RE, Kontoyiannis DP. Chen SC, et al. Virulence. 2011 Jul-Aug;2(4):280-95. doi: 10.4161/viru.2.4.16764. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Virulence. 2011. PMID: 21701255 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Butler KV, Kozikowski AP. Chemical origins of isoform selectivity in histone deacetylase inhibitors. Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14:505–528. - PubMed
- Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2006;5:769–784. and references cited therein. - PubMed
- Paris M, Porcelloni M, Binaschi M, Fattori D. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: From Bench to Clinic. J Med Chem. 2008;51:1505–1528. - PubMed
- Grunstein M. Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription. Nature. 1997;389:349–352. - PubMed
- Wolffe AP, Guschin D. Review: Chromatin structural features and targets that regulate transcription. J Struct Biol. 2000;129:102–122. - PubMed
- Kurdistani SK, Grunstein M, Grunstein M. Histone acetylation and deacetylation in yeast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:276–284. - PubMed
- Struhl K, Moqtaderi Z. The TAFs in the HAT. Cell. 1998;94:1–4. - PubMed
- Marks PA, Richon VM, Rifkind RA. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: inducers of differentiation or apoptosis of transformed cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:1210–1216. - PubMed
- Kelly WK, Zhu AX, Scher H, Curley T, Fallon M, Slovin S, Schwartz L, Larson S, Tong W, Hartley-Asp B, Pellizzoni C, Rocchetti M. Dose escalation study of intravenous estramustine phosphate in combination with Paclitaxel and Carboplatin in patients with advanced prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:2098. - PubMed
- Carducci MA, Gilbert J, Bowling MK, Noe D, Eisenberger MA, Sinibaldi V, Zabelina Y, Chen TL, Grochow LB, Donehower RC. Phase I clinical and pharmacological evaluation of sodium phenylbutyrate on an 120 h infusion schedule. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:3047–3055. - PubMed
- Sasakawa Y, Naoe Y, Inoue T, Sasakawa T, Matsuo M, Manda T, Mutoh S. Effects of FK228, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, on human lymphoma U-937 cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002;64:1079–1090. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous