Transcriptional regulation of neuronal differentiation: the epigenetic layer of complexity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Transcriptional regulation of neuronal differentiation: the epigenetic layer of complexity
Mary E Hamby et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Aug.
Abstract
The transcriptional programs of neural progenitor cells change dynamically during neurogenesis, a process regulated by both intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Although many of the transcription factors required for neuronal differentiation have long been identified, we are only at the brink of understanding how epigenetic mechanisms influence transcriptional activity and the accessibility of transcription factors to bind consensus cis-elements. Herein, we delineate the chief epigenetic modifications and the machinery responsible for these alterations. Further, we review the epigenetic modifications presently known to participate in the maintenance of the neural progenitor cell state and in the regulation of neuronal differentiation.
Figures
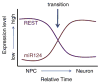
Fig. 1
Key events in the NPC to neuron transition. During neurogenesis, many events in the cell are orchestrated to ensure proper neuronal differentiation. Although there are a number of players, miR-124 expression and the downregulation of REST play key roles in globally decreasing expression of non-neuronal genes while simultaneously enhancing neuron-specific gene expression. When REST expression is downregulated, this enables the derepression of numerous pro-neuronal genes allowing for pro-neural bHLHs to instigate the further induction of neuronal genes. Moreover, dismissal of REST from the RE1 sites on miR-124 eradicates the silencing effect that REST has on miR-124 [57], allowing for induction of miR-124 expression. Once miR-124 is induced, it can then degrade its numerous non-neuronal targets [57,76]. Collectively, the downregulation of REST and upregulation of miRNA provide a swift transition from NPC to neuron.
Similar articles
- Temporal and epigenetic regulation of neurodevelopmental plasticity.
Allen ND. Allen ND. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2008 Jan 12;363(1489):23-38. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2006.2010. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2008. PMID: 17311782 Free PMC article. Review. - Epigenetic choreographers of neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain.
Ma DK, Marchetto MC, Guo JU, Ming GL, Gage FH, Song H. Ma DK, et al. Nat Neurosci. 2010 Nov;13(11):1338-44. doi: 10.1038/nn.2672. Nat Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20975758 Free PMC article. Review. - Aging and neuronal replacement.
Brazel CY, Rao MS. Brazel CY, et al. Ageing Res Rev. 2004 Nov;3(4):465-83. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2004.04.003. Ageing Res Rev. 2004. PMID: 15541712 Review. - Transcriptional regulation of neuronal phenotype in mammals.
Ma Q. Ma Q. J Physiol. 2006 Sep 1;575(Pt 2):379-87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.113449. Epub 2006 Jul 6. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16825304 Free PMC article. Review. - The many faces of REST oversee epigenetic programming of neuronal genes.
Ballas N, Mandel G. Ballas N, et al. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2005 Oct;15(5):500-6. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2005.08.015. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16150588 Review.
Cited by
- Direct Potential Modulation of Neurogenic Differentiation Markers by Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) in the Rodent Brain.
Kozole J, Heydn R, Wirkert E, Küspert S, Aigner L, Bruun TH, Bogdahn U, Peters S, Johannesen S. Kozole J, et al. Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 2;14(9):1858. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091858. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36145606 Free PMC article. - ZMYND8 suppresses MAPT213 LncRNA transcription to promote neuronal differentiation.
Adhikary S, Singh V, Choudhari R, Yang B, Adhikari S, Ramos EI, Chaudhuri S, Roy S, Gadad SS, Das C. Adhikary S, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2022 Sep 5;13(9):766. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05212-x. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36064715 Free PMC article. - Role of Bioactive Compounds in the Regulation of Mitochondrial Dysfunctions in Brain and Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases.
Kessas K, Chouari Z, Ghzaiel I, Zarrouk A, Ksila M, Ghrairi T, El Midaoui A, Lizard G, Kharoubi O. Kessas K, et al. Cells. 2022 Jan 13;11(2):257. doi: 10.3390/cells11020257. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35053373 Free PMC article. Review. - Tet2-mediated epigenetic drive for astrocyte differentiation from embryonic neural stem cells.
He F, Wu H, Zhou L, Lin Q, Cheng Y, Sun YE. He F, et al. Cell Death Discov. 2020 Apr 29;6:30. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-0264-5. eCollection 2020. Cell Death Discov. 2020. PMID: 32377393 Free PMC article. - Glycosphingolipid metabolic reprogramming drives neural differentiation.
Russo D, Della Ragione F, Rizzo R, Sugiyama E, Scalabrì F, Hori K, Capasso S, Sticco L, Fioriniello S, De Gregorio R, Granata I, Guarracino MR, Maglione V, Johannes L, Bellenchi GC, Hoshino M, Setou M, D'Esposito M, Luini A, D'Angelo G. Russo D, et al. EMBO J. 2018 Apr 3;37(7):e97674. doi: 10.15252/embj.201797674. Epub 2017 Dec 27. EMBO J. 2018. PMID: 29282205 Free PMC article.
References
- Sauvageot CM, Stiles CD. Molecular mechanisms controlling cortical gliogenesis. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2002;12:244–249. - PubMed
- Lian G, Sheen V. Cerebral developmental disorders. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2006;18:614–620. - PubMed
- Wu H, Sun YE. Epigenetic regulation of stem cell differentiation. Pediatr Res. 2006;59:21R–25R. - PubMed
- Bird A. Perceptions of epigenetics. Nature. 2007;447:396–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical