Metabolic changes in schizophrenia and human brain evolution - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-8-r124. Epub 2008 Aug 5.
Helen E Lockstone, Matthew T Wayland, Tsz M Tsang, Samantha D Jayatilaka, Arfu J Guo, Jie Zhou, Mehmet Somel, Laura W Harris, Elaine Holmes, Svante Pääbo, Sabine Bahn
Affiliations
- PMID: 18681948
- PMCID: PMC2575514
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-8-r124
Metabolic changes in schizophrenia and human brain evolution
Philipp Khaitovich et al. Genome Biol. 2008.
Abstract
Background: Despite decades of research, the molecular changes responsible for the evolution of human cognitive abilities remain unknown. Comparative evolutionary studies provide detailed information about DNA sequence and mRNA expression differences between humans and other primates but, in the absence of other information, it has proved very difficult to identify molecular pathways relevant to human cognition.
Results: Here, we compare changes in gene expression and metabolite concentrations in the human brain and compare them to the changes seen in a disorder known to affect human cognitive abilities, schizophrenia. We find that both genes and metabolites relating to energy metabolism and energy-expensive brain functions are altered in schizophrenia and, at the same time, appear to have changed rapidly during recent human evolution, probably as a result of positive selection.
Conclusion: Our findings, along with several previous studies, suggest that the evolution of human cognitive abilities was accompanied by adaptive changes in brain metabolism, potentially pushing the human brain to the limit of its metabolic capabilities.
Figures
Figure 1
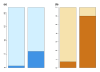
The proportion of biological processes showing evidence of recent positive selection on the human lineage that is differentially expressed in schizophrenia. The height of the bar represents the number of GO groups showing evidence of recent positive selection on the human lineage; (a) all 22 and (b) the 7 relating to energy metabolism. The darker shade of color represents the number of GO groups differentially expressed in schizophrenia among the 22 or the 7 GO groups (Wilcoxon rank sum test, p < 0.03, FDR = 11%). Left bar, expected by chance; right bar, observed.
Figure 2
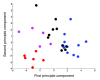
Principal component analysis of the metabolite abundance profiles in 33 individuals. The analysis is based on 21 detected metabolites. Each point represents an individual. The colors indicate: blue, human controls; black, human schizophrenia patients; purple, chimpanzees; red, rhesus macaques.
Figure 3
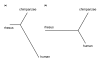
Divergence in metabolite abundance on the human and chimpanzee lineages. The trees are based on the abundance measurements of (a) 9 metabolites with significant concentration difference between human controls and schizophrenia patients and (b) 12 metabolites with no difference between these two groups. The trees were built using a neighbor-joining algorithm.
Similar articles
- Comparative metabolomics in primates reveals the effects of diet and gene regulatory variation on metabolic divergence.
Blekhman R, Perry GH, Shahbaz S, Fiehn O, Clark AG, Gilad Y. Blekhman R, et al. Sci Rep. 2014 Jul 28;4:5809. doi: 10.1038/srep05809. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25069065 Free PMC article. - Intra- and interspecific variation in primate gene expression patterns.
Enard W, Khaitovich P, Klose J, Zöllner S, Heissig F, Giavalisco P, Nieselt-Struwe K, Muchmore E, Varki A, Ravid R, Doxiadis GM, Bontrop RE, Pääbo S. Enard W, et al. Science. 2002 Apr 12;296(5566):340-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1068996. Science. 2002. PMID: 11951044 - Comparative genomics. Gene expression differs in human and chimp brains.
Normile D. Normile D. Science. 2001 Apr 6;292(5514):44-5. doi: 10.1126/science.292.5514.44. Science. 2001. PMID: 11294209 No abstract available. - Induced gene expression in human brain after the split from chimpanzee.
Gu J, Gu X. Gu J, et al. Trends Genet. 2003 Feb;19(2):63-5. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(02)00040-9. Trends Genet. 2003. PMID: 12547510 Review. - Is schizophrenia the price of human central nervous system complexity?
Dean B. Dean B. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2009 Jan;43(1):13-24. doi: 10.1080/00048670802534416. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19085524 Review.
Cited by
- Cell Type and Species-specific Patterns in Neuronal and Non-neuronal Methylomes of Human and Chimpanzee Cortices.
Böck J, Remmele CW, Dittrich M, Müller T, Kondova I, Persengiev S, Bontrop RE, Ade CP, Kraus TFJ, Giese A, El Hajj N, Schneider E, Haaf T. Böck J, et al. Cereb Cortex. 2018 Oct 1;28(10):3724-3739. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhy180. Cereb Cortex. 2018. PMID: 30085031 Free PMC article. - A dual comparative approach: integrating lines of evidence from human evolutionary neuroanatomy and neurodevelopmental disorders.
Hanson KL, Hrvoj-Mihic B, Semendeferi K. Hanson KL, et al. Brain Behav Evol. 2014;84(2):135-55. doi: 10.1159/000365409. Epub 2014 Sep 20. Brain Behav Evol. 2014. PMID: 25247986 Free PMC article. - Identification of targeted analyte clusters for studies of schizophrenia.
Cheng TM, Lu YE, Guest PC, Rahmoune H, Harris LW, Wang L, Ma D, Stelzhammer V, Umrania Y, Wayland MT, Lió P, Bahn S. Cheng TM, et al. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010 Mar;9(3):510-22. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900372-MCP200. Epub 2009 Dec 10. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 20007949 Free PMC article. - Cognition is entangled with metabolism: relevance for resting-state EEG-fMRI.
Jacob M, Ford J, Deacon T. Jacob M, et al. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023 Apr 11;17:976036. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.976036. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37113322 Free PMC article.
References
- Mikkelsen T, Hillier L, Eichler E, Zody M, Jaffe D, Yang S, Enard W, Hellmann I, Lindblad-Toh K, Altheide T, Archidiacono N, Bork P, Butler J, Chang J, Cheng Z, Chinwalla A, deJong P, Delehaunty K, Fronick C, Fulton L, Gilad Y, Glusman G, Gnerre S, Graves T, Hayakawa T, Hayden K, Huang X, Ji H, Kent W, King M, et al. Initial sequence of the chimpanzee genome and comparison with the human genome. Nature. 2005;437:69–87. - PubMed
- Khaitovich P, Hellmann I, Enard W, Nowick K, Leinweber M, Franz H, Weiss G, Lachmann M, Paabo S. Parallel patterns of evolution in the genomes and transcriptomes of humans and chimpanzees. Science. 2005;309:1850–1854. - PubMed
- Kimura M. The Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution. Cambridge, UK, New York: Cambridge University Press; 1983.
- Varki A, Altheide TK. Comparing the human and chimpanzee genomes: searching for needles in a haystack. Genome Res. 2005;15:1746–1758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical