CD4 T cells: fates, functions, and faults - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
CD4 T cells: fates, functions, and faults
Jinfang Zhu et al. Blood. 2008.
Abstract
In 1986, Mosmann and Coffman identified 2 subsets of activated CD4 T cells, Th1 and Th2 cells, which differed from each other in their pattern of cytokine production and their functions. Our understanding of the importance of the distinct differentiated forms of CD4 T cells and of the mechanisms through which they achieve their differentiated state has greatly expanded over the past 2 decades. Today at least 4 distinct CD4 T-cell subsets have been shown to exist, Th1, Th2, Th17, and iTreg cells. Here we summarize much of what is known about the 4 subsets, including the history of their discovery, their unique cytokine products and related functions, their distinctive expression of cell surface receptors and their characteristic transcription factors, the regulation of their fate determination, and the consequences of their abnormal activation.
Figures
Jinfang Zhu
William E. Paul
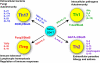
Figure 1
Summary of the 4 CD4 T helper cell fates: their functions, their unique products, their characteristic transcription factors, and cytokines critical for their fate determination.
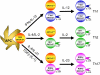
Figure 2
T-cell differentiation involves instructive differentiation as well as selective expansion of differentiated cells. The cytokines critical for the differentiation of each lineage instruct activated CD4 T cells to express their master transcription factors, T-bet for Th1, GATA-3 for Th2 and RORγt for Th17, as well as other lineage specific factors, IL-12R for Th1, Gfi-1 for Th2 and IL-23R for Th17. In many instances, only a portion of cells expresses the indicated transcription factors and adopts the differentiated phenotype. Such differentiated cells express the factors that determine responsiveness to particular cytokines, IL-12 for Th1, IL-2 for Th2 and IL-23 for Th17 cells, thus leading to selective expansion of those differentiated cells.
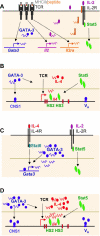
Figure 3
Th2 differentiation driven by low concentration of peptide stimulation in vitro consists of an IL-4–independent initiation phase and an IL-4–dependent amplification phase. (A) TCR stimulation by low concentration of peptide induces IL-4–independent GATA-3 expression and IL-2–mediated Stat5 activation. (B) GATA-3 binds to CNS-1 and VA whereas activated Stat5 binds to HSII and HSIII of Il4 locus. Both are critical for TCR-mediated IL-4 production at the initial phase of Th2 cell differentiation. (C) IL-4 produced by T cells can further induce GATA-3 expression through Stat6 activation. GATA-3 also regulates itself once it reaches a certain threshold. Thus, IL-4–mediated GATA-3 expression together with IL-2–mediated Stat5 activation drives full Th2 differentiation. (D) High levels of GATA-3 and activated Stat5 play critical roles in inducing large amount of IL-4 production.
Figure 4
Cross regulation among the factors that are involved in Th1 and Th2 differentiation.
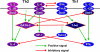
Figure 5
Positive and negative regulatory elements within Il4/Il13 loci and their binding to transcription factors.
Similar articles
- In Vitro Differentiation of Effector CD4+ T Helper Cell Subsets.
Read KA, Powell MD, Sreekumar BK, Oestreich KJ. Read KA, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1960:75-84. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9167-9_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30798522 - Modulation of chemokine receptor expression and chemotactic responsiveness during differentiation of human naive T cells into Th1 or Th2 cells.
Colantonio L, Recalde H, Sinigaglia F, D'Ambrosio D. Colantonio L, et al. Eur J Immunol. 2002 May;32(5):1264-73. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200205)32:5<1264::AID-IMMU1264>3.0.CO;2-S. Eur J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11981813 - C-C chemokine receptor 4 expression defines a major subset of circulating nonintestinal memory T cells of both Th1 and Th2 potential.
Andrew DP, Ruffing N, Kim CH, Miao W, Heath H, Li Y, Murphy K, Campbell JJ, Butcher EC, Wu L. Andrew DP, et al. J Immunol. 2001 Jan 1;166(1):103-11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.1.103. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11123282 - CD4⁺T cells: differentiation and functions.
Luckheeram RV, Zhou R, Verma AD, Xia B. Luckheeram RV, et al. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:925135. doi: 10.1155/2012/925135. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22474485 Free PMC article. Review. - Specifying helper T cell fates during immunity.
Chang JT, Reiner SL. Chang JT, et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008 Apr;46 Suppl 1:E19-20. doi: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000313832.47207.0e. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18354322 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Decoding mutational hotspots in human disease through the gene modules governing thymic regulatory T cells.
Raposo AASF, Rosmaninho P, Silva SL, Paço S, Brazão ME, Godinho-Santos A, Tokunaga-Mizoro Y, Nunes-Cabaço H, Serra-Caetano A, Almeida ARM, Sousa AE. Raposo AASF, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 15;15:1458581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1458581. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39483472 Free PMC article. - Basophils are required for the induction of Th2 immunity to haptens and peptide antigens.
Otsuka A, Nakajima S, Kubo M, Egawa G, Honda T, Kitoh A, Nomura T, Hanakawa S, Sagita Moniaga C, Kim B, Matsuoka S, Watanabe T, Miyachi Y, Kabashima K. Otsuka A, et al. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1739. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2740. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23612279 Free PMC article. - Huaier Extractum Promotes Dendritic Cells Maturation and Favors them to Induce Th1 Immune Response: One of the Mechanisms Underlying Its Anti-Tumor Activity.
Pan J, Jiang Z, Wu D, Yang C, Wang Z, Huang J. Pan J, et al. Integr Cancer Ther. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1534735420946830. doi: 10.1177/1534735420946830. Integr Cancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 33054422 Free PMC article. - The Role of GSK3β in T Lymphocytes in the Tumor Microenvironment.
Dimou A, Syrigos KN. Dimou A, et al. Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 24;10:1221. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01221. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32850361 Free PMC article. Review. - An Investigation into the Re-Emergence of Disease Following Cessation of Antibiotic Treatment in Balb/c Mice Infected with Inhalational Burkholderia pseudomallei.
Laws TR, Barnes KB, Jenner DC, Núñez A, Richards MI, Thwaite JE, Vente A, Rushton D, Nelson M, Harding SV. Laws TR, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Oct 20;11(10):1442. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11101442. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290100 Free PMC article.
References
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986;136:2348–2357. - PubMed
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory T cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:531–562. - PubMed
- Shevach EM. From vanilla to 28 flavors: multiple varieties of T regulatory cells. Immunity. 2006;25:195–201. - PubMed
- Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:297–336. - PubMed
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous