Metallic iron nanoparticles for MRI contrast enhancement and local hyperthermia - PubMed (original) (raw)
Metallic iron nanoparticles for MRI contrast enhancement and local hyperthermia
Costas G Hadjipanayis et al. Small. 2008 Nov.
No abstract available
Figures
Figure 1
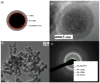
Transmission electron microscopy data: a) schematic image of the polymer-coated Fe-based metallic nanoparticles, b) high-resolution image, c) bright-field image showing coated FeNPs. d) SAED image confirming the body-centered cubic (bcc) structure of α Fe together with a small amount of FeO.
Figure 2
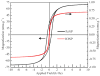
Hysteresis loops for FeNP and IONP taken at room temperature.
Figure 3
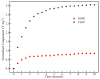
Hyperthermia data for FeNPs and IONPs using 500 MHz and 4 Oe AC magnetic field.
Figure 4
Decreasing signal density at different echo times showed typical paramagnetic-induced _T_2 decay in different samples (A). A set of _T_2-weighted fast spin–echo images showed the strong _T_2 contrast from FeNPs and IONPs (darkening effect) in contrast to the H2O phantom (B, upper panel) while a _T_2 relaxometry map derived from the multi-TE T2 measurement showed a substantially lower _T_2 value of the FeNPs (B, lower panel). _T_2 images were recorded using a multi-TE fast spin–echo imaging sequence with a TR of 3 s and 32 TE points (starting at 6 ms with increments of 6 ms). The sample concentrations of IONPs and FeNPs shown in the Figure are 0.11 and 0.12 m
m
, respectively.
Similar articles
- Simple synthesis and functionalization of iron nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging.
Cheong S, Ferguson P, Feindel KW, Hermans IF, Callaghan PT, Meyer C, Slocombe A, Su CH, Cheng FY, Yeh CS, Ingham B, Toney MF, Tilley RD. Cheong S, et al. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2011 Apr 26;50(18):4206-9. doi: 10.1002/anie.201100562. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2011. PMID: 21472950 No abstract available. - Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications.
Laurent S, Bridot JL, Elst LV, Muller RN. Laurent S, et al. Future Med Chem. 2010 Mar;2(3):427-49. doi: 10.4155/fmc.09.164. Future Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 21426176 Review. - The effect of ligands on FePt-Fe3O4 core-shell magnetic nanoparticles.
Kim DH, Tamada Y, Ono T, Bader SD, Rozhkova EA, Novosad V. Kim DH, et al. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014 Mar;14(3):2648-52. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2014.8471. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24745278 - Targeted nanoscale magnetic hyperthermia: challenges and potentials of peptide-based targeting.
Fourmy D, Carrey J, Gigoux V. Fourmy D, et al. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015;10(6):893-6. doi: 10.2217/nnm.14.236. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25867854 No abstract available. - Designed synthesis of uniformly sized iron oxide nanoparticles for efficient magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents.
Lee N, Hyeon T. Lee N, et al. Chem Soc Rev. 2012 Apr 7;41(7):2575-89. doi: 10.1039/c1cs15248c. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Chem Soc Rev. 2012. PMID: 22138852 Review.
Cited by
- Biocorona-induced modifications in engineered nanomaterial-cellular interactions impacting biomedical applications.
Kobos L, Shannahan J. Kobos L, et al. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2020 May;12(3):e1608. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1608. Epub 2019 Dec 1. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31788989 Free PMC article. Review. - Magnetic nanoparticle-based hyperthermia for cancer treatment.
Bañobre-López M, Teijeiro A, Rivas J. Bañobre-López M, et al. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2013 Nov 1;18(6):397-400. doi: 10.1016/j.rpor.2013.09.011. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2013. PMID: 24416585 Free PMC article. Review. - Iron-Loaded Magnetic Nanocapsules for pH-Triggered Drug Release and MRI Imaging.
Chen H, Sulejmanovic D, Moore T, Colvin DC, Qi B, Mefford OT, Gore JC, Alexis F, Hwu SJ, Anker JN. Chen H, et al. Chem Mater. 2014 Mar 25;26(6):2105-2112. doi: 10.1021/cm404168a. Epub 2014 Feb 26. Chem Mater. 2014. PMID: 24748722 Free PMC article. - Tumor initiating cells in malignant gliomas: biology and implications for therapy.
Hadjipanayis CG, Van Meir EG. Hadjipanayis CG, et al. J Mol Med (Berl). 2009 Apr;87(4):363-74. doi: 10.1007/s00109-009-0440-9. Epub 2009 Feb 3. J Mol Med (Berl). 2009. PMID: 19189072 Free PMC article. Review. - Nearly complete regression of tumors via collective behavior of magnetic nanoparticles in hyperthermia.
Dennis CL, Jackson AJ, Borchers JA, Hoopes PJ, Strawbridge R, Foreman AR, van Lierop J, Grüttner C, Ivkov R. Dennis CL, et al. Nanotechnology. 2009 Sep 30;20(39):395103. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/20/39/395103. Epub 2009 Sep 3. Nanotechnology. 2009. PMID: 19726837 Free PMC article.
References
- Jain KK. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2005;4:407–416. - PubMed
- Nasongkla N, Bey E, Ren J, Ai H, Khemtong C, Guthi JS, Chin SF, Sherry AD, Boothman DA, Gao J. Nano Lett. 2006;6:2427–2430. - PubMed
- Alexiou C, Arnold W, Klein RJ, Parak FG, Hulin P, Bergemann C, Erhardt W, Wagenpfeil S, Lubbe AS. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6641–6648. - PubMed
- Huh YM, Jun YW, Song HT, Kim S, Choi JS, Lee JH, Yoon S, Kim KS, Shin JS, Suh JS, Cheon J. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:12387–12391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical