Excess protein synthesis in Drosophila fragile X mutants impairs long-term memory - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2008 Oct;11(10):1143-5.
doi: 10.1038/nn.2175. Epub 2008 Sep 7.
Affiliations
- PMID: 18776892
- PMCID: PMC3038669
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2175
Excess protein synthesis in Drosophila fragile X mutants impairs long-term memory
François V Bolduc et al. Nat Neurosci. 2008 Oct.
Abstract
We used Drosophila olfactory memory as a model to study the molecular basis of cognitive defects in Fragile X syndrome in vivo. We observed that fragile X protein was acutely required and interacted with argonaute1 and staufen in the formation of long-term memory. Occlusion of long-term memory formation in Fragile X mutants could be rescued by protein synthesis inhibitors, suggesting that excess baseline protein synthesis could negatively affect cognition.
Figures
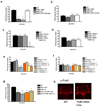
Figure 1. Drosophila FMRP is required for olfactory learning and 1-day memory after ST
A) One-day memory after ST is defective in FMR1(3) (vs. WT, P < 0.0001) and FMR B55 (vs. WT, P < 0.0001) and rescued with FMR1(3)+GENOMIC (vs. Fmr13, P < 0.0001; vs. WT, P = 0.715). B) In contrast, one-day memory after MT was normal. N = 8 PIs per group. C) Defective one-day memory after ST in FMR B55/FMR 1(3) (vs. WT, P = 0.0001), D) but normal after MT. N = 8 PIs per group. E) One-day memory after ST was significantly lower than WT in OK107;FMRRNAi(1-7) (vs. WT, P < 0.0001), OK107;FMRRNAi(1-10) (vs. WT, P = 0.001), 747;FMRRNAi(1-7) (vs. WT, P = 0.0046) and in 747;FMRRNAi(2-1) (vs. WT, P = 0.001) flies, but normal in the control genotypes: OK107/WT , FMRRNAi(1-7)/WT, 747/WT and FMRRNAi(2-1)/WT. N = 8, 8, 4, 8, 8, 8, 8 and 8 PIs. F) One-day memory after MT for any of the groups in E) was normal. N = 4–8 PIs for each genotype. G) Learning was significantly lower than WT in FMR B55 (vs. WT, P = 0.0062), FMR 1(3) (vs. WT, P = 0.0002), FMR B55/FMR 1(3) (vs. WT, P = 0.0045) or OK107;FMR-RNAi(1-7) (vs. WT, P = 0.034). N = 4 PIs per group. All graphs depict mean +/− S.E.M. H) elavGAL4/+;UAS-FmrRNAi (1-7)/+ present MB midline crossing defect (N=20).
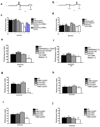
Figure 2. Drosophila FMRP is required acutely for LTM formation and interacts with Staufen and Argonaute 1
A) Protocol used to overexpress _UAS-Fmr_+ before training or B) after training. C) One-day memory in HSGAL4;U-FMR flies heat-shocked (+) before ST (<TRAIN) was significantly reduced (P = 0.0015) as opposed to those heat-shocked after ST (<TEST) (P = 0.242). No effect was observed in the genetic controls, HSGAL4/WT or UAS-FMR/WT. N = 8 PIs per group. D) One-day memory after MT did not differ. N = 8 PIs per group. E) Adult UAS-FmrRNAi(1-7) expression in MB of GAL80;747;FMRRNAI(1-7) flies for 3 days caused defect in one-day memory after ST compared to WT (P = 0.0021), FMRRNAI(1-7)/WT) (P < 0.0001) or GAL80;747/WT (P = 0.0028) genetic controls. N = 8 PIs per group. F) One-day memory after MT is not affected. N = 8 PIs per group. G) One-day memory after ST is reduced in STAU/WT;FMR1(3)/WT compared to wild-type flies WT (P = 0.0002), FMR1(3)/WT (P = 0.0004) or STAU/WT (P < 0.0001). N = 8 PIs per group. H) One-day memory after MT was normal in these genotypes. N = 8 PIs per group. I) One-day memory after ST is reduced in AGO1/WT;FMR1(3)/WT compared to controls WT (P = 0.0016), FMR1(3)/WT (P = 0.0007) or AGO1/WT (P < 0.0001). N = 16 PIs per group. J) One-day memory after MT was normal in these same genotypes. N = 8 PIs per group. All graphs depict mean +/− S.E.M.
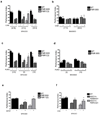
Figure 3. Inhibition of protein synthesis ameliorates the LTM defect of Fmr1 mutants
A) At the low cycloheximide dose (8.75mM or 17.5mM), one day memory after ST in wild-type flies was not affected (P=0.682, P = 0.977). FMR B55 performance was not modified at 8.75mM (P=0.4229) but was ameliorated at 17.5mM (P = 0.0244), as was FMR1(3) (P=0.0196). At the 35mM, performance in wild-type flies was reduced (P = 0.018), while FMR B55 was unaffected (P = 0.806). N = 8 PIs per group. B) One-day memory after MT was unaffected. N = 8 PIs per group. C) Puromycin at low dose (2.5mM and 5mM) had no effect in wild-type (P = 0.278, P = 0.133). No effect for FMR B55 with 2.5mM (P = 0.174) but 5mM Puromycin ameliorated performance of both FMR B55 (P = 0.0233) and FMR1(3) (P = 0.0173), while puromycin 10mM disrupted memory in wild-type (P = 0.0059) but had no effect on FMR B55 (P = 0.979). N = 8 – 12 PIs per group. D) One-day memory after MT was unaffected by puromycin in wild-type or FMR B55. N = 8 PIs per group. E) MPEP, ameliorated one-day memory after ST in Fmr1 mutants (Fmr1B55: P =0.0355; Fmr13: P =0.0024). N = 8 PIs per group. F) CXM (17.5mM) ameliorated the deficit in one-day memory after ST in AGO1/+; FMR1B55/+ (P=0.0452) and AGO1/+;FMR1(3)/+ (P = 0.0058). N = 8 PIs per group. All graphs depict mean +/− S.E.M.
Similar articles
- Learning and memory deficits consequent to reduction of the fragile X mental retardation protein result from metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated inhibition of cAMP signaling in Drosophila.
Kanellopoulos AK, Semelidou O, Kotini AG, Anezaki M, Skoulakis EM. Kanellopoulos AK, et al. J Neurosci. 2012 Sep 19;32(38):13111-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1347-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22993428 Free PMC article. - Insulin signaling misregulation underlies circadian and cognitive deficits in a Drosophila fragile X model.
Monyak RE, Emerson D, Schoenfeld BP, Zheng X, Chambers DB, Rosenfelt C, Langer S, Hinchey P, Choi CH, McDonald TV, Bolduc FV, Sehgal A, McBride SMJ, Jongens TA. Monyak RE, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2017 Aug;22(8):1140-1148. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.51. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Mol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27090306 Free PMC article. - Metabotropic receptor-dependent long-term depression persists in the absence of protein synthesis in the mouse model of fragile X syndrome.
Nosyreva ED, Huber KM. Nosyreva ED, et al. J Neurophysiol. 2006 May;95(5):3291-5. doi: 10.1152/jn.01316.2005. Epub 2006 Feb 1. J Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16452252 - RNA interference: a new mechanism by which FMRP acts in the normal brain? What can Drosophila teach us?
Siomi H, Ishizuka A, Siomi MC. Siomi H, et al. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2004;10(1):68-74. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20011. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2004. PMID: 14994291 Review. - Molecular and cellular aspects of mental retardation in the Fragile X syndrome: from gene mutation/s to spine dysmorphogenesis.
De Rubeis S, Fernández E, Buzzi A, Di Marino D, Bagni C. De Rubeis S, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;970:517-51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-0932-8_23. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22351071 Review.
Cited by
- Using Drosophila as a tool to identify Pharmacological Therapies for Fragile X Syndrome.
McBride SM, Holloway SL, Jongens TA. McBride SM, et al. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2012 Sep 24;10(1):e129-e136. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2012.09.005. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2012. PMID: 23730322 Free PMC article. - An "Omic" Overview of Fragile X Syndrome.
Dionne O, Corbin F. Dionne O, et al. Biology (Basel). 2021 May 13;10(5):433. doi: 10.3390/biology10050433. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34068266 Free PMC article. Review. - Regulation of synaptic structure and function by FMRP-associated microRNAs miR-125b and miR-132.
Edbauer D, Neilson JR, Foster KA, Wang CF, Seeburg DP, Batterton MN, Tada T, Dolan BM, Sharp PA, Sheng M. Edbauer D, et al. Neuron. 2010 Feb 11;65(3):373-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.01.005. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20159450 Free PMC article. - Everolimus, a mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor, ameliorated streptozotocin-induced learning and memory deficits via neurochemical alterations in male rats.
Fanoudi S, Hosseini M, Alavi MS, Boroushaki MT, Hosseini A, Sadeghnia HR. Fanoudi S, et al. EXCLI J. 2018 Oct 29;17:999-1017. doi: 10.17179/excli2018-1626. eCollection 2018. EXCLI J. 2018. PMID: 30564080 Free PMC article. - Pharmacological and genetic reversal of age-dependent cognitive deficits attributable to decreased presenilin function.
McBride SM, Choi CH, Schoenfeld BP, Bell AJ, Liebelt DA, Ferreiro D, Choi RJ, Hinchey P, Kollaros M, Terlizzi AM, Ferrick NJ, Koenigsberg E, Rudominer RL, Sumida A, Chiorean S, Siwicki KK, Nguyen HT, Fortini ME, McDonald TV, Jongens TA. McBride SM, et al. J Neurosci. 2010 Jul 14;30(28):9510-22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1017-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20631179 Free PMC article.
References
- Bear MF, Huber KM, Warren ST. The mGluR theory of fragile X mental retardation. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:370–377. - PubMed
- Dubnau J, et al. The staufen/pumilio pathway is involved in Drosophila long-term memory. Curr Biol. 2003;13:286–296. - PubMed
- Jin P, et al. Biochemical and genetic interaction between the fragile X mental retardation protein and the microRNA pathway. Nat Neurosci. 2004;7:113–117. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases