Structural basis for DNA recognition by FoxO1 and its regulation by posttranslational modification - PubMed (original) (raw)
Structural basis for DNA recognition by FoxO1 and its regulation by posttranslational modification
Michael M Brent et al. Structure. 2008.
Abstract
FoxO transcription factors regulate the transcription of genes that control metabolism, cellular proliferation, stress tolerance, and possibly life span. A number of posttranslational modifications within the forkhead DNA-binding domain regulate FoxO-mediated transcription. We describe the crystal structures of FoxO1 bound to three different DNA elements and measure the change in FoxO1-DNA affinity with acetylation and phosphorylation. The structures reveal additional contacts and increased DNA distortion for the highest affinity DNA site. The flexible wing 2 region of the forkhead domain was not observed in the structures but is necessary for DNA binding, and we show that p300 acetylation in wing 2 reduces DNA affinity. We also show that MST1 phosphorylation of FoxO1 prevents high-affinity DNA binding. The observation that FoxO-DNA affinity varies between response elements and with posttranslational modifications suggests that modulation of FoxO-DNA affinity is an important component of FoxO regulation in health and misregulation in disease.
Figures
Figure 1
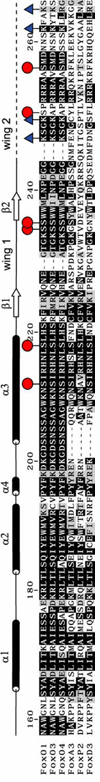
FoxO1 secondary structure and sequence alignment of human FoxO1 DBD with other forkhead domains. Residues that undergo phosphorylation or acetylation are marked with a red circle or a blue triangle respectively.
Figure 2
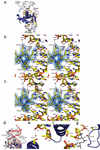
Structures of FoxO1/DNA complexes (a) Representative FoxO1 DBD/DNA complex - 2.1 Å structure of FoxO1 bound to the DBE1 sequence. The eight base DBE sequence is in CDK coloring and flanking bases are gray. (b and c) Stereo view of helix 3 interactions with DNA showing the different interactions with IRE (b) and DBE (c) DNA mediated by Asn211 and His215. Electron density shown is from a simulated annealing omit map contoured at 1.0 σ around the DNA recognition helix. (d) Superposition of FoxO1 DBD bound to DBE1 and DBE2 DNAs to illustrate the larger amount of bend in the DNA for the DBE2 structure. FoxO1 DBD bound to DBE1 is colored in blue and gray. FoxO1 DBD bound to DBE2 is colored in tan and red. (e–g) The targets of MST1 phosphorylation and their interactions with the phosphate backbone of DNA. Structure shown is FoxO1 DBD/DBE1 DNA. The interactions are conserved in the FoxO1/IRE DNA structure. (e) Ser212. (f) Ser218. (g) Ser234 and Ser235.
Figure 3
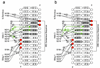
Schematic showing FoxO1 DBD interactions with IRE (a) and DBE1 (b) DNA sequences. Differences in hydrogen bonding between the DBE and IRE sequences are highlighted in green. Bases that are contacted directly or through water mediated interactions are shaded. Phosphates that are contacted directly or through water mediated interactions are highlighted in red.
Figure 4
(a–d) Measurement of binding affinity to IRE and DBE2 DNA for C-terminally truncated FoxO1 DBD constructs.
Figure 5
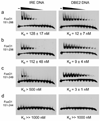
(a) EMSA results showing the difference in affinity for FoxO1 151–266 binding to IRE, DBE2 and DBE1 DNA sequences. (b–e) EMSA results showing the effects of FoxO1 151–266 modifications on binding affinity for IRE and DBE2 DNA sequences.
Similar articles
- Structural basis for DNA recognition by FOXO proteins.
Obsil T, Obsilova V. Obsil T, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov;1813(11):1946-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.11.025. Epub 2010 Dec 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21146564 Review. - Crystal structure of the human FOXO3a-DBD/DNA complex suggests the effects of post-translational modification.
Tsai KL, Sun YJ, Huang CY, Yang JY, Hung MC, Hsiao CD. Tsai KL, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(20):6984-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm703. Epub 2007 Oct 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17940099 Free PMC article. - Forkhead Domains of FOXO Transcription Factors Differ in both Overall Conformation and Dynamics.
Psenakova K, Kohoutova K, Obsilova V, Ausserlechner MJ, Veverka V, Obsil T. Psenakova K, et al. Cells. 2019 Aug 24;8(9):966. doi: 10.3390/cells8090966. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31450545 Free PMC article. - FoxO6, a novel member of the FoxO class of transcription factors with distinct shuttling dynamics.
Jacobs FM, van der Heide LP, Wijchers PJ, Burbach JP, Hoekman MF, Smidt MP. Jacobs FM, et al. J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 19;278(38):35959-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302804200. Epub 2003 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12857750 - Structure/function relationships underlying regulation of FOXO transcription factors.
Obsil T, Obsilova V. Obsil T, et al. Oncogene. 2008 Apr 7;27(16):2263-75. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.20. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18391969 Review.
Cited by
- Assessing the Activity of Transcription Factor FoxO1.
Shi L, Tao Z, Cheng Z. Shi L, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2594:97-106. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2815-7_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36264491 - A mutant allele encoding DNA binding-deficient FoxO1 differentially regulates hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism.
Cook JR, Matsumoto M, Banks AS, Kitamura T, Tsuchiya K, Accili D. Cook JR, et al. Diabetes. 2015 Jun;64(6):1951-65. doi: 10.2337/db14-1506. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 25576059 Free PMC article. - Mitochondria and FOXO3: breath or die.
Hagenbuchner J, Ausserlechner MJ. Hagenbuchner J, et al. Front Physiol. 2013 Jun 20;4:147. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00147. eCollection 2013. Front Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23801966 Free PMC article. - aPKC controls endothelial growth by modulating c-Myc via FoxO1 DNA-binding ability.
Riddell M, Nakayama A, Hikita T, Mirzapourshafiyi F, Kawamura T, Pasha A, Li M, Masuzawa M, Looso M, Steinbacher T, Ebnet K, Potente M, Hirose T, Ohno S, Fleming I, Gattenlöhner S, Aung PP, Phung T, Yamasaki O, Yanagi T, Umemura H, Nakayama M. Riddell M, et al. Nat Commun. 2018 Dec 17;9(1):5357. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07739-0. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30559384 Free PMC article. - FoxO4 controls sGCβ transcription in vascular smooth muscle.
Galley JC, Miller MP, Sanker S, Liu M, Sharina I, Martin E, Gomez D, Straub AC. Galley JC, et al. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Mar 1;322(3):H417-H426. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00551.2021. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35089807 Free PMC article.
References
- Anderson MJ, Viars CS, Czekay S, Cavenee WK, Arden KC. Cloning and characterization of three human forkhead genes that comprise an FKHR-like gene subfamily. Genomics. 1998;47:187–199. - PubMed
- Borkhardt A, Repp R, Haas OA, Leis T, Harbott J, Kreuder J, Hammermann J, Henn T, Lampert F. Cloning and characterization of AFX, the gene that fuses to MLL in acute leukemias with a t(X;11)(q13;q23) Oncogene. 1997;14:195–202. - PubMed
- Boura E, Silhan J, Herman P, Vecer J, Sulc M, Teisinger J, Obsilova V, Obsil T. Both the N-terminal loop and wing W2 of the forkhead domain of transcription factor Foxo4 are important for DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:8265–8275. - PubMed
- Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell. 1999;96:857–868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous