A dendritic cell-based tumour vaccine for lung cancer: full-length XAGE-1b protein-pulsed dendritic cells induce specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vitro - PubMed (original) (raw)
A dendritic cell-based tumour vaccine for lung cancer: full-length XAGE-1b protein-pulsed dendritic cells induce specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in vitro
Q Zhou et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008 Sep.
Abstract
XAGE-1b is regarded as one of the most immunogenic antigens and the most promising targets for lung adenocarcinoma immunotherapy. In this study, we sought to determine whether monocyte-derived dendritic cells (DCs) pulsed with purified full-length XAGE-1b could induce specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) against tumour cells from patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in vitro. XAGE-1b mRNA expression was examined in primary cultures of lung cancer cells and normal lung epithelial cells established from fresh tissues surgically resected from 30 patients with NSCLC using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). XAGE-1b mRNA expression was observed in 11 of 18 (61.1%) adenocarcinomas and one of 12 (8.3%) lung cancers of other histological types (P = 0.015). The 246-base pairs XAGE-1b gene was inserted into a recombinant expression vector. Full-length XAGE-1b was then expressed in BL21 (DE3) Escherichia coli and purified by AKTA-fast performance liquid chromatography (FPLC). DCs generated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells were pulsed with XAGE-1b by incubation with the protein at an immature stage. The XAGE-1b-pulsed DCs induced CTLs following 14 days of co-culture. Finally, an adherent target detachment (ATD) assay was performed to test the cytotoxicity of the XAGE-1b-specific CTLs against cancer cells and normal lung epithelial cells. The XAGE-1b-specific CTLs had a stronger lytic effect on autologous XAGE-1b mRNA-positive cancer cells than on autologous XAGE-1b mRNA-negative cancer cells or allogenous XAGE-1b mRNA-positive cancer cells. The CTLs had no lytic activity against normal lung epithelial cells. These results can be used to develop simple and effective cancer/testis antigen-based immunotherapies for NSCLC.
Figures
Fig. 1
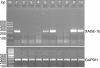
XAGE-1b mRNA expression status in tumour tissues of 10 patients with non-small cell lung cancer. M, DNA marker; lanes 1, 5, 6, 9, 10, XAGE-1b mRNA expression positive; lanes 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, XAGE-1b mRNA expression negative.
Fig. 2
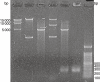
Restriction enzyme analysis and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) identification of recombinant vector B01/XAGE. M, DNA markers; lane 1, pReceiver-B01a expression vector; lane 2, restriction digest analysis of pReceiver-B01a using _Xmn_I and _Xho_I; lane 3, recombinant vector B01/XAGE; lane 4, restriction digest analysis of recombinant vector B01/XAGE using _Xmn_I and _Xho_I; lane 5, amplification of XAGE-1b by PCR using recombinant vector B01/XAGE as templates.
Fig. 3
Purification profile of recombinant XAGE-1b analysis by 18% sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis before and after purification. Lane 1, supernatants of cell lysates in non-induced culture; lane 2, pellets of cell lysates in non-induced culture; lane 3, supernatants of cell lysates in induced culture; lane 4, pellets of cell lysates in induced culture; M, protein marker; lane 5, flow; lane 6, 20 mmol/l imidazole wash; lane 7, 50 mmol/l imidazole eluate; lane 8, 100 mmol/l imidazole eluate; lane 9, 200 mmol/l imidazole eluate; lane 10, 300 mmol/l imidazole eluate; lane 11, 500 mmol/l imidazole eluate.
Fig. 4
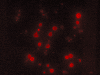
Immunofluorescence analysis of the XAGE-1b-pulsed dendritic cells (DCs). Intense fluorescence in the cytoplasm and membranes of mature XAGE-1b-pulsed DCs were observed under fluorescence microscope.
Fig. 5
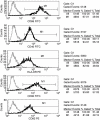
Flow cytometric analysis of mature XAGE-1b-pulsed dendritic cells (DCs). High levels of CD86, CD40, human leucocyte antigen D-related, CD80 and CD83 were expressed on the mature XAGE-1b-pulsed DCs.
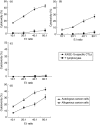
Fig. 6
Cytotoxicity of XAGE-1b-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) against cancer cells and normal lung epithelial cells. Mean ± standard deviation from five patients. T lymphocytes co-cultured with mock-pulsed dendritic cells (DCs) were used as control effector cells. (a) XAGE-1b mRNA-positive autologous cancer cells were used as target cells; (b) XAGE-1b mRNA-negative autologous cancer cells were used as target cells; (c) normal lung epithelial cells were used as target cells; D, XAGE-1b mRNA-positive allogenous cancer cells were used as target cells with the XAGE-1b-specific CTLs.
References
- Banchereau J, Steinman RM. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 1998;392:245–52. - PubMed
- Van der Bruggen P, Traversari C, Chomez P, et al. A gene encoding an antigen recognized by cytolytic T lymphocytes on a human melanoma. Science. 1991;254:1643–7. - PubMed
- Van den Eynde BJ, van der Bruggen P. T cell defined tumor antigens. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:684–93. - PubMed
- Brass N, Heckel D, Sahin U, Pfreundschuh M, Sybrecht GW, Meese E. Translation initiation factor eIF-4gamma is encoded by an amplified gene and induces an immune response in squamous cell lung carcinoma. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6:33–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials