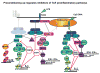Toll-like receptor signaling in endogenous neuroprotection and stroke - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Toll-like receptor signaling in endogenous neuroprotection and stroke
B J Marsh et al. Neuroscience. 2009.
Abstract
Stroke and other cerebral vascular diseases are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the United States. Despite intensive research to identify interventions that lessen cerebrovascular injury, no major therapies exist. Development of stroke prophylaxis involves an understanding of the mechanisms of damage following cerebral ischemia, and elucidation of the endogenous mechanisms that combat further brain injury. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are critical components of the innate immune system that have been shown recently to mediate ischemic injury. Paradoxically, TLR ligands administered systemically induce a state of tolerance to subsequent ischemic injury. Herein we suggest that stimulation of TLRs prior to ischemia reprograms TLR signaling that occurs following ischemic injury. Such reprogramming leads to suppressed expression of pro-inflammatory molecules and enhanced expression of numerous anti-inflammatory mediators that collectively confer robust neuroprotection. Our findings indicate that numerous preconditioning stimuli lead to TLR activation, an event that occurs prior to ischemia and ultimately leads to TLR reprogramming. Thus genomic reprogramming of TLR signaling may be a unifying principle of tolerance to cerebral ischemia.
Figures
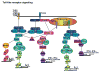
Figure 1
Toll-like receptor signaling
Figure 2
Cerebral ischemia induces Toll-like receptor signaling
Figure 3
Preconditioning up-regulates inhibitors of TLR proinflammatory pathways
Figure 4
Preconditioning reprograms TLR signaling following cerebral ischemia
Similar articles
- Inhibition of toll-like receptor and cytokine signaling--a unifying theme in ischemic tolerance.
Karikó K, Weissman D, Welsh FA. Karikó K, et al. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004 Nov;24(11):1288-304. doi: 10.1097/01.WCB.0000145666.68576.71. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004. PMID: 15545925 Review. - Function and mechanism of toll-like receptors in cerebral ischemic tolerance: from preconditioning to treatment.
Wang PF, Xiong XY, Chen J, Wang YC, Duan W, Yang QW. Wang PF, et al. J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Apr 28;12:80. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0301-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 25928750 Free PMC article. Review. - Prevention of inflammation is a mechanism of preconditioning-induced neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischemia.
Bowen KK, Naylor M, Vemuganti R. Bowen KK, et al. Neurochem Int. 2006 Jul;49(2):127-35. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2006.02.011. Epub 2006 Jun 6. Neurochem Int. 2006. PMID: 16759752 - Toll-like receptors and ischemic brain injury.
Gesuete R, Kohama SG, Stenzel-Poore MP. Gesuete R, et al. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2014 May;73(5):378-86. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0000000000000068. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24709682 Free PMC article. Review. - Multiple preconditioning paradigms converge on interferon regulatory factor-dependent signaling to promote tolerance to ischemic brain injury.
Stevens SL, Leung PY, Vartanian KB, Gopalan B, Yang T, Simon RP, Stenzel-Poore MP. Stevens SL, et al. J Neurosci. 2011 Jun 8;31(23):8456-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0821-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21653850 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Serial Systemic Injections of Endotoxin (LPS) Elicit Neuroprotective Spinal Cord Microglia through IL-1-Dependent Cross Talk with Endothelial Cells.
Freria CM, Brennan FH, Sweet DR, Guan Z, Hall JC, Kigerl KA, Nemeth DP, Liu X, Lacroix S, Quan N, Popovich PG. Freria CM, et al. J Neurosci. 2020 Nov 18;40(47):9103-9120. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0131-20.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 13. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33051350 Free PMC article. - Interplay Between Exosomes, microRNAs and Toll-Like Receptors in Brain Disorders.
Paschon V, Takada SH, Ikebara JM, Sousa E, Raeisossadati R, Ulrich H, Kihara AH. Paschon V, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Apr;53(3):2016-2028. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9142-1. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25862375 Review. - Comparative study of the effect of baicalin and its natural analogs on neurons with oxygen and glucose deprivation involving innate immune reaction of TLR2/TNFα.
Li HY, Hu J, Zhao S, Yuan ZY, Wan HJ, Lei F, Ding Y, Xing DM, Du LJ. Li HY, et al. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:267890. doi: 10.1155/2012/267890. Epub 2012 Mar 21. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22536016 Free PMC article. - Neuroprotection by Neurotropin through Crosstalk of Neurotrophic and Innate Immune Receptors in PC12 Cells.
Fukuda Y, Nakajima K, Mutoh T. Fukuda Y, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 4;21(18):6456. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186456. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32899630 Free PMC article. - Comparison of volatile anesthetic-induced preconditioning in cardiac and cerebral system: molecular mechanisms and clinical aspects.
Chen S, Lotz C, Roewer N, Broscheit JA. Chen S, et al. Eur J Med Res. 2018 Feb 20;23(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40001-018-0308-y. Eur J Med Res. 2018. PMID: 29458412 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Ahmed S, He Y, Nassief A, Xu J, Xu X, Hsu C. Effects of Lipopolysaccharide priming on acute ischemic brain injury. Stroke. 2000;31:193–199. - PubMed
- Aneja R, Odoms K, Dunsmore K, Shanley TP, Wong HR. Extracellular heat shock protein-70 induces endotoxin tolerance in THP-1 cells. J Immunol. 2006;177:7184–7192. - PubMed
- Bagchi A, Herrup EA, Warren HS, Trigilio J, Shin HS, Valentine C, Hellman J. MyD88-dependent and MyD88-independent pathways in synergy, priming, and tolerance between TLR agonists. J Immunol. 2007;178:1164–1171. - PubMed
- Bastide M, Gele P, Petrault O, Pu Q, Caliz A, Robin E, Deplanque D, Duriez P, Bordet R. Delayed cerebrovascular protective effect of lipopolysaccharide in parallel to brain ischemic tolerance. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003;23:399–405. - PubMed
- Bond R, Rerkasem K, Shearman CP, Rothwell PM. Time trends in the published risks of stroke and death due to endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004;18:37–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS050567-01A1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS050567/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS035965/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 NS070359/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01 NS050567/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases