Identifying polymer-forming SAM domains - PubMed (original) (raw)
Identifying polymer-forming SAM domains
Alejandro D Meruelo et al. Proteins. 2009 Jan.
Abstract
Sterile alpha motif (SAM) domains are common protein modules in eukaryotic cells. It has not been possible to assign functions to uncharacterized SAM domains because they have been found to participate in diverse functions ranging from protein-protein interactions to RNA binding. Here we computationally identify likely members of the subclass of SAM domains that form polymers. Sequences were virtually threaded onto known polymer structures and then evaluated for compatibility with the polymer. We find that known SAM polymers score better than the vast majority of known nonpolymers: 100% (7 of 7) of known polymers and only 8% of known nonpolymers (1 of 12) score above a defined threshold value. Of 2901 SAM family members, we find 694 that score above the threshold and are likely polymers, including SAM domains from the proteins Lethal Malignant Brain Tumor, Bicaudal-C, Liprin-beta, Adenylate Cyclase, and Atherin.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
Figure 1. SAM polymer architecture
The structure shown is the SAM domain from TEL. Every other SAM domain is shaded dark or light.
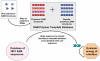
Figure 2. Outline of the polymer compatibility test algorithm
See text.
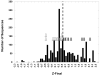
Figure 3. Histogram of the Z-final score distribution
The scores for the known polymers are indicated by the positions of the shaded arrows and the scores for the known non-polymers are indicated by the positions of the white arrows. The dotted line indicates the Z-final cutoff used to separate polymers from non-polymers.
Similar articles
- A human sterile alpha motif domain polymerizome.
Knight MJ, Leettola C, Gingery M, Li H, Bowie JU. Knight MJ, et al. Protein Sci. 2011 Oct;20(10):1697-706. doi: 10.1002/pro.703. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Protein Sci. 2011. PMID: 21805519 Free PMC article. - SAM domains: uniform structure, diversity of function.
Kim CA, Bowie JU. Kim CA, et al. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003 Dec;28(12):625-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2003.11.001. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003. PMID: 14659692 - Solution structures, dynamics, and lipid-binding of the sterile alpha-motif domain of the deleted in liver cancer 2.
Li H, Fung KL, Jin DY, Chung SS, Ching YP, Ng IO, Sze KH, Ko BC, Sun H. Li H, et al. Proteins. 2007 Jun 1;67(4):1154-66. doi: 10.1002/prot.21361. Proteins. 2007. PMID: 17380510 - Computational prediction of protein-protein interactions.
Obenauer JC, Yaffe MB. Obenauer JC, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2004;261:445-68. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-762-9:445. Methods Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15064475 Review. - Creativity comes from interactions: modules of protein interactions in plants.
Allen JR, Wilkinson EG, Strader LC. Allen JR, et al. FEBS J. 2022 Mar;289(6):1492-1514. doi: 10.1111/febs.15847. Epub 2021 May 1. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 33774929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Solution structure of the first Sam domain of Odin and binding studies with the EphA2 receptor.
Mercurio FA, Marasco D, Pirone L, Pedone EM, Pellecchia M, Leone M. Mercurio FA, et al. Biochemistry. 2012 Mar 13;51(10):2136-45. doi: 10.1021/bi300141h. Epub 2012 Mar 5. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22332920 Free PMC article. - Crystal structure of the central coiled-coil domain from human liprin-β2.
Stafford RL, Tang MY, Sawaya MR, Phillips ML, Bowie JU. Stafford RL, et al. Biochemistry. 2011 May 10;50(18):3807-15. doi: 10.1021/bi200141e. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21462929 Free PMC article. - Evolution and divergence of the mammalian SAMD9/SAMD9L gene family.
Lemos de Matos A, Liu J, McFadden G, Esteves PJ. Lemos de Matos A, et al. BMC Evol Biol. 2013 Jun 12;13:121. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-13-121. BMC Evol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23758988 Free PMC article. - NMR structure of a heterodimeric SAM:SAM complex: characterization and manipulation of EphA2 binding reveal new cellular functions of SHIP2.
Lee HJ, Hota PK, Chugha P, Guo H, Miao H, Zhang L, Kim SJ, Stetzik L, Wang BC, Buck M. Lee HJ, et al. Structure. 2012 Jan 11;20(1):41-55. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2011.11.013. Structure. 2012. PMID: 22244754 Free PMC article. - Loss of a highly conserved sterile alpha motif domain gene (WEEP) results in pendulous branch growth in peach trees.
Hollender CA, Pascal T, Tabb A, Hadiarto T, Srinivasan C, Wang W, Liu Z, Scorza R, Dardick C. Hollender CA, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 May 15;115(20):E4690-E4699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1704515115. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29712856 Free PMC article.
References
- Pawson T, Nash P. Assembly of cell regulatory systems through protein interaction domains. Science. 2003;300:445–452. - PubMed
- Qiao F, Bowie JU. The many faces of SAM. Sci STKE. 2005;2005:re7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM063919/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM063919-08/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008042/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32-GM08042/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources