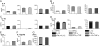Human eosinophils constitutively express multiple Th1, Th2, and immunoregulatory cytokines that are secreted rapidly and differentially - PubMed (original) (raw)
Human eosinophils constitutively express multiple Th1, Th2, and immunoregulatory cytokines that are secreted rapidly and differentially
Lisa A Spencer et al. J Leukoc Biol. 2009 Jan.
Abstract
Eosinophils are innate immune leukocytes implicated in the initiation and maintenance of type 2 immune responses, including asthma and allergy. The ability to store and rapidly secrete preformed cytokines distinguishes eosinophils from most lymphocytes, which must synthesize cytokine proteins prior to secretion and may be a factor in the apparent Th2 bias of eosinophils. Multiple studies confirm that human eosinophils from atopic or hypereosinophilic donors can secrete over 30 cytokines with a varying and often opposing immune-polarizing potential. However, it remains unclear whether all of these cytokines are constitutively preformed and available for rapid secretion from eosinophils in the circulation of healthy individuals or are restricted to eosinophils from atopic donors. Likewise, the relative concentrations of cytokines stored within eosinophils have not been studied. Here, we demonstrate that human blood eosinophils are not singularly outfitted with Th2-associated cytokines but rather, constitutively store a cache of cytokines with nominal Th1, Th2, and regulatory capacities, including IL-4, IL-13, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, IFN-gamma, and TNF-alpha. We demonstrate further rapid and differential release of each cytokine in response to specific stimuli. As agonists, strong Th1 and inflammatory cytokines elicited release of Th2-promoting IL-4 but not Th1-inducing IL-12. Moreover, a large quantity of IFN-gamma was secreted in response to Th1, Th2, and inflammatory stimuli. Delineations of the multifarious nature of preformed eosinophil cytokines and the varied stimulus-dependent profiles of rapid cytokine secretion provide insights into the functions of human eosinophils in mediating inflammation and initiation of specific immunity.
Figures
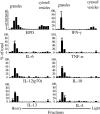
Fig. 1.
Preformed cytokines are stored within intracellular granules. Eosinophil subcellular fractions, prepared and evaluated per Materials and Methods, were analyzed by multiplex analysis for cytokine content. Fractions containing granules and small, less-dense vesicles and cytosol are indicated. Data are from eosinophils from one donor and are representative of studies of eosinophils from three donors.
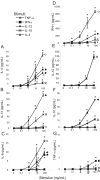
Fig. 2.
Dose-dependent release of cytokines from eosinophils in response to cytokine stimuli. Eosinophils (3×106/mL) were incubated for 30 min at 37°C with increasing doses of indicated cytokine stimuli. Following stimulation, cell-free supernatants were analyzed by multiplex analysis for the presence of IL-4 (A), IL-13 (B), IL-6 (C), IFN-γ (D), IL-12(p70) (E), IL-10 (F), and TNF-α (G). Data are presented as means (±
sd
) of duplicate or triplicate wells of one experiment representative of at least three independent experiments. *, P ≤ 0.05, versus nonstimulated controls.
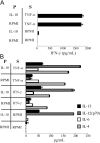
Fig. 3.
Pretreatment with IL-10 does not affect eosinophil cytokine secretion. Eosinophils (3×106/mL) were preincubated for 20 min at 37°C ± 100 ng/mL rIL-10 (P) prior to addition of 100 ng/mL rTNF-α or rIFN-γ for a subsequent 20 min stimulation (S). Cell-free supernatants were analyzed as above. Data are the means (±
sd
) of duplicate wells from one experiment, representative of three independent experiments.
Fig. 4.
Simultaneous stimulation with multiple cytokines elicits additive effects on eosinophil cytokine secretion. Eosinophils (3×106 per mL) were stimulated with 100 ng/mL IFN-γ, IL-12, and TNF-α, alone or in various combinations, for 30 min at 37°C. Cell-free supernatants were analyzed as above for the presence of IL-4 (A), IL-6 (B), IL-10 (C), IL-13 (D), TNF-α (E), IL-12 (F), and IFN-γ (G). Means (±
sd
) of stimulation with individual cytokines are stacked and plotted beside results from the appropriate dual stimulation.
Similar articles
- Expression of Th1 and Th2 immunoregulatory cytokines by human eosinophils.
Woerly G, Roger N, Loiseau S, Capron M. Woerly G, et al. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999 Feb-Apr;118(2-4):95-7. doi: 10.1159/000024038. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10224349 Review. - Synthesis of type 1 (IFN gamma) and type 2 (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10) cytokines by human eosinophils.
Lamkhioued B, Gounni AS, Aldebert D, Delaporte E, Prin L, Capron A, Capron M. Lamkhioued B, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996 Oct 31;796:203-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1996.tb32582.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996. PMID: 8906227 Review. - Nickel-induced IL-10 down-regulates Th1- but not Th2-type cytokine responses to the contact allergen nickel.
Minang JT, Areström I, Zuber B, Jönsson G, Troye-Blomberg M, Ahlborg N. Minang JT, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 Mar;143(3):494-502. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03018.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16487249 Free PMC article. - Differential modulation of T helper type 1 (Th1) and T helper type 2 (Th2) cytokine secretion by prostaglandin E2 critically depends on interleukin-2.
Hilkens CM, Vermeulen H, van Neerven RJ, Snijdewint FG, Wierenga EA, Kapsenberg ML. Hilkens CM, et al. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jan;25(1):59-63. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250112. Eur J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7843254 - Serial estimation of Th1:th2 cytokines profile in women undergoing in-vitro fertilization-embryo transfer.
Kalu E, Bhaskaran S, Thum MY, Vishwanatha R, Croucher C, Sherriff E, Ford B, Bansal AS. Kalu E, et al. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2008 Mar;59(3):206-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2007.00565.x. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18275514
Cited by
- A MR-PheWAS and bidirectional Mendelian randomization study: Exploring for causal relationships of pancreatic cancer.
Guan A, Li Z, Guo X. Guan A, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 11;103(41):e40047. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040047. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39465831 Free PMC article. - Blood Eosinophils Matter in Post-COVID-19 Pneumonia.
Bernardinello N, Castelli G, Pasin D, Grisostomi G, Cola M, Giraudo C, Cocconcelli E, Cattelan A, Spagnolo P, Balestro E. Bernardinello N, et al. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Oct 18;14(20):2320. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14202320. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451643 Free PMC article. - Endogenous PGD2 acting on DP2 receptor counter regulates Schistosoma mansoni infection-driven hepatic granulomatous fibrosis.
Pezzella-Ferreira GN, Pão CRR, Bellas I, Luna-Gomes T, Muniz VS, Paiva LA, Amorim NRT, Canetti C, Bozza PT, Diaz BL, Bandeira-Melo C. Pezzella-Ferreira GN, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2024 Aug 22;20(8):e1011812. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011812. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39173086 Free PMC article. - Concurrent Ascaris infection modulates host immunity resulting in impaired control of Salmonella infection in pigs.
Midha A, Oser L, Schlosser-Brandenburg J, Laubschat A, Mugo RM, Musimbi ZD, Höfler P, Kundik A, Hayani R, Adjah J, Groenhagen S, Tieke M, Elizalde-Velázquez LE, Kühl AA, Klopfleisch R, Tedin K, Rausch S, Hartmann S. Midha A, et al. mSphere. 2024 Sep 25;9(9):e0047824. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00478-24. Epub 2024 Aug 14. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39140728 Free PMC article. - Cytokines and chemokines skin gene expression in correlation with immune cells in blood and severity in equine insect bite hypersensitivity.
Jebbawi F, Chemnitzer A, Dietrich M, Pantelyushin S, Lam J, Rhiner T, Keller G, Waldern N, Canonica F, Fettelschoss-Gabriel A. Jebbawi F, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 15;15:1414891. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1414891. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39076967 Free PMC article.
References
- Shinkai K, Mohrs M, Locksley R M. Helper T cells regulate type-2 innate immunity in vivo. Nature. 2002;420:825–829. - PubMed
- Voehringer D, Shinkai K, Locksley R M. Type 2 immunity reflects orchestrated recruitment of cells committed to IL-4 production. Immunity. 2004;20:267–277. - PubMed
- Mattes J, Yang M, Mahalingam S, Kuehr J, Webb D C, Simson L, Hogan S P, Koskinen A, McKenzie A N, Dent L A, Rothenberg M E, Matthaei K I, Young I G, Foster P S. Intrinsic defect in T cell production of interleukin (IL)-13 in the absence of both IL-5 and eotaxin precludes the development of eosinophilia and airways hyperreactivity in experimental asthma. J Exp Med. 2002;195:1433–1444. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL70270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI020241/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI022571/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095699/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI20241/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI020241/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI051645/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI051645/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials