Site-directed mutagenesis reveals putative substrate binding residues in the Escherichia coli RND efflux pump AcrB - PubMed (original) (raw)
Site-directed mutagenesis reveals putative substrate binding residues in the Escherichia coli RND efflux pump AcrB
Jürgen A Bohnert et al. J Bacteriol. 2008 Dec.
Abstract
The Escherichia coli multidrug efflux pump protein AcrB has recently been cocrystallized with various substrates, suggesting that there is a phenylalanine-rich binding site around F178 and F615. We found that F610A was the point mutation that had the most significant impact on substrate MICs, while other targeted mutations, including conversion of phenylalanines 136, 178, 615, 617, and 628 to alanine, had smaller and more variable effects.
Figures
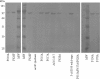
FIG. 1.
Western blot analysis of mutant AcrB production. Total protein extracts of E. coli 3-AG100 mutants (14 μg protein) were separated by NuPAGE Novex bis-Tris (Invitrogen, California) gel electrophoresis and probed with polyclonal anti-AcrB antibodies. Lanes MW contained molecular weight markers.
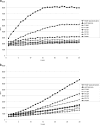
FIG. 2.
Increases in EtBr (a) and PAβN (b) fluorescence in AcrB phenylalanine mutants compared to pseudomutant AcrB strain F628F. Fluorescence was recorded for 30 min after addition of 2.5 μM EtBr or 200 μM PAβN. The values are means of at least duplicate experiments. RFU, relative fluorescence units.
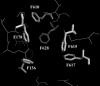
FIG. 3.
AcrB binding pocket based on the “tight” monomer 2GIF structure coordinates (12). Phenylalanines are indicated by sticks. The image was generated using the molecular visualization software PyMol (
).
Similar articles
- Reversal of the Drug Binding Pocket Defects of the AcrB Multidrug Efflux Pump Protein of Escherichia coli.
Soparkar K, Kinana AD, Weeks JW, Morrison KD, Nikaido H, Misra R. Soparkar K, et al. J Bacteriol. 2015 Oct;197(20):3255-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.00547-15. Epub 2015 Aug 3. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26240069 Free PMC article. - Altered spectrum of multidrug resistance associated with a single point mutation in the Escherichia coli RND-type MDR efflux pump YhiV (MdtF).
Bohnert JA, Schuster S, Fähnrich E, Trittler R, Kern WV. Bohnert JA, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007 Jun;59(6):1216-22. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl426. Epub 2006 Oct 24. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17062614 - Site-directed mutagenesis reveals amino acid residues in the Escherichia coli RND efflux pump AcrB that confer macrolide resistance.
Wehmeier C, Schuster S, Fähnrich E, Kern WV, Bohnert JA. Wehmeier C, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Jan;53(1):329-30. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00921-08. Epub 2008 Oct 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 18936189 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - AcrB multidrug efflux pump of Escherichia coli: composite substrate-binding cavity of exceptional flexibility generates its extremely wide substrate specificity.
Yu EW, Aires JR, Nikaido H. Yu EW, et al. J Bacteriol. 2003 Oct;185(19):5657-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.19.5657-5664.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 13129936 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available. - Structural and functional aspects of the multidrug efflux pump AcrB.
Eicher T, Brandstätter L, Pos KM. Eicher T, et al. Biol Chem. 2009 Aug;390(8):693-9. doi: 10.1515/BC.2009.090. Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19453279 Review.
Cited by
- Structural and functional analysis of the promiscuous AcrB and AdeB efflux pumps suggests different drug binding mechanisms.
Ornik-Cha A, Wilhelm J, Kobylka J, Sjuts H, Vargiu AV, Malloci G, Reitz J, Seybert A, Frangakis AS, Pos KM. Ornik-Cha A, et al. Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 25;12(1):6919. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27146-2. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34824229 Free PMC article. - Structural and functional diversity of Resistance-Nodulation-Division (RND) efflux pump transporters with implications for antimicrobial resistance.
Kavanaugh LG, Dey D, Shafer WM, Conn GL. Kavanaugh LG, et al. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024 Sep 26;88(3):e0008923. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00089-23. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39235227 Review. - Pimozide Inhibits the AcrAB-TolC Efflux Pump in Escherichia coli.
Bohnert JA, Schuster S, Kern WV. Bohnert JA, et al. Open Microbiol J. 2013;7:83-6. doi: 10.2174/1874285801307010083. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Open Microbiol J. 2013. PMID: 23560030 Free PMC article. - Reversal of the Drug Binding Pocket Defects of the AcrB Multidrug Efflux Pump Protein of Escherichia coli.
Soparkar K, Kinana AD, Weeks JW, Morrison KD, Nikaido H, Misra R. Soparkar K, et al. J Bacteriol. 2015 Oct;197(20):3255-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.00547-15. Epub 2015 Aug 3. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26240069 Free PMC article. - Substrate path in the AcrB multidrug efflux pump of Escherichia coli.
Husain F, Nikaido H. Husain F, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2010 Oct;78(2):320-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07330.x. Epub 2010 Aug 20. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20804453 Free PMC article.
References
- Bohnert, J. A., S. Schuster, E. Fähnrich, R. Trittler, and W. V. Kern. 2007. Altered spectrum of multidrug resistance associated with a single point mutation in the Escherichia coli RND-type MDR efflux pump YhiV (MdtF). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 591216-1222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases