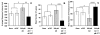Microdialysis elevation of adenosine in the basal forebrain produces vigilance impairments in the rat psychomotor vigilance task - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2008 Oct;31(10):1393-8.
Affiliations
- PMID: 18853936
- PMCID: PMC2572744
Microdialysis elevation of adenosine in the basal forebrain produces vigilance impairments in the rat psychomotor vigilance task
Michael A Christie et al. Sleep. 2008 Oct.
Abstract
Study objective: The inhibitory neuromodulator adenosine has been proposed as a homeostatic sleep factor that acts potently in the basal forebrain (BF) to increase sleepiness. Here 300 microM of adenosine was dialyzed in the BF of rats, and the effect on vigilance was determined in the rat Psychomotor Vigilance Task (rPVT).
Design: Rats experienced all experimental conditions in a repeated-measures, cross-over design.
Patients or participants: Twelve young adult male Fischer-Norway rats.
Interventions: Sustained attention performance in the rPVT was evaluated following 2 hours of bilateral microdialysis perfusion of vehicle, adenosine (300 microM), or codialysis of 300 microM of adenosine with the A1 receptor antagonist 8-cyclopentyltheophylline.
Measurements and results: During rPVT performance, response latencies and performance lapses increased significantly after adenosine dialysis when compared with baseline (no dialysis) or vehicle dialysis sessions. The codialysis of 8-cyclopentyltheophylline with adenosine completely blocked the effects produced by adenosine alone, resulting in performance equivalent to that of the vehicle sessions.
Conclusions: Pharmacologic elevation of BF adenosine in rats produced vigilance impairments resembling the effect of sleep deprivation on vigilance performance in both man and rats. This effect of exogenous adenosine was completely blocked by codialysis with an adenosine A1 receptor antagonist. The results are consistent with the hypothesis that sleep loss induces elevations of BF adenosine that, acting via A1 receptors, lead to increased sleepiness and impaired vigilance.
Figures
Figure 1
Rat Psychomotor Vigilance Task. Response latencies are slowed (Panel A), and the mean number of lapses, including omissions, increased significantly (Panel B) after a 300-μM adenosine (AD) infusion into the basal forebrain (BF), compared with baseline and artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) controls. These behavior effects are reversed by codialysis of 300 μM of adenosine with 1 μM of 8-cyclopentyltheophyline (CPT, an adenosine A1 receptor antagonist) in comparison with the 300-μM adenosine-only condition (Panels A & B). The number of premature errors per session decreased after the 300-μM adenosine infusion into the CBF, compared with baseline and aCSF control, but this reduction was reversed after codialysis of 300 μM of adenosine with 1 μM of CPT (Panel C). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.025, ***P < 0.01, ****P < 0.005. Base refers to nondialysis baseline. Error bars ± SEM.
Similar articles
- Sleep deprivation and time-on-task performance decrement in the rat psychomotor vigilance task.
Oonk M, Davis CJ, Krueger JM, Wisor JP, Van Dongen HP. Oonk M, et al. Sleep. 2015 Mar 1;38(3):445-51. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4506. Sleep. 2015. PMID: 25515099 Free PMC article. - 24 hours of sleep deprivation in the rat increases sleepiness and decreases vigilance: introduction of the rat-psychomotor vigilance task.
Christie MA, McKenna JT, Connolly NP, McCarley RW, Strecker RE. Christie MA, et al. J Sleep Res. 2008 Dec;17(4):376-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2869.2008.00698.x. Epub 2008 Oct 6. J Sleep Res. 2008. PMID: 19021853 Free PMC article. - A1 receptor and adenosinergic homeostatic regulation of sleep-wakefulness: effects of antisense to the A1 receptor in the cholinergic basal forebrain.
Thakkar MM, Winston S, McCarley RW. Thakkar MM, et al. J Neurosci. 2003 May 15;23(10):4278-87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-10-04278.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12764116 Free PMC article. - Adenosine, caffeine, and performance: from cognitive neuroscience of sleep to sleep pharmacogenetics.
Urry E, Landolt HP. Urry E, et al. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2015;25:331-66. doi: 10.1007/7854_2014_274. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 24549722 Review. - Adenosine as a biological signal mediating sleepiness following prolonged wakefulness.
Basheer R, Porkka-Heiskanen T, Strecker RE, Thakkar MM, McCarley RW. Basheer R, et al. Biol Signals Recept. 2000 Nov-Dec;9(6):319-27. doi: 10.1159/000014655. Biol Signals Recept. 2000. PMID: 11025338 Review.
Cited by
- Sleep deprivation impairs performance in the 5-choice continuous performance test: similarities between humans and mice.
van Enkhuizen J, Acheson D, Risbrough V, Drummond S, Geyer MA, Young JW. van Enkhuizen J, et al. Behav Brain Res. 2014 Mar 15;261:40-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.12.003. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Behav Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24333377 Free PMC article. - Psychomotor vigilance task performance during and following chronic sleep restriction in rats.
Deurveilher S, Bush JE, Rusak B, Eskes GA, Semba K. Deurveilher S, et al. Sleep. 2015 Apr 1;38(4):515-28. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4562. Sleep. 2015. PMID: 25515100 Free PMC article. - Sleep deprivation and time-on-task performance decrement in the rat psychomotor vigilance task.
Oonk M, Davis CJ, Krueger JM, Wisor JP, Van Dongen HP. Oonk M, et al. Sleep. 2015 Mar 1;38(3):445-51. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4506. Sleep. 2015. PMID: 25515099 Free PMC article. - Sleep Disruption Impairs Sustained Attention in Food-Restricted Rats Using a Food-Reinforced Rodent Psychomotor Vigilance Test.
Davis CM, Elliott VE, Smith J. Davis CM, et al. Nat Sci Sleep. 2024 Nov 9;16:1771-1777. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S475672. eCollection 2024. Nat Sci Sleep. 2024. PMID: 39539357 Free PMC article. - Rat psychomotor vigilance task with fast response times using a conditioned lick behavior.
Walker JL, Walker BM, Fuentes FM, Rector DM. Walker JL, et al. Behav Brain Res. 2011 Jan 1;216(1):229-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.07.041. Epub 2010 Aug 7. Behav Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 20696188 Free PMC article.
References
- McGaughy J, Sarter M. Sustained attention performance in rats with intracortical infusions of 192 IgG-saporin-induced cortical cholinergic deafferentation: effects of physostigmine and FG 7142. Behav Neurosci. 1998;112:1519–25. - PubMed
- Baxter MG, Chiba AA. Cognitive functions of the basal forebrain. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1999;9:178–83. - PubMed
- Detrain L, Rasmusson DD, Semba K. The role of basal forebrain neurons in tonic and phasic activation of the cerebral cortex. Prog Neurobiol. 1999;58:249–77. - PubMed
- Lin SC, Gervasoni D, Nicolelis MA. Fast modulation of prefrontal cortex activity by basal forebrain noncholinergic neuronal ensembles. J Neurophysiol. 2006;96:3209–19. - PubMed
- Manns ID, Alonso A, Jones BE. Rhythmically discharging basal forebrain units comprise cholinergic, GABAergic, and putative glutamatergic cells. J Neurophysiol. 2003;89:1057–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 MH070156/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL060292/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007901/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH039683/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL07901/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous