Immune activation in advanced cancer patients treated with recombinant IL-21: multianalyte profiling of serum proteins - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
Immune activation in advanced cancer patients treated with recombinant IL-21: multianalyte profiling of serum proteins
Michael G Dodds et al. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009 Jun.
Abstract
Purpose: Recombinant interleukin-21 (rIL-21) is an immune stimulating cytokine recently tested in two Phase 1 trials for immune responsive cancers. A secondary objective of these trials was to characterize pharmacodynamic responses to rIL-21 in patients. Here, we report the effects of systemic rIL-21 on serum markers of immune stimulation.
Experimental design: Recombinant IL-21 was administered by intravenous bolus injection at dose levels from 1 to 100 microg/kg using two distinct treatment regimens: thrice weekly ('3/w') for 6 weeks; or once daily for five consecutive days followed by nine dose-free days ('5 + 9'). In the absence of dose limiting toxicity, additional cycles of dosing were initiated immediately following the nine dose-free days. An array of 70 different proteins was profiled in subject serum samples from several time points during the course of the study. Hierarchical clustering analysis was performed on a normalized subset of these data.
Results: Systemic administration of rIL-21 affected the serum levels of several cytokines, chemokines, acute-phase proteins and cell adhesion proteins. The magnitude and duration of response were dose dependent for a subset of these biomarkers. The 5 + 9 dosing regimen generally produced cyclic changes that were of greater magnitude, as compared to a more chronic stimulation with the 3/w dosing regimen. Despite these differences, rIL-21 effects on many analytes were similar between regimens when averaged over the time of treatment. Based on similar temporal, between-subject and dose response changes, groups of analytes were identified that exhibited distinct components of the rIL-21-mediated immune activation. Biomarkers indicative of lymphocyte activation (increased IL-16, decreased RANTES), acute phase response (increased CRP, ferritin), myeloid activation (increased MDC, MIP-1 alpha), and leukocyte chemotaxis/trafficking (increased sCAMs, MCP-1) were strongly modulated in subjects treated with rIL-21.
Conclusions: Administration of rIL-21 resulted in activation of multiple cell types and immune response pathways. The changes observed in serum proteins were consistent with coincident processes of lymphoid and myeloid cell activation and trafficking, and acute phase response.
Figures
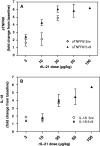
Fig. 1
Changes in serum concentrations of sTNFRII (a), and IL-18 (b). Mean change from baseline (±SD) on Day 19 of treatment is shown for each rIL-21 treatment cohort
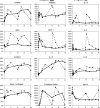
Fig. 2
Changes in serum concentration relative to baseline for selected analytes in subjects treated with 30 μg/kg rIL-21. Effects of the different dose regimens, 5 + 9 (dashed line) and 3/w (solid line), are compared
Fig. 3
Dendrogram of the distance measures (unweighted average Pearson correlation coefficient between the members of linked cluster) of the serum markers for each Subject treated with 30 μg/kg rIL-21 on the 5 + 9 regimen
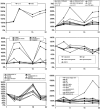
Fig. 4
Group average percent change from group average baseline (_y_-axis, %) over time (_x_-axis, days) for serum markers grouped in clusters identified in Fig. 3 for Subjects treated with 30 μg/kg rIL-21 on the 5 + 9 regimen (n = 12)
Similar articles
- IL-21 induces in vivo immune activation of NK cells and CD8(+) T cells in patients with metastatic melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.
Frederiksen KS, Lundsgaard D, Freeman JA, Hughes SD, Holm TL, Skrumsager BK, Petri A, Hansen LT, McArthur GA, Davis ID, Skak K. Frederiksen KS, et al. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2008 Oct;57(10):1439-49. doi: 10.1007/s00262-008-0479-4. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2008. PMID: 18286285 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Phase I trial of high-dose bolus interleukin-2 and interferon alfa-2a in patients with metastatic malignancy.
Budd GT, Murthy S, Finke J, Sergi J, Gibson V, Medendorp S, Barna B, Boyett J, Bukowski RM. Budd GT, et al. J Clin Oncol. 1992 May;10(5):804-9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1992.10.5.804. J Clin Oncol. 1992. PMID: 1569452 Clinical Trial. - An open-label, two-arm, phase I trial of recombinant human interleukin-21 in patients with metastatic melanoma.
Davis ID, Skrumsager BK, Cebon J, Nicholaou T, Barlow JW, Moller NP, Skak K, Lundsgaard D, Frederiksen KS, Thygesen P, McArthur GA. Davis ID, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Jun 15;13(12):3630-6. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0410. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17575227 Clinical Trial. - Interleukin-2-based therapy for metastatic renal cell cancer: the Cytokine Working Group experience, 1989-1997.
Dutcher JP, Atkins M, Fisher R, Weiss G, Margolin K, Aronson F, Sosman J, Lotze M, Gordon M, Logan T, Mier J. Dutcher JP, et al. Cancer J Sci Am. 1997 Dec;3 Suppl 1:S73-8. Cancer J Sci Am. 1997. PMID: 9457399 Review. - Role of interleukin-2 in patients with HIV infection.
Pett SL, Kelleher AD, Emery S. Pett SL, et al. Drugs. 2010 Jun 18;70(9):1115-30. doi: 10.2165/10898620-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20518579 Review.
Cited by
- Interleukin-21 combined with PD-1 or CTLA-4 blockade enhances antitumor immunity in mouse tumor models.
Lewis KE, Selby MJ, Masters G, Valle J, Dito G, Curtis WR, Garcia R, Mink KA, Waggie KS, Holdren MS, Grosso JF, Korman AJ, Jure-Kunkel M, Dillon SR. Lewis KE, et al. Oncoimmunology. 2017 Oct 4;7(1):e1377873. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1377873. eCollection 2017. Oncoimmunology. 2017. PMID: 29296539 Free PMC article. - Recombinant IL-21 and anti-CD4 antibodies cooperate in syngeneic neuroblastoma immunotherapy and mediate long-lasting immunity.
Rigo V, Corrias MV, Orengo AM, Brizzolara A, Emionite L, Fenoglio D, Filaci G, Croce M, Ferrini S. Rigo V, et al. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014 May;63(5):501-11. doi: 10.1007/s00262-014-1536-9. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014. PMID: 24647609 Free PMC article. - Iacta Alea Est: The Inexorable Advance of Tofacitinib in the Treatment of Dermatomyositis-Associated Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease. A Case Report.
Conca W, Weheba I, Abouzied ME, Abdelsayed A, Aleyouni Y, Al-Mutairy E, Bakshi N, Khalid M. Conca W, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 15;11:585761. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.585761. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33384600 Free PMC article. - IL-21 Enhances Natural Killer Cell Response to Cetuximab-Coated Pancreatic Tumor Cells.
McMichael EL, Jaime-Ramirez AC, Guenterberg KD, Luedke E, Atwal LS, Campbell AR, Hu Z, Tatum AS, Kondadasula SV, Mo X, Tridandapani S, Bloomston M, Ellison EC, Williams TM, Bekaii-Saab T, Carson WE 3rd. McMichael EL, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 15;23(2):489-502. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0004. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 27435400 Free PMC article. - Comparison of vascular leak syndrome in mice treated with IL21 or IL2.
Sivakumar PV, Garcia R, Waggie KS, Anderson-Haley M, Nelson A, Hughes SD. Sivakumar PV, et al. Comp Med. 2013 Feb;63(1):13-21. Comp Med. 2013. PMID: 23561933 Free PMC article.
References
- Damle NK, Doyle LV. IL-2-activated human killer lymphocytes but not their secreted products mediate increase in albumin flux across cultured endothelial monolayers. Implications for vascular leak syndrome. J Immunol. 1989;142(8):2660–2669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous