Dense genomewide linkage scan for alcohol dependence in African Americans: significant linkage on chromosome 10 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Multicenter Study
Dense genomewide linkage scan for alcohol dependence in African Americans: significant linkage on chromosome 10
Joel Gelernter et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2009.
Abstract
Background: Alcohol dependence (AD) is costly to societies worldwide, moderately heritable, and genetically complex. Risk loci in several populations have been identified with genetic linkage analysis. To date, there has been no published linkage study of AD focused on African Americans (AAs).
Methods: We completed a genomewide linkage scan with approximately 6000 single nucleotide polymorphism markers to map loci increasing risk for DSM-IV AD in a set of 238 small nuclear families ascertained on the basis of multiple individuals affected with cocaine or opioid dependence. Model free linkage analysis was completed with Merlin software. A modified marker set was used to avoid bias due to markers in strong linkage disequilibrium.
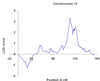
Results: We identified a genomewide-significant linkage to markers near 117.2 centiMorgans on chromosome 10q23.3-24.1 (logarithm of odds score 3.32; p = 5.0E-05; empirical genomewide p = .033).
Conclusions: These data add to the growing evidence for locations for AD risk loci and provide the first linkage evidence for such a locus in the AA population.
Figures
Figure 1
Chromosome 10 linkage results. LOD, logarithm of odds.
Similar articles
- Confirmation and generalization of an alcohol-dependence locus on chromosome 10q.
Panhuysen CI, Kranzler HR, Yu Y, Weiss RD, Brady K, Poling J, Farrer LA, Gelernter J. Panhuysen CI, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 May;35(6):1325-32. doi: 10.1038/npp.2010.1. Epub 2010 Feb 10. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010. PMID: 20147890 Free PMC article. - Genomewide linkage scan for nicotine dependence: identification of a chromosome 5 risk locus.
Gelernter J, Panhuysen C, Weiss R, Brady K, Poling J, Krauthammer M, Farrer L, Kranzler HR. Gelernter J, et al. Biol Psychiatry. 2007 Jan 1;61(1):119-26. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.08.023. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Biol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17081504 - Autosomal linkage scan for loci predisposing to comorbid dependence on multiple substances.
Yang BZ, Han S, Kranzler HR, Farrer LA, Elston RC, Gelernter J. Yang BZ, et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2012 Jun;159B(4):361-9. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32037. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2012. PMID: 22354695 Free PMC article. - Genomewide scan of ocular refraction in African-American families shows significant linkage to chromosome 7p15.
Ciner E, Wojciechowski R, Ibay G, Bailey-Wilson JE, Stambolian D. Ciner E, et al. Genet Epidemiol. 2008 Jul;32(5):454-63. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20318. Genet Epidemiol. 2008. PMID: 18293391 Free PMC article. - A genomewide linkage scan of cocaine dependence and major depressive episode in two populations.
Yang BZ, Han S, Kranzler HR, Farrer LA, Gelernter J. Yang BZ, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011 Nov;36(12):2422-30. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.122. Epub 2011 Aug 17. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21849985 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- A brief history of research on the genetics of alcohol and other drug use disorders.
Schuckit MA. Schuckit MA. J Stud Alcohol Drugs Suppl. 2014;75(17):59-67. doi: 10.15288/jsads.2014.s17.59. J Stud Alcohol Drugs Suppl. 2014. PMID: 24565312 Free PMC article. Review. - A Critical Review of Methods and Results in the Search for Genetic Contributors to Alcohol Sensitivity.
Schuckit MA. Schuckit MA. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2018 May;42(5):822-835. doi: 10.1111/acer.13628. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2018. PMID: 29623680 Free PMC article. Review. - Emerging roles for ncRNAs in alcohol use disorders.
Mayfield RD. Mayfield RD. Alcohol. 2017 May;60:31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Apr 15. Alcohol. 2017. PMID: 28438526 Free PMC article. Review. - Confirmation and generalization of an alcohol-dependence locus on chromosome 10q.
Panhuysen CI, Kranzler HR, Yu Y, Weiss RD, Brady K, Poling J, Farrer LA, Gelernter J. Panhuysen CI, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 May;35(6):1325-32. doi: 10.1038/npp.2010.1. Epub 2010 Feb 10. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010. PMID: 20147890 Free PMC article. - Application of polygenic scores to a deeply phenotyped sample enriched for substance use disorders reveals extensive pleiotropy with psychiatric and somatic traits.
Hartwell EE, Jinwala Z, Milone J, Ramirez S, Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Kember RL. Hartwell EE, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Dec;49(13):1958-1967. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01922-2. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39043921 Free PMC article.
References
- Kendler KS, Heath AC, Neale MC, Kessler RC, Eaves LJ. A population-based twin study of alcoholism in women. JAMA. 1992;268:1877–1882. - PubMed
- Kendler KS, Prescott CA, Neale MC, Pedersen NL. Temperance board registration for alcohol abuse in a national sample of Swedish male twins, born 1902 to 1949. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1997;54:178–184. - PubMed
- Prescott CA, Kendler KS. Genetic and environmental contributions to alcohol abuse and dependence in a population-based sample of male twins. Am J Psychiatry. 1999;56:34–40. - PubMed
- Whitfield JB, Zhu G, Madden PA, Neale MC, Heath AC, Martin NG. The Genetics of Alcohol Intake and of Alcohol Dependence. Alcoholism: Clin Exp Res. 2004;8:1153–1160. - PubMed
- Hasin DS, Stinson FS, Ogburn E, Grant BF. Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence in the United States: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64:830–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 DA012690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HG065403/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA015105/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AA 13736/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA022288/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA 022288/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA 15105/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA 12690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA 11330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA 12849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HG 65403/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AA013736/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006192/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases