Evidence for persistent low-level viremia in individuals who control human immunodeficiency virus in the absence of antiretroviral therapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1128/JVI.01763-08. Epub 2008 Oct 22.
Eric L Delwart, Philip J Norris, Tzong-Hae Lee, Joan Dunn-Williams, Peter W Hunt, Rebecca Hoh, Susan L Stramer, Jeffrey M Linnen, Joseph M McCune, Jeffrey N Martin, Michael P Busch, Steven G Deeks
Affiliations
- PMID: 18945778
- PMCID: PMC2612329
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01763-08
Evidence for persistent low-level viremia in individuals who control human immunodeficiency virus in the absence of antiretroviral therapy
Hiroyu Hatano et al. J Virol. 2009 Jan.
Abstract
A subset of antiretroviral-untreated, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals are able to maintain undetectable plasma HIV RNA levels in the absence of antiretroviral therapy. These "elite" controllers are of high interest as they may provide novel insights regarding host mechanisms of virus control. The degree to which these individuals have residual plasma viremia has not been well defined. We performed a longitudinal study of 46 elite controllers, defined as HIV-seropositive, antiretroviral-untreated individuals with plasma HIV RNA levels of <50 to 75 copies/ml. The median duration of HIV diagnosis was 13 years, the median baseline CD4(+) T-cell count was 753 cells/mm(3), and the median duration of follow-up was 16 months. Plasma and cellular HIV RNA levels were measured using the transcription-mediated amplification (TMA) assay (estimated limit of detection of <3.5 copies RNA/ml). A total of 1,117 TMA assays were performed (median of five time points/subject and four replicates/time point). All but one subject had detectable plasma HIV RNA on at least one time point, and 15 (33%) subjects had detectable RNA at all time points. The majority of controllers also had detectable cell-associated RNA and proviral DNA. A mixed-effect linear model showed no strong evidence of change in plasma RNA levels over time. In conclusion, the vast majority (98%) of elite controllers had measurable plasma HIV RNA, often at levels higher than that observed in antiretroviral-treated patients. This confirms the failure to eradicate the virus, even in these unique individuals who are able to reduce plasma viremia to very low levels without antiretroviral therapy.
Figures
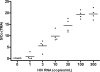
FIG. 1.
In vitro spiking experiments showing the relationship between HIV RNA levels and S/Co ratio using the TMA assay. Each dot represents the mean of the results for four replicates (randomly selected from 20 replicates) performed by four different laboratory technicians; the lines represent the mean S/Co ratio for each viral load copy number (0, 1, 3, 10, 30, 100, and 300 copies/ml).
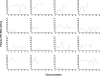
FIG. 2.
Plasma HIV RNA levels in elite controllers. Plasma HIV RNA levels (S/Co ratio) using the TMA assay in a subset (n = 16) of elite controllers with ≥20 months of follow-up. Each panel represents longitudinal plasma HIV RNA levels for one subject.
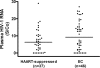
FIG. 3.
Baseline plasma HIV RNA level for 37 HAART-suppressed subjects and 46 elite controllers (EC). The lines represent the median S/Co ratio for each group.
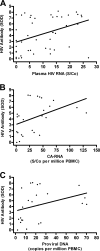
FIG. 4.
(A) Association between baseline plasma HIV RNA and HIV antibody levels (n = 46; Spearman's rho = 0.43; P < 0.01). (B) Association between baseline CA-RNA and HIV antibody levels (n = 25; Spearman's rho = 0.50; P = 0.01). (C) Association between baseline proviral HIV DNA and HIV antibody levels (n = 24; Spearman's rho = 0.40; P = 0.06). Plot excludes one outlier.
Similar articles
- Relationship between T cell activation and CD4+ T cell count in HIV-seropositive individuals with undetectable plasma HIV RNA levels in the absence of therapy.
Hunt PW, Brenchley J, Sinclair E, McCune JM, Roland M, Page-Shafer K, Hsue P, Emu B, Krone M, Lampiris H, Douek D, Martin JN, Deeks SG. Hunt PW, et al. J Infect Dis. 2008 Jan 1;197(1):126-33. doi: 10.1086/524143. J Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18171295 Free PMC article. - Residual viraemia in HIV-1-infected patients with plasma viral load <or=20 copies/ml is associated with increased blood levels of soluble immune activation markers.
Ostrowski SR, Katzenstein TL, Pedersen BK, Gerstoft J, Ullum H. Ostrowski SR, et al. Scand J Immunol. 2008 Dec;68(6):652-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2008.02184.x. Scand J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19055701 - Highly divergent patterns of genetic diversity and evolution in proviral quasispecies from HIV controllers.
de Azevedo SSD, Caetano DG, Côrtes FH, Teixeira SLM, Dos Santos Silva K, Hoagland B, Grinsztejn B, Veloso VG, Morgado MG, Bello G. de Azevedo SSD, et al. Retrovirology. 2017 May 2;14(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12977-017-0354-5. Retrovirology. 2017. PMID: 28464889 Free PMC article. - Single-molecule techniques to quantify and genetically characterise persistent HIV.
Wang XQ, Palmer S. Wang XQ, et al. Retrovirology. 2018 Jan 9;15(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12977-017-0386-x. Retrovirology. 2018. PMID: 29316955 Free PMC article. Review. - Total HIV-1 DNA, a Marker of Viral Reservoir Dynamics with Clinical Implications.
Avettand-Fènoël V, Hocqueloux L, Ghosn J, Cheret A, Frange P, Melard A, Viard JP, Rouzioux C. Avettand-Fènoël V, et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016 Oct;29(4):859-80. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00015-16. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27559075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Antiretroviral therapy initiated within 6 months of HIV infection is associated with lower T-cell activation and smaller HIV reservoir size.
Jain V, Hartogensis W, Bacchetti P, Hunt PW, Hatano H, Sinclair E, Epling L, Lee TH, Busch MP, McCune JM, Pilcher CD, Hecht FM, Deeks SG. Jain V, et al. J Infect Dis. 2013 Oct 15;208(8):1202-11. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit311. Epub 2013 Jul 12. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23852127 Free PMC article. - Persistent HIV-1 replication during antiretroviral therapy.
Martinez-Picado J, Deeks SG. Martinez-Picado J, et al. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2016 Jul;11(4):417-23. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000287. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2016. PMID: 27078619 Free PMC article. Review. - Circulating monocytes are not a major reservoir of HIV-1 in elite suppressors.
Spivak AM, Salgado M, Rabi SA, O'Connell KA, Blankson JN. Spivak AM, et al. J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(19):10399-403. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05409-11. Epub 2011 Jul 27. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21795348 Free PMC article. - Suboptimal Immune Reconstitution among HIV-Infected Saudi Patients following Successful Antiretroviral Treatment.
Al-Majid F, Shakoor Z, Barry M. Al-Majid F, et al. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2019 Jan 10;2019:1842106. doi: 10.1155/2019/1842106. eCollection 2019. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30755782 Free PMC article. - Targeting Inflammation to Reduce Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in People With HIV Infection.
Titanji B, Gavegnano C, Hsue P, Schinazi R, Marconi VC. Titanji B, et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Feb 4;9(3):e014873. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.014873. Epub 2020 Jan 24. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 31973607 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
- Alexander, L., E. Weiskopf, T. C. Greenough, N. C. Gaddis, M. R. Auerbach, M. H. Malim, S. J. O'Brien, B. D. Walker, J. L. Sullivan, and R. C. Desrosiers. 2000. Unusual polymorphisms in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 associated with nonprogressive infection. J. Virol. 744361-4376. - PMC - PubMed
- Amanna, I. J., N. E. Carlson, and M. K. Slifka. 2007. Duration of humoral immunity to common viral and vaccine antigens. N. Engl. J. Med. 3571903-1915. - PubMed
- Bernardin, F., L. Tobler, I. Walsh, J. D. Williams, M. Busch, and E. Delwart. 2008. Clearance of hepatitis C virus RNA from the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of blood donors who spontaneously or therapeutically control their plasma viremia. Hepatology 471446-1452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 MH062246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI067854/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI055273/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR16482/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23AI075985/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 RR016482/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI052745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 OD000329/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH59037/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5-MO1-RR00083-37/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI055273/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AI075985/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI067854/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000083/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH62246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI27763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI052745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials