HC-030031, a TRPA1 selective antagonist, attenuates inflammatory- and neuropathy-induced mechanical hypersensitivity - PubMed (original) (raw)
HC-030031, a TRPA1 selective antagonist, attenuates inflammatory- and neuropathy-induced mechanical hypersensitivity
Samer R Eid et al. Mol Pain. 2008.
Abstract
Background: Safe and effective treatment for chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain remains a key unmet medical need for many patients. The recent discovery and description of the transient receptor potential family of receptors including TRPV1 and TRPA1 has provided a number of potential new therapeutic targets for treating chronic pain. Recent reports have suggested that TRPA1 may play an important role in acute formalin and CFA induced pain. The current study was designed to further explore the therapeutic potential of pharmacological TRPA1 antagonism to treat inflammatory and neuropathic pain.
Results: The in vitro potencies of HC-030031 versus cinnamaldehyde or allyl isothiocyanate (AITC or Mustard oil)-induced TRPA1 activation were 4.9 +/- 0.1 and 7.5 +/- 0.2 microM respectively (IC50). These findings were similar to the previously reported IC50 of 6.2 microM against AITC activation of TRPA1 1. In the rat, oral administration of HC-030031 reduced AITC-induced nocifensive behaviors at a dose of 100 mg/kg. Moreover, oral HC-030031 (100 mg/kg) significantly reversed mechanical hypersensitivity in the more chronic models of Complete Freunds Adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain and the spinal nerve ligation model of neuropathic pain.
Conclusion: Using oral administration of the selective TRPA1 antagonist HC-030031, our results demonstrated that TRPA1 plays an important role in the mechanisms responsible for mechanical hypersensitivity observed in inflammatory and neuropathic pain models. These findings suggested that TRPA1 antagonism may be a suitable new approach for the development of a potent and selective therapeutic agent to treat both inflammatory and neuropathic pain.
Figures
Figure 1
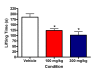
The effect of TRPA1 antagonism on _AITC_-induced nocifensive behaviors. Both 100 mg/kg (red bar) and 300 mg/kg (blue bar) of HC-030031 significantly reduced lifting behavior relative to vehicle treated rats given plantar injection of 1% AITC (white bar; * p, 0.05).
Figure 2
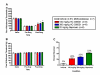
The effect of TRPA1 antagonism on complete Freund's adjuvant induced mechanical hypersensitivity. A. Paw withdrawal thresholds for the injected hind paw were assessed using the Randall-Selitto device prior to intraplantar CFA injections, prior to dosing with vehicle (white bars), 20 mg/kg naproxen (green bars), 100 mg/kg HC-030031 (red bars) or 300 mg/kg HC-030031 (blue bars), and at one hour post p.o. dosing. Naproxen, 100 mg/kg and 300 mg/kg HC-030031 produced a significant attenuation in mechanical hypersensitivity at one hour post dose (*p < 0.05). B. Paw withdrawal thresholds for the noninjected hind paw assessed using the Randall-Selitto device prior to intraplantar CFA injections, prior to dosing with vehicle (white bars), 20 mg/kg naproxen (green bars), 100 mg/kg HC-030031 (red bars) or 300 mg/kg HC-030031 (blue bars), and at one hour post p.o. dosing. C. Percent reversal seen at one hour post p.o. dosing with vehicle (white bars), 20 mg/kg naproxen (green bars), 100 mg/kg HC-030031 (red bars) or 300 mg/kg HC-030031 (blue bars).
Figure 3
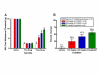
The effect of HC-030031 on spinal nerve ligation induced mechanical hypersensitivity. A. Fifty percent paw withdrawal thresholds for the L5/L6 spinal nerve ligated rats assessed using the Dixon up/down method prior to surgery, prior to dosing with vehicle (white bars), 20 mg/kg pregabalin (green bars), 100 mg/kg HC-030031 (red bars) or 300 mg/kg HC-030031 (blue bars), and at one hour post p.o. dosing. Pregabalin and 300 mg/kg HC-030031 produced a significant attenuation in mechanical hypersensitivity at one hour post dose (*p < 0.05). B. Percent reversal seen at one hour post p.o. dosing with vehicle (white bars), 20 mg/kg pregabalin (green bars), 100 mg/kg HC-030031 (red bars) or 300 mg/kg HC-030031 (blue bars).
Figure 4
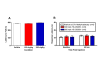
The effect of HC-030031 on locomotor coordination and thermal sensitivity. A. Neither the 100 mg/kg (red bar) nor the 300 mg/kg (blue bar) dose of HC-030031 had a significant impact on the latency to fall off the rotarod during locomotor testing relative to vehicle treated rats (white bar). B. HC-030031 also failed to produce a significant change in thermal latencies on the hot plate test for rats dosed at 100 mg/kg (red bar) or 300 mg/kg (blue bar) relative to vehicle treated rats (white bar).
Similar articles
- The involvement of the TRPA1 receptor in a mouse model of sympathetically maintained neuropathic pain.
Pinheiro Fde V, Villarinho JG, Silva CR, Oliveira SM, Pinheiro Kde V, Petri D, Rossato MF, Guerra GP, Trevisan G, Antonello Rubin M, Geppetti P, Ferreira J, André E. Pinheiro Fde V, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan 15;747:105-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.11.039. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25498793 - The TRPA1 channel in inflammatory and neuropathic pain and migraine.
Nassini R, Materazzi S, Benemei S, Geppetti P. Nassini R, et al. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;167:1-43. doi: 10.1007/112_2014_18. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24668446 Review. - Activation of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 by eugenol.
Chung G, Im ST, Kim YH, Jung SJ, Rhyu MR, Oh SB. Chung G, et al. Neuroscience. 2014 Mar 7;261:153-60. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.12.047. Epub 2013 Dec 30. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24384226 - 7-Substituted-pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine-2,4-dione derivatives as antagonists of the transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) channel: a promising approach for treating pain and inflammation.
Baraldi PG, Romagnoli R, Saponaro G, Aghazadeh Tabrizi M, Baraldi S, Pedretti P, Fusi C, Nassini R, Materazzi S, Geppetti P, Preti D. Baraldi PG, et al. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012 Mar 1;20(5):1690-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.01.020. Epub 2012 Jan 24. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22325155 - A new tr(i)p to sense pain: TRPA1 channel as a target for novel analgesics.
Cai X. Cai X. Expert Rev Neurother. 2008 Nov;8(11):1675-81. doi: 10.1586/14737175.8.11.1675. Expert Rev Neurother. 2008. PMID: 18986238 Review.
Cited by
- Sensory TRP channels: the key transducers of nociception and pain.
Mickle AD, Shepherd AJ, Mohapatra DP. Mickle AD, et al. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;131:73-118. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 25744671 Free PMC article. Review. - Ion channel therapeutics for pain.
Skerratt SE, West CW. Skerratt SE, et al. Channels (Austin). 2015;9(6):344-51. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2015.1075105. Channels (Austin). 2015. PMID: 26218246 Free PMC article. Review. - Transient receptor potential channel involvement in antinociceptive effect of citral in orofacial acute and chronic pain models.
Alves Rodrigues Santos SA, de Barros Mamede Vidal Damasceno M, Alves Magalhães FE, Sessle BJ, Amaro de Oliveira B, Alves Batista FL, Vieira-Neto AE, Rolim Campos A. Alves Rodrigues Santos SA, et al. EXCLI J. 2022 Jun 24;21:869-887. doi: 10.17179/excli2022-5042. eCollection 2022. EXCLI J. 2022. PMID: 36172071 Free PMC article. - Angiotensin II Triggers Peripheral Macrophage-to-Sensory Neuron Redox Crosstalk to Elicit Pain.
Shepherd AJ, Copits BA, Mickle AD, Karlsson P, Kadunganattil S, Haroutounian S, Tadinada SM, de Kloet AD, Valtcheva MV, McIlvried LA, Sheahan TD, Jain S, Ray PR, Usachev YM, Dussor G, Krause EG, Price TJ, Gereau RW 4th, Mohapatra DP. Shepherd AJ, et al. J Neurosci. 2018 Aug 8;38(32):7032-7057. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3542-17.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 5. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29976627 Free PMC article. - Molecular basis determining inhibition/activation of nociceptive receptor TRPA1 protein: a single amino acid dictates species-specific actions of the most potent mammalian TRPA1 antagonist.
Banzawa N, Saito S, Imagawa T, Kashio M, Takahashi K, Tominaga M, Ohta T. Banzawa N, et al. J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 14;289(46):31927-31939. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.586891. Epub 2014 Sep 30. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25271161 Free PMC article.
References
- Corey DP, Garcia-Anoveros J, Holt JR, Kwan KY, Lin SY, Vollrath MA, Amalfitano A, Cheung EL, Derfler BH, Duggan A, Geleoc GS, Gray PA, Hoffman MP, Rehm HL, Tamasauskas D, Zhang DS. TRPA1 is a candidate for the mechanosensitive transduction channel of vertebrate hair cells. Nature. 2004;432:723–730. doi: 10.1038/nature03066. - DOI - PubMed
- Diogenes A, Akopian AN, Hargreaves KM. NGF up-regulates TRPA1: implications for orofacial pain. J Dent Res. 2007;86:550–555. - PubMed
- Story GM, Peier AM, Reeve AJ, Eid SR, Mosbacher J, Hricik TR, Earley TJ, Hergarden AC, Andersson DA, Hwang SW, McIntyre P, Jegla T, Bevan S, Patapoutian A. ANKTM1, a TRP-like channel expressed in nociceptive neurons, is activated by cold temperatures. Cell. 2003;112:819–829. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00158-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases