Whole population, genome-wide mapping of hidden relatedness - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Whole population, genome-wide mapping of hidden relatedness
Alexander Gusev et al. Genome Res. 2009 Feb.
Abstract
We present GERMLINE, a robust algorithm for identifying segmental sharing indicative of recent common ancestry between pairs of individuals. Unlike methods with comparable objectives, GERMLINE scales linearly with the number of samples, enabling analysis of whole-genome data in large cohorts. Our approach is based on a dictionary of haplotypes that is used to efficiently discover short exact matches between individuals. We then expand these matches using dynamic programming to identify long, nearly identical segmental sharing that is indicative of relatedness. We use GERMLINE to comprehensively survey hidden relatedness both in the HapMap as well as in a densely typed island population of 3000 individuals. We verify that GERMLINE is in concordance with other methods when they can process the data, and also facilitates analysis of larger scale studies. We bolster these results by demonstrating novel applications of precise analysis of hidden relatedness for (1) identification and resolution of phasing errors and (2) exposing polymorphic deletions that are otherwise challenging to detect. This finding is supported by concordance of detected deletions with other evidence from independent databases and statistical analyses of fluorescence intensity not used by GERMLINE.
Figures
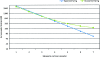
Figure 1.
Expected and detected genome-wide sharing (Kosrae Cohort). (Blue, ▲) Expected genome-wide sharing; (green, ■) detected genome-wide sharing.
Figure 2.
PLINK metrics and share length for equally related pairs. Comparison of PLINK  and _Z_1 values with GERMLINE share length for individuals of equal relationship coefficients. (Left) PLINK
and _Z_1 values with GERMLINE share length for individuals of equal relationship coefficients. (Left) PLINK  values; (middle) PLINK _Z_1 values; (right) GERMLINE share length (cM). Error bars, 99% CI.
values; (middle) PLINK _Z_1 values; (right) GERMLINE share length (cM). Error bars, 99% CI.
Figure 3.
Candidate deletion fluorescence intensity. (Black line) Population average; (open circles) individuals identified as having the deletion; (blue bar at bottom) deletion identified by GERMLINE.
Figure 4.
Verified candidate deletion regions (top 200). (dbGV) Identified in Database of Genomic Variants; (CNAT) verified by Affymetrix Copy Number Analysis Tool; (Intensity) verified as deviation from population average intensity.
Similar articles
- Unexpected relationships and inbreeding in HapMap phase III populations.
Stevens EL, Baugher JD, Shirley MD, Frelin LP, Pevsner J. Stevens EL, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049575. Epub 2012 Nov 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23185369 Free PMC article. - LDMAP: the construction of high-resolution linkage disequilibrium maps of the human genome.
Kuo TY, Lau W, Collins AR. Kuo TY, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2007;376:47-57. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-389-9_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17984537 - Inbreeding coefficient estimation with dense SNP data: comparison of strategies and application to HapMap III.
Gazal S, Sahbatou M, Perdry H, Letort S, Génin E, Leutenegger AL. Gazal S, et al. Hum Hered. 2014;77(1-4):49-62. doi: 10.1159/000358224. Epub 2014 Jul 29. Hum Hered. 2014. PMID: 25060269 - Navigating the HapMap.
Barnes MR. Barnes MR. Brief Bioinform. 2006 Sep;7(3):211-24. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbl021. Epub 2006 Jul 28. Brief Bioinform. 2006. PMID: 16877472 Review. - Computing genetic imprinting expressed by haplotypes.
Cheng Y, Berg A, Wu S, Li Y, Wu R. Cheng Y, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;573:189-212. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-247-6_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19763929 Review.
Cited by
- Evaluation of Four Forensic Investigative Genetic Genealogy Analysis Approaches with Decreased Numbers of SNPs and Increased Genotyping Errors.
Zang Y, Wu E, Li T, Liu J, Wu R, Li R, Sun H. Zang Y, et al. Genes (Basel). 2024 Oct 15;15(10):1329. doi: 10.3390/genes15101329. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457453 Free PMC article. - Extended haplotype association study in Crohn's disease identifies a novel, Ashkenazi Jewish-specific missense mutation in the NF-κB pathway gene, HEATR3.
Zhang W, Hui KY, Gusev A, Warner N, Ng SM, Ferguson J, Choi M, Burberry A, Abraham C, Mayer L, Desnick RJ, Cardinale CJ, Hakonarson H, Waterman M, Chowers Y, Karban A, Brant SR, Silverberg MS, Gregersen PK, Katz S, Lifton RP, Zhao H, Nuñez G, Pe'er I, Peter I, Cho JH. Zhang W, et al. Genes Immun. 2013 Jul-Aug;14(5):310-6. doi: 10.1038/gene.2013.19. Epub 2013 Apr 25. Genes Immun. 2013. PMID: 23615072 Free PMC article. - Improving the accuracy and efficiency of identity-by-descent detection in population data.
Browning BL, Browning SR. Browning BL, et al. Genetics. 2013 Jun;194(2):459-71. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.150029. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23535385 Free PMC article. - Low-pass genome-wide sequencing and variant inference using identity-by-descent in an isolated human population.
Gusev A, Shah MJ, Kenny EE, Ramachandran A, Lowe JK, Salit J, Lee CC, Levandowsky EC, Weaver TN, Doan QC, Peckham HE, McLaughlin SF, Lyons MR, Sheth VN, Stoffel M, De La Vega FM, Friedman JM, Breslow JL, Pe'er I. Gusev A, et al. Genetics. 2012 Feb;190(2):679-89. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.134874. Epub 2011 Nov 30. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22135348 Free PMC article. - A Genealogical Look at Shared Ancestry on the X Chromosome.
Buffalo V, Mount SM, Coop G. Buffalo V, et al. Genetics. 2016 Sep;204(1):57-75. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.190041. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27356612 Free PMC article.
References
- Altschul S.F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E.W., Lipman D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
- Ayers K.L., Sabatti C., Lange K. Reconstructing ancestral haplotypes with a dictionary model. J. Comput. Biol. 2006;13:767–785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 5R01 DK60089/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK060089/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA121852/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- 5 U54 CA121852/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials