SNAP: a web-based tool for identification and annotation of proxy SNPs using HapMap - PubMed (original) (raw)
SNAP: a web-based tool for identification and annotation of proxy SNPs using HapMap
Andrew D Johnson et al. Bioinformatics. 2008.
Abstract
Summary: The interpretation of genome-wide association results is confounded by linkage disequilibrium between nearby alleles. We have developed a flexible bioinformatics query tool for single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to identify and to annotate nearby SNPs in linkage disequilibrium (proxies) based on HapMap. By offering functionality to generate graphical plots for these data, the SNAP server will facilitate interpretation and comparison of genome-wide association study results, and the design of fine-mapping experiments (by delineating genomic regions harboring associated variants and their proxies).
Availability: SNAP server is available at http://www.broad.mit.edu/mpg/snap/.
Figures
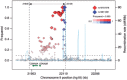
Fig. 1.
Regional LD plot for SNPs rs10757278 and rs10811661 at 9p21.3, associated with coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes, respectively.
Similar articles
- SNPsnap: a Web-based tool for identification and annotation of matched SNPs.
Pers TH, Timshel P, Hirschhorn JN. Pers TH, et al. Bioinformatics. 2015 Feb 1;31(3):418-20. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu655. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25316677 Free PMC article. - CandiSNPer: a web tool for the identification of candidate SNPs for causal variants.
Schmitt AO, Assmus J, Bortfeldt RH, Brockmann GA. Schmitt AO, et al. Bioinformatics. 2010 Apr 1;26(7):969-70. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq068. Epub 2010 Feb 19. Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20172942 - GLIDERS--a web-based search engine for genome-wide linkage disequilibrium between HapMap SNPs.
Lawrence R, Day-Williams AG, Mott R, Broxholme J, Cardon LR, Zeggini E. Lawrence R, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Oct 31;10:367. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-367. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19878600 Free PMC article. - Should we have blind faith in bioinformatics software? Illustrations from the SNAP web-based tool.
Robiou-du-Pont S, Li A, Christie S, Sohani ZN, Meyre D. Robiou-du-Pont S, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 5;10(3):e0118925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118925. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25742008 Free PMC article. - Navigating the HapMap.
Barnes MR. Barnes MR. Brief Bioinform. 2006 Sep;7(3):211-24. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbl021. Epub 2006 Jul 28. Brief Bioinform. 2006. PMID: 16877472 Review.
Cited by
- Comparative genomics reveals carbohydrate enzymatic fluctuations and herbivorous adaptations in arthropods.
Ojeda-Martinez D, Diaz I, Santamaria ME, Ortego F. Ojeda-Martinez D, et al. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 Oct 18;23:3744-3758. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.10.027. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 39525084 Free PMC article. - Breast cancer and neoplasms of the thyroid gland: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study.
Sun Y, Wan B, Liu X, Dong J, Yin S, Wu Y. Sun Y, et al. Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 14;14:1422009. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1422009. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39469634 Free PMC article. - Whole-Genome Sequencing of the Entomopathogenic Fungus Fusarium solani KMZW-1 and Its Efficacy Against Bactrocera dorsalis.
Yu J, Hussain M, Wu M, Shi C, Li S, Ji Y, Hussain S, Qin D, Xiao C, Wu G. Yu J, et al. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Oct 17;46(10):11593-11612. doi: 10.3390/cimb46100688. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39451568 Free PMC article. - Acquisition and evolution of the neurotoxin domoic acid biosynthesis gene cluster in Pseudo-nitzschia species.
He Z, Xu Q, Chen Y, Liu S, Song H, Wang H, Leaw CP, Chen N. He Z, et al. Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 23;7(1):1378. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07068-7. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39443678 Free PMC article. - An acidophilic fungus promotes prey digestion in a carnivorous plant.
Sun PF, Lu MR, Liu YC, Shaw BJP, Lin CP, Chen HW, Lin YF, Hoh DZ, Ke HM, Wang IF, Lu MJ, Young EB, Millett J, Kirschner R, Lin YJ, Chen YL, Tsai IJ. Sun PF, et al. Nat Microbiol. 2024 Oct;9(10):2522-2537. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01766-y. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Nat Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39090391 Free PMC article.
References
- Barrett JC, et al. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:263–265. - PubMed
- Helgadottir A, et al. A common variant on chromosome 9p21 affects the risk of myocardial infarction. Science. 2007;316:1491–1493. - PubMed
- Liefeld T, et al. GeneCruiser: a web service for the annotation of microarray data. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:3681–3682. - PubMed
- Marchini J, et al. A new multipoint method for genome-wide association studies by imputation of genotypes. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:906–913. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01-HC-25195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65226/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC25195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-65226/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials