Genome-wide association analysis reveals putative Alzheimer's disease susceptibility loci in addition to APOE - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.10.008. Epub 2008 Oct 30.
Christoph Lange, Kristina Mullin, Michele Parkinson, Monica Hsiao, Meghan F Hogan, Brit M M Schjeide, Basavaraj Hooli, Jason Divito, Iuliana Ionita, Hongyu Jiang, Nan Laird, Thomas Moscarillo, Kari L Ohlsen, Kathryn Elliott, Xin Wang, Diane Hu-Lince, Marie Ryder, Amy Murphy, Steven L Wagner, Deborah Blacker, K David Becker, Rudolph E Tanzi
Affiliations
- PMID: 18976728
- PMCID: PMC2668052
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.10.008
Genome-wide association analysis reveals putative Alzheimer's disease susceptibility loci in addition to APOE
Lars Bertram et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2008 Nov.
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a genetically complex and heterogeneous disorder. To date four genes have been established to either cause early-onset autosomal-dominant AD (APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2(1-4)) or to increase susceptibility for late-onset AD (APOE5). However, the heritability of late-onset AD is as high as 80%, (6) and much of the phenotypic variance remains unexplained to date. We performed a genome-wide association (GWA) analysis using 484,522 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on a large (1,376 samples from 410 families) sample of AD families of self-reported European descent. We identified five SNPs showing either significant or marginally significant genome-wide association with a multivariate phenotype combining affection status and onset age. One of these signals (p = 5.7 x 10(-14)) was elicited by SNP rs4420638 and probably reflects APOE-epsilon4, which maps 11 kb proximal (r2 = 0.78). The other four signals were tested in three additional independent AD family samples composed of nearly 2700 individuals from almost 900 families. Two of these SNPs showed significant association in the replication samples (combined p values 0.007 and 0.00002). The SNP (rs11159647, on chromosome 14q31) with the strongest association signal also showed evidence of association with the same allele in GWA data generated in an independent sample of approximately 1,400 AD cases and controls (p = 0.04). Although the precise identity of the underlying locus(i) remains elusive, our study provides compelling evidence for the existence of at least one previously undescribed AD gene that, like APOE-epsilon4, primarily acts as a modifier of onset age.
Figures
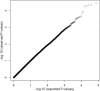
Figure 1
Q-Q Plot of Markers Tested in the GWA Screening Phase Distribution of FBAT-GEE p values for all 404,604 SNPs on the 500K array with ≥20 informative families as Q-Q plot depicting observed versus expected p values.
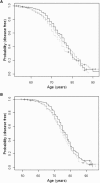
Figure 2
Kaplan-Meier Survival Curves for rs11159647 in 500K Screening Sample and Combined Follow-Up Data Set Dotted lines represent carriers of the A/A genotype, broken lines are A/G-carriers, solid lines are G/G-carriers. (A) shows the NIMH sample used in the 500K screen. (B) shows the sample after combining all follow-up samples (NIA, NCRAD, and CAG).
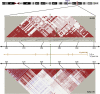
Figure 3
Genomic Context of the Chromosome 14q31 Association Signal Linkage disequilibrium structure and location of Genscan Gene predictions (NTSs) in a 500 kb interval encompassing rs11159647 on chromosome 14q31.2.
Figure 4
Association Results of Markers within 500 kb of the Chromosome 14q31 Association Signal Distribution of association results of SNPs on the 500K array within ±250 kb of SNP rs11159647 on chromosome 14q31 showing genome-wide significance in the NIMH-CAU sample (FBAT-GEE statistic, additive model).
Similar articles
- A high-density whole-genome association study reveals that APOE is the major susceptibility gene for sporadic late-onset Alzheimer's disease.
Coon KD, Myers AJ, Craig DW, Webster JA, Pearson JV, Lince DH, Zismann VL, Beach TG, Leung D, Bryden L, Halperin RF, Marlowe L, Kaleem M, Walker DG, Ravid R, Heward CB, Rogers J, Papassotiropoulos A, Reiman EM, Hardy J, Stephan DA. Coon KD, et al. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007 Apr;68(4):613-8. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v68n0419. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17474819 - Family-based association analyses of imputed genotypes reveal genome-wide significant association of Alzheimer's disease with OSBPL6, PTPRG, and PDCL3.
Herold C, Hooli BV, Mullin K, Liu T, Roehr JT, Mattheisen M, Parrado AR, Bertram L, Lange C, Tanzi RE. Herold C, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2016 Nov;21(11):1608-1612. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.218. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Mol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26830138 Free PMC article. - APOE and other loci affect age-at-onset in Alzheimer's disease families with PS2 mutation.
Wijsman EM, Daw EW, Yu X, Steinbart EJ, Nochlin D, Bird TD, Schellenberg GD. Wijsman EM, et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005 Jan 5;132B(1):14-20. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30087. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005. PMID: 15389756 - The genetics of Alzheimer disease.
Tanzi RE. Tanzi RE. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012 Oct 1;2(10):a006296. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006296. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012. PMID: 23028126 Free PMC article. Review. - The current status of Alzheimer's disease genetics: what do we tell the patients?
Bertram L, Tanzi RE. Bertram L, et al. Pharmacol Res. 2004 Oct;50(4):385-96. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2003.11.018. Pharmacol Res. 2004. PMID: 15304236 Review.
Cited by
- Phosphodiesterase 4D Gene Modifies the Functional Network of Patients With Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer's Disease.
Xiang J, Wang X, Gao Y, Li T, Cao R, Yan T, Ma Y, Niu Y, Xue J, Wang B. Xiang J, et al. Front Genet. 2020 Aug 6;11:890. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00890. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32849849 Free PMC article. - Genetic architecture of Alzheimer's disease.
Neuner SM, Tcw J, Goate AM. Neuner SM, et al. Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Sep;143:104976. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104976. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32565066 Free PMC article. Review. - Microglia in Alzheimer's Disease in the Context of Tau Pathology.
Perea JR, Bolós M, Avila J. Perea JR, et al. Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 14;10(10):1439. doi: 10.3390/biom10101439. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33066368 Free PMC article. Review. - The heterogeneity of microglial activation and its epigenetic and non-coding RNA regulations in the immunopathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases.
Li C, Ren J, Zhang M, Wang H, Yi F, Wu J, Tang Y. Li C, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Sep 6;79(10):511. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04536-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36066650 Free PMC article. Review. - A genome-wide study shows a limited contribution of rare copy number variants to Alzheimer's disease risk.
Chapman J, Rees E, Harold D, Ivanov D, Gerrish A, Sims R, Hollingworth P, Stretton A; GERAD1 Consortium; Holmans P, Owen MJ, O'Donovan MC, Williams J, Kirov G. Chapman J, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Feb 15;22(4):816-24. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds476. Epub 2012 Nov 11. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23148125 Free PMC article.
References
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M.C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991;349:704–706. - PubMed
- Levy-Lahad E., Wasco W., Poorkaj P., Romano D.M., Oshima J., Pettingell W.H., Yu C.E., Jondro P.D., Schmidt S.D., Wang K. Candidate gene for the chromosome 1 familial Alzheimer's disease locus. Science. 1995;269:973–977. - PubMed
- Rogaev E.I., Sherrington R., Rogaeva E.A., Levesque G., Ikeda M., Liang Y., Chi H., Lin C., Holman K., Tsuda T. Familial Alzheimer's disease in kindreds with missense mutations in a gene on chromosome 1 related to the Alzheimer's disease type 3 gene. Nature. 1995;376:775–778. - PubMed
- Sherrington R., Rogaev E.I., Liang Y., Rogaeva E.A., Levesque G., Ikeda M., Chi H., Lin C., Li G., Holman K. Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1995;375:754–760. - PubMed
- Saunders A.M., Strittmatter W.J., Schmechel D., George-Hyslop P.H., Pericak-Vance M.A., Joo S.H., Rosi B.L., Gusella J.F., Crapper-MacLachlan D.R., Alberts M.J. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1993;43:1467–1472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous