Epigenetic mechanisms in mammals - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Epigenetic mechanisms in mammals
J K Kim et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Feb.
Abstract
DNA and histone methylation are linked and subjected to mitotic inheritance in mammals. Yet how methylation is propagated and maintained between successive cell divisions is not fully understood. A series of enzyme families that can add methylation marks to cytosine nucleobases, and lysine and arginine amino acid residues has been discovered. Apart from methyltransferases, there are also histone modification enzymes and accessory proteins, which can facilitate and/or target epigenetic marks. Several lysine and arginine demethylases have been discovered recently, and the presence of an active DNA demethylase is speculated in mammalian cells. A mammalian methyl DNA binding protein MBD2 and de novo DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A and DNMT3B are shown experimentally to possess DNA demethylase activity. Thus, complex mammalian epigenetic mechanisms appear to be dynamic yet reversible along with a well-choreographed set of events that take place during mammalian development.
Figures
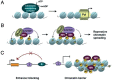
Figure 1
Other nuclear proteins crucial for epigenetic modifications and gene regulation. (A) A simplified example for the role of chromatin remodeling complexes recruited by transcription factors or specific modifications on chromatin [72]. ATP hydrolysis-driven repositioning of nucleosomes exposes an occluded DNA region to allow access of transcriptionalmachinery. (B) Modified histones serve as recognition sites for effector proteins. The illustration shows that trimethylated H3K9 (hexagons) is recognized by HP1 that recruits SUV39H1 and DNMTsto facilitate further H3K9 methylation, HP1 binding, and DNA methylation on adjacent nucleosomes, resulting in repressive chromatin spreading [75, 76]. (C) A model illustrating two major functions of insulators. Insulators (I) placed between an enhancer (E) and promoter blocks enhancer-promoter communication, thereby preventing inappropriate activation of promoters by distant enhancers (left panel). Insulators can also function as a chromatin barrier that limits heterochromatin spreading and prevents repression of neighboring genes (right panel). Condensed heterochromatin is decorated with repressive marks such as H3K9 methylation (hexagons) and DNA methylation (circles).
Similar articles
- Genomic profiling of DNA methyltransferases reveals a role for DNMT3B in genic methylation.
Baubec T, Colombo DF, Wirbelauer C, Schmidt J, Burger L, Krebs AR, Akalin A, Schübeler D. Baubec T, et al. Nature. 2015 Apr 9;520(7546):243-7. doi: 10.1038/nature14176. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25607372 - Coordinated chromatin control: structural and functional linkage of DNA and histone methylation.
Cheng X, Blumenthal RM. Cheng X, et al. Biochemistry. 2010 Apr 13;49(14):2999-3008. doi: 10.1021/bi100213t. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20210320 Free PMC article. Review. - The DNMT3A ADD domain is required for efficient de novo DNA methylation and maternal imprinting in mouse oocytes.
Uehara R, Au Yeung WK, Toriyama K, Ohishi H, Kubo N, Toh H, Suetake I, Shirane K, Sasaki H. Uehara R, et al. PLoS Genet. 2023 Aug 1;19(8):e1010855. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010855. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37527244 Free PMC article. - Expression analysis of the epigenetic methyltransferases and methyl-CpG binding protein families in the normal B-cell and B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Kn H, Bassal S, Tikellis C, El-Osta A. Kn H, et al. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004 Oct;3(10):989-94. doi: 10.4161/cbt.3.10.1137. Epub 2004 Oct 2. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15467427 - SET7/9 mediated methylation of non-histone proteins in mammalian cells.
Pradhan S, Chin HG, Estève PO, Jacobsen SE. Pradhan S, et al. Epigenetics. 2009 Aug 16;4(6):383-7. doi: 10.4161/epi.4.6.9450. Epub 2009 Aug 6. Epigenetics. 2009. PMID: 19684477 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Can Environmental Enrichment Modulate Epigenetic Processes in the Central Nervous System Under Adverse Environmental Conditions? A Systematic Review.
de Sousa Fernandes MS, Costa MR, Badicu G, Yagin FH, Santos GCJ, da Costa JM, de Souza RF, Lagranha CJ, Ardigò LP, Souto FO. de Sousa Fernandes MS, et al. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Oct 21;44(1):69. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01506-0. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39432132 Free PMC article. - Impact of Physical Activity on DNA Methylation Signatures in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review with Bioinformatic Analysis.
Moulton C, Lisi V, Silvestri M, Ceci R, Grazioli E, Sgrò P, Caporossi D, Dimauro I. Moulton C, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 3;16(17):3067. doi: 10.3390/cancers16173067. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272925 Free PMC article. Review. - Assessing DNA methylation of ATG 5 and MAP1LC3Av1 gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma and oral leukoplakia- a cross sectional study.
Raja N, Ganesan A, Chandrasekar Lakshmi K, Aniyan Y. Raja N, et al. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2024 Sep-Oct;14(5):534-539. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2024.07.001. Epub 2024 Jul 6. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2024. PMID: 39070885 Free PMC article. - Beneficial Effects of _Manilkara zapota_-Derived Bioactive Compounds in the Epigenetic Program of Neurodevelopment.
Russo C, Valle MS, D'Angeli F, Surdo S, Giunta S, Barbera AC, Malaguarnera L. Russo C, et al. Nutrients. 2024 Jul 11;16(14):2225. doi: 10.3390/nu16142225. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064669 Free PMC article. Review. - Microbiota and Resveratrol: How Are They Linked to Osteoporosis?
Meyer C, Brockmueller A, Ruiz de Porras V, Shakibaei M. Meyer C, et al. Cells. 2024 Jul 3;13(13):1145. doi: 10.3390/cells13131145. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38994996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous