The SIRT2 deacetylase regulates autoacetylation of p300 - PubMed (original) (raw)
The SIRT2 deacetylase regulates autoacetylation of p300
Joshua C Black et al. Mol Cell. 2008.
Abstract
Autoacetylation of the p300 histone acetyltransferase controls the transition between VP16-mediated chromatin acetylation and preinitiation complex (PIC) assembly. Currently, it is unknown if and how autoacetylated p300 is deacetylated. We found that the NAD(+)-dependent histone deacetylase SIRT2 deacetylates p300 in vitro and in cells. SIRT2 deacetylates lysine residues in the catalytic domain of p300 and restores binding of p300 to the PIC. RNAi-mediated depletion or chemical inhibition of SIRT2 in cells results in accumulation of acetylated p300. The altered ac-p300/p300 ratio in SIRT2-depleted cells results in decreased p300 recruitment to an integrated VP16-responsive gene and inhibition of transcription. We conclude that p300 undergoes a dynamic cycle of autoacetylation and deacetylation.
Figures
Figure 1
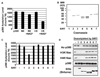
SIRT2 Deacetylates p300. A.) Cellular extracts contain an NAD+ dependent p300 deacetylase activity. Dialyzed nuclear (NE) or cytoplasmic extract (CE) from equal number of cells were incubated with 3H ac-p300 in the presence of NAD+ as indicated. Error bars represent the standard deviation. B.) Coomassie-blue stained gel of purified Sirtuins (300ng). C.) SIRT2 deacetylates p300 in vitro. Filter binding assays of purified Sirtuins incubated with 3H ac-p300. Error bars represent the standard deviation. D.) SIRT1, 2 and 3 deacetylate histones. Sirtuins were incubated with NAD+, ac-p300 and HeLa core histones. Deacetylation was monitored by immunoblot.
Figure 2
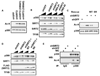
SIRT2 deacetylation of p300 restores p300 binding to GAL4-VP16-Mediator complexes. A.) SIRT2 deacetylates p300. Ac-p300 or ac-p300 HAT domain treated with SIRT2 in the presence of NAD+ or Nicotinamide (NIC) as indicated. Deacetylation was assayed by immunoblot with anti-acetyl-lysine antibody. B.) Amount of lysine acetylation detected in p300 MudPIT analyses. The percent lysine acetylation represents the number of spectral counts for acetylated lysine residues divided by the total spectral counts for lysine residues. The data is expressed as an average +/− standard deviation. A two-tailed student's t-test was performed and gave a p-value = 0.009691. C.) Representative lysines from MudPIT analysis. Data are shown as percent of peptides acetylated divided by the total number of peptides identified for each residue. D.) Immobilized template assay. Immobilized template was prebound by GAL4-VP16 followed by incubation with Mediator and p300, ac-p300, or SIRT2 treated ac-p300 as indicated. Binding was analyzed by immunoblot. Titrations represent 2-fold steps. E.) SIRT2 restores p300 binding to Mediator. Immobilized DNA was prebound by GAL4-VP16 and Mediator followed by incubation with p300, ac-p300, or SIRT1-7 treated ac-p300 as indicated. Input indicates levels of p300 and ac-p300 included in each immobilized template reaction.
Figure 3
SIRT2 deacetylates p300 in vivo. A.) Depletion of SIRT2 by shRNA increases ac-p300. U2OS cells treated with shGFP, OBS #1, OBS #2 and shSIRT2. The p300 was immunoprecipitated and analyzed by acetyl-lysine immunoblot. The immunoblot signals correspond to mRNA levels measured by qPCR (data not shown) B.) Knockdown of SIRT2. Whole cell extracts from panel a immunoblotted for SIRT2 levels. Titrations are 3-fold steps. C.) Expression of shRNA resistant FLAG-SIRT2 in U2OS cells restores p300 deacetylation. Immunoprecipitated p300 analyzed for acetylation by immunoblot. WT= wildtype SIRT2, SR= shRNA resistant SIRT2. D.) Expression of FLAG-SIRT2 and SR FLAG-SIRT2. Whole cell extract immunoblots. Titrations are 3-fold steps. E.) Depletion or inhibition of SIRT2 increases cellular ac-p300. U2OS Cells treated with Nicotinamide (NIC), shGFP, or shSIRT2 were lysed and p300 immunoprecipitated. Immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with anti acetyl-lysine antibody.
Figure 4
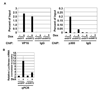
Ablation of SIRT2 regulates VP16-dependent recruitment of p300 and gene expression. A.) Increased acetylated p300 levels result in decreased p300 recruitment. qPCR of ChIP analysis of p300 binding to Luciferase promoter in Tet-ON U2OS cells treated with shSIRT2 shRNAs. Error bars represent standard deviation of three biological replicates. B.) Loss of p300 recruitment inhibits Luciferase expression. qPCR analysis of Luciferase RNA was normalized to β-Actin (p=.031 using two-tailed student’s T test). Error bars represent standard deviation of three biological replicates.
Similar articles
- Acetylation of Sirt2 by p300 attenuates its deacetylase activity.
Han Y, Jin YH, Kim YJ, Kang BY, Choi HJ, Kim DW, Yeo CY, Lee KY. Han Y, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Oct 31;375(4):576-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.08.042. Epub 2008 Aug 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18722353 - Histone deacetylase inhibitors synergize p300 autoacetylation that regulates its transactivation activity and complex formation.
Stiehl DP, Fath DM, Liang D, Jiang Y, Sang N. Stiehl DP, et al. Cancer Res. 2007 Mar 1;67(5):2256-2264. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3985. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17332356 Free PMC article. - Autoacetylation regulates P/CAF nuclear localization.
Blanco-García N, Asensio-Juan E, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás MA. Blanco-García N, et al. J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 16;284(3):1343-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806075200. Epub 2008 Nov 17. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19015268 - HATs off to PIC assembly.
Pugh BF. Pugh BF. Mol Cell. 2006 Sep 15;23(6):776-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.08.022. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16973430 Review. - Will Sirtuin 2 Be a Promising Target for Neuroinflammatory Disorders?
Fan Z, Bin L. Fan Z, et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 22;16:915587. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.915587. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35813508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- HDAC8-mediated inhibition of EP300 drives a transcriptional state that increases melanoma brain metastasis.
Emmons MF, Bennett RL, Riva A, Gupta K, Carvalho LADC, Zhang C, Macaulay R, Dupéré-Richér D, Fang B, Seto E, Koomen JM, Li J, Chen YA, Forsyth PA, Licht JD, Smalley KSM. Emmons MF, et al. Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 29;14(1):7759. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43519-1. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38030596 Free PMC article. - Micromanaging aerobic respiration and glycolysis in cancer cells.
Orang AV, Petersen J, McKinnon RA, Michael MZ. Orang AV, et al. Mol Metab. 2019 May;23:98-126. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.01.014. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Mol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30837197 Free PMC article. Review. - Auto Arginine-GlcNAcylation Is Crucial for Bacterial Pathogens in Regulating Host Cell Death.
Xue J, Pan X, Peng T, Duan M, Du L, Zhuang X, Cai X, Yi X, Fu Y, Li S. Xue J, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 May 5;10:197. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00197. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32432056 Free PMC article. - The diversity of histone versus nonhistone sirtuin substrates.
Martínez-Redondo P, Vaquero A. Martínez-Redondo P, et al. Genes Cancer. 2013 Mar;4(3-4):148-63. doi: 10.1177/1947601913483767. Genes Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24020006 Free PMC article. - Functional genetic variants within the SIRT2 gene promoter in acute myocardial infarction.
Yang W, Gao F, Zhang P, Pang S, Cui Y, Liu L, Wei G, Yan B. Yang W, et al. PLoS One. 2017 Apr 26;12(4):e0176245. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176245. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28445509 Free PMC article.
References
- Arif M, Kumar GV, Narayana C, Kundu TK. Autoacetylation induced specific structural changes in histone acetyltransferase domain of p300: probed by surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B. 2007;111:11877–11879. - PubMed
- Bergel M, Herrera JE, Thatcher BJ, Prymakowska-Bosak M, Vassilev A, Nakatani Y, Martin B, Bustin M. Acetylation of novel sites in the nucleosomal binding domain of chromosomal protein HMG-14 by p300 alters its interaction with nucleosomes. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:11514–11520. - PubMed
- Black JC, Choi JE, Lombardo SR, Carey M. A mechanism for coordinating chromatin modification and preinitiation complex assembly. Mol Cell. 2006;23:809–818. - PubMed
- Bouras T, Fu M, Sauve AA, Wang F, Quong AA, Perkins ND, Hay RT, Gu W, Pestell RG. SIRT1 deacetylation and repression of p300 involves lysine residues 1020/1024 within the cell cycle regulatory domain 1. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:10264–10276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM074701/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM074701-04/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007185/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM074701/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous