Nutritional regulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Nutritional regulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion
Gwen Tolhurst et al. J Physiol. 2009.
Abstract
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), released from L-cells in the intestinal epithelium, plays an important role in postprandial glucose homeostasis and appetite control. Following the recent therapeutic successes of antidiabetic drugs aimed at either mimicking GLP-1 or preventing its degradation, attention is now turning towards the L-cell, and addressing whether it would be both possible and beneficial to stimulate the endogenous release of GLP-1 in vivo. Understanding the mechanisms underlying GLP-1 release from L-cells is key to this type of approach, and the use of cell line models has led to the identification of a variety of pathways that may underlie the physiological responses of L-cells to food ingestion. This review focuses on our current understanding of the signalling mechanisms that underlie L-cell nutrient responsiveness.
Figures
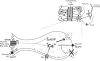
Figure 1. A working model for nutrient-stimulated GLP-1 release
Upper panel: enteroendocrine cells in the intestinal epithelium (grey) detect nutrients passing in the lumen, but also respond to paracrine, neural and hormonal stimuli. Lower panel: potential nutrient-sensing pathways in an individual L-cell include electrogenic uptake pathways, such as SGLT1, metabolic closure of KATP channels and activation of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Downstream signalling pathways include elevated cAMP and [Ca2+], which stimulate vesicle fusion and the consequent release of GLP-1.
Similar articles
- Bitter tastant quinine modulates glucagon-like peptide-1 exocytosis from clonal GLUTag enteroendocrine L cells via actin reorganization.
Harada K, Sakaguchi H, Sada S, Ishida R, Hayasaka Y, Tsuboi T. Harada K, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jun 7;500(3):723-730. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.143. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29684353 - Taurine promotes glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in enteroendocrine L cells.
Osuga Y, Harada K, Yamauchi T, Kitaguchi T, Hirai MY, Matsumoto M, Tsuboi T. Osuga Y, et al. FEBS Lett. 2025 Jun;599(11):1595-1608. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.70014. Epub 2025 Mar 3. FEBS Lett. 2025. PMID: 40026256 Free PMC article. - Fructose stimulates GLP-1 but not GIP secretion in mice, rats, and humans.
Kuhre RE, Gribble FM, Hartmann B, Reimann F, Windeløv JA, Rehfeld JF, Holst JJ. Kuhre RE, et al. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Apr 1;306(7):G622-30. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00372.2013. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24525020 Free PMC article. - The gut endocrine system as a coordinator of postprandial nutrient homoeostasis.
Gribble FM. Gribble FM. Proc Nutr Soc. 2012 Nov;71(4):456-62. doi: 10.1017/S0029665112000705. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Proc Nutr Soc. 2012. PMID: 22906726 Review. - Molecular mechanisms underlying nutrient-stimulated incretin secretion.
Parker HE, Reimann F, Gribble FM. Parker HE, et al. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2010 Jan 5;12:e1. doi: 10.1017/S146239940900132X. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20047700 Review.
Cited by
- Bariatric surgery and T2DM improvement mechanisms: a mathematical model.
Toghaw P, Matone A, Lenbury Y, De Gaetano A. Toghaw P, et al. Theor Biol Med Model. 2012 May 15;9:16. doi: 10.1186/1742-4682-9-16. Theor Biol Med Model. 2012. PMID: 22587410 Free PMC article. - Food protein-derived bioactive peptides in management of type 2 diabetes.
Patil P, Mandal S, Tomar SK, Anand S. Patil P, et al. Eur J Nutr. 2015 Sep;54(6):863-80. doi: 10.1007/s00394-015-0974-2. Epub 2015 Jul 8. Eur J Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26154777 Review. - Postprandial metabolite profiles reveal differential nutrient handling after bariatric surgery compared with matched caloric restriction.
Khoo CM, Muehlbauer MJ, Stevens RD, Pamuklar Z, Chen J, Newgard CB, Torquati A. Khoo CM, et al. Ann Surg. 2014 Apr;259(4):687-93. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318296633f. Ann Surg. 2014. PMID: 23787216 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - GPR119 Agonist AS1269574 Activates TRPA1 Cation Channels to Stimulate GLP-1 Secretion.
Chepurny OG, Holz GG, Roe MW, Leech CA. Chepurny OG, et al. Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Jun;30(6):614-29. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1306. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27082897 Free PMC article. - Glucagon-related peptides and the regulation of food intake in chickens.
Honda K. Honda K. Anim Sci J. 2016 Sep;87(9):1090-8. doi: 10.1111/asj.12619. Epub 2016 May 6. Anim Sci J. 2016. PMID: 27150835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Abello J, Ye F, Bosshard A, Bernard C, Cuber JC, Chayvialle JA. Stimulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion by muscarinic agonist in a murine intestinal endocrine cell line. Endocrinology. 1994;134:2011–2017. - PubMed
- Balks HJ, Holst JJ, von zur Mühlen A, Brabant G. Rapid oscillations in plasma glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in humans: cholinergic control of GLP-1 secretion via muscarinic receptors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82:786–790. - PubMed
- Brubaker PL. Control of glucagon-like immunoreactive peptide secretion from fetal rat intestinal cultures. Endocrinology. 1988;123:220–226. - PubMed
- Brubaker PL, Drucker DJ. Glucagon-like peptides regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis in the pancreas, gut, and central nervous system. Endocrinology. 2004;145:2653–2659. - PubMed
- Brubaker PL, Schloos J, Drucker DJ. Regulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 synthesis and secretion in the GLUTag enteroendocrine cell line. Endocrinology. 1998;139:4108–4114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases