The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2009 Jan;37(Database issue):D141-5.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn879. Epub 2008 Nov 12.
Affiliations
- PMID: 19004872
- PMCID: PMC2686447
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn879
The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis
J R Cole et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan.
Abstract
The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) provides researchers with quality-controlled bacterial and archaeal small subunit rRNA alignments and analysis tools. An improved alignment strategy uses the Infernal secondary structure aware aligner to provide a more consistent higher quality alignment and faster processing of user sequences. Substantial new analysis features include a new Pyrosequencing Pipeline that provides tools to support analysis of ultra high-throughput rRNA sequencing data. This pipeline offers a collection of tools that automate the data processing and simplify the computationally intensive analysis of large sequencing libraries. In addition, a new Taxomatic visualization tool allows rapid visualization of taxonomic inconsistencies and suggests corrections, and a new class Assignment Generator provides instructors with a lesson plan and individualized teaching materials. Details about RDP data and analytical functions can be found at http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/.
Figures
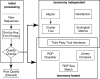
Figure 1.
Tools available in the RDP for processing pyrosequencing data.
Figure 2.
Taxomatic sample screenshot demonstrating a taxonomic anomaly. Yellow indicates more close sequences and teal more distant, with intermediate distances black. The screen is zoomed-in to show a portion of proteobacterial type-strain sequences. α: Alphaproteobacteria. β: Betaproteobacteria. The mouse points to the genus Shinella, originally placed in the Alphaproteobacteria (21), but incorrectly moved to the Betaproteobacteria in the Taxonomic Outline of the Bacteria and Archaea (9).
Similar articles
- The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP-II): previewing a new autoaligner that allows regular updates and the new prokaryotic taxonomy.
Cole JR, Chai B, Marsh TL, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam SA, Chandra S, McGarrell DM, Schmidt TM, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM; Ribosomal Database Project. Cole JR, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jan 1;31(1):442-3. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg039. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12520046 Free PMC article. - The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP-II): sequences and tools for high-throughput rRNA analysis.
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam SA, McGarrell DM, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM. Cole JR, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jan 1;33(Database issue):D294-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki038. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15608200 Free PMC article. - The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): introducing myRDP space and quality controlled public data.
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Bandela AM, Cardenas E, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM. Cole JR, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jan;35(Database issue):D169-72. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl889. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17090583 Free PMC article. - 25 years of serving the community with ribosomal RNA gene reference databases and tools.
Glöckner FO, Yilmaz P, Quast C, Gerken J, Beccati A, Ciuprina A, Bruns G, Yarza P, Peplies J, Westram R, Ludwig W. Glöckner FO, et al. J Biotechnol. 2017 Nov 10;261:169-176. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.06.1198. Epub 2017 Jun 23. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28648396 Review. - The structural basis of large ribosomal subunit function.
Moore PB, Steitz TA. Moore PB, et al. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:813-50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.110601.135450. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003. PMID: 14527328 Review.
Cited by
- The relationship between the vaginal and vulvar microbiomes and lichen sclerosus symptoms in post-menopausal women.
Taylor OA, Birse KD, Hill D'J, Knodel S, Noel-Romas L, Myers A, Marino J, Burgener AD, Pope R, Farr Zuend C. Taylor OA, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 7;14(1):27094. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78372-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39511372 Free PMC article. - Nepali oral microbiomes reflect a gradient of lifestyles from traditional to industrialized.
Ryu EP, Gautam Y, Proctor DM, Bhandari D, Tandukar S, Gupta M, Gautam GP, Relman DA, Shibl AA, Sherchand JB, Jha AR, Davenport ER. Ryu EP, et al. Microbiome. 2024 Nov 4;12(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01941-7. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 39497165 Free PMC article. - Metagenomics unravel distinct taxonomic and functional diversities between terrestrial and aquatic biomes.
Fu Q, Ma K, Zhao J, Li J, Wang X, Zhao M, Fu X, Huang D, Chen H. Fu Q, et al. iScience. 2024 Sep 26;27(10):111047. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111047. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39435150 Free PMC article. - The reverse transsulfuration pathway affects the colonic microbiota and contributes to colitis in mice.
Gobert AP, Latour YL, McNamara KM, Hawkins CV, Williams KJ, Asim M, Barry DP, Allaman MM, Delgado AG, Milne GL, Zhao S, Piazuelo MB, Washington MK, Coburn LA, Wilson KT. Gobert AP, et al. Amino Acids. 2024 Oct 19;56(1):63. doi: 10.1007/s00726-024-03423-4. Amino Acids. 2024. PMID: 39427081 Free PMC article. - Microbial diversity in primary endodontic infections: demographics and radiographic characteristics.
Schuweiler D, Ordinola-Zapata R, Dietz M, Lima BP, Noblett WC, Staley C. Schuweiler D, et al. Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Oct 11;28(11):591. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05982-y. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 39390089
References
- Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Bandela AM, Cardenas E, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, et al. The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): introducing myRDP space and quality controlled public data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:D169–D172. (doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl889) - PMC - PubMed
- Brown MPS. Small subunit ribosomal RNA modeling using stochastic context-free grammar. In. In: Bourne P, Gribskov M, Altman R, Jensen N, Hope D, Lengauer T, Mitchell J, Scheeff E, Smith C, Strande S, et al., editors. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology (ISMB 2000); San Diego, CA. 2000. pp. 57–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials