Bioactive sphingolipids: metabolism and function - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Bioactive sphingolipids: metabolism and function
Nana Bartke et al. J Lipid Res. 2009 Apr.
Abstract
Sphingolipids (SLs) are essential constituents of eukaryotic cells. Besides playing structural roles in cellular membranes, some metabolites, including ceramide, sphingosine, and sphingosine-1-phosphate, have drawn attention as bioactive signaling molecules involved in the regulation of cell growth, differentiation, senescence, and apoptosis. Understanding the many cell regulatory functions of SL metabolites requires an advanced knowledge of how and where in the cell they are generated, converted, or degraded. This review will provide a short overview of the metabolism, localization, and compartmentalization of SLs. Also, a discussion on bioactive members of the SL family and inducers of SL enzymes that lead to ceramide generation will be presented.
Figures
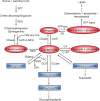
Fig. 1.
Scheme of SL metabolism. Pathways are shown as described in the text. Bioactive SL metabolites are highlighted in red. SPT, serine palmitoyl transferase; KDS, 3-keto-dihydrosphingosine reductase; DES, dihydroceramide desaturase; SPPase, Sph phosphate phosphatase; CK, Cer kinase; C1PP, C1P phosphatase; SMS, SM synthase; PC, phosphatidylcholine; DAG, diacylglycerol; GCS, glucosylceramide synthase; GCase, glucosyl CDase.
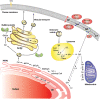
Fig. 2.
Compartmentalization of metabolites and enzymes of the SL pathway. 3KdhSph, 3-keto-dihydrosphingosine; dhSph, dihydrosphingosine; CERT, Cer transfer protein; MAMs, mitochondria associated membranes.
References
- Simons K., and E. Ikonen. 1997. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature. 387 569–572. - PubMed
- Kolesnick R. N., A. Haimovitz-Friedman, and Z. Fuks. 1994. The sphingomyelin signal transduction pathway mediates apoptosis for tumor necrosis factor, Fas, and ionizing radiation. Biochem. Cell Biol. 72 471–474. - PubMed
- Becker K. P., K. Kitatani, J. Idkowiak-Baldys, J. Bielawski, and Y. A. Hannun. 2005. Selective inhibition of juxtanuclear translocation of protein kinase C betaII by a negative feedback mechanism involving ceramide formed from the salvage pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 280 2606–2612. - PubMed
- Jenkins G. M., L. A. Cowart, P. Signorelli, B. J. Pettus, C. E. Chalfant, and Y. A. Hannun. 2002. Acute activation of de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis upon heat shock causes an accumulation of ceramide and subsequent dephosphorylation of SR proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 277 42572–42578. - PubMed
- Goldkorn T., N. Balaban, M. Shannon, V. Chea, K. Matsukuma, D. Gilchrist, H. Wang, and C. Chan. 1998. H2O2 acts on cellular membranes to generate ceramide signaling and initiate apoptosis in tracheobronchial epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 111 3209–3220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources