Ensembl 2009 - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2009 Jan;37(Database issue):D690-7.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn828. Epub 2008 Nov 25.
B L Aken, S Ayling, B Ballester, K Beal, E Bragin, S Brent, Y Chen, P Clapham, L Clarke, G Coates, S Fairley, S Fitzgerald, J Fernandez-Banet, L Gordon, S Graf, S Haider, M Hammond, R Holland, K Howe, A Jenkinson, N Johnson, A Kahari, D Keefe, S Keenan, R Kinsella, F Kokocinski, E Kulesha, D Lawson, I Longden, K Megy, P Meidl, B Overduin, A Parker, B Pritchard, D Rios, M Schuster, G Slater, D Smedley, W Spooner, G Spudich, S Trevanion, A Vilella, J Vogel, S White, S Wilder, A Zadissa, E Birney, F Cunningham, V Curwen, R Durbin, X M Fernandez-Suarez, J Herrero, A Kasprzyk, G Proctor, J Smith, S Searle, P Flicek
Affiliations
- PMID: 19033362
- PMCID: PMC2686571
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn828
Ensembl 2009
T J P Hubbard et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan.
Abstract
The Ensembl project (http://www.ensembl.org) is a comprehensive genome information system featuring an integrated set of genome annotation, databases, and other information for chordate, selected model organism and disease vector genomes. As of release 51 (November 2008), Ensembl fully supports 45 species, and three additional species have preliminary support. New species in the past year include orangutan and six additional low coverage mammalian genomes. Major additions and improvements to Ensembl since our previous report include a major redesign of our website; generation of multiple genome alignments and ancestral sequences using the new Enredo-Pecan-Ortheus pipeline and development of our software infrastructure, particularly to support the Ensembl Genomes project (http://www.ensemblgenomes.org/).
Figures
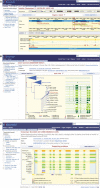
Figure 1.
Screenshots of the Release 51 Ensembl website illustrating the principles of the new design and some of the new features. The figure shows an example of three of the four classes of display view using human gene SLC24A5 as the context. (A) An example of a location based view, showing a region of the genome around the gene. (B) An example of a gene based view, showing the gene tree. (C) An example of a transcript based view, showing supporting evidence for the transcript model. The three tabs across the top of the page, allow rapid navigation between the three classes of view. The fourth variation tab (data not shown) appears if an individual SNP is selected. For each class, the left hand menu lists the different views available. For the location-based views (A), this includes views of a genome at a range of resolutions and genome sequence based comparative genomic views. For the gene-based views (B), this includes textual information about the gene, views of its local genomic environment, views of the gene in the context of its orthologs and paralog relationships with other genomes in the Ensembl system and views of sequence variation within that population. The transcript based views (C) have views similar to the gene based views, but focused around individual transcript structures with more detail. As well as the overall redesign of the navigation between views, there are substantial improvements to many individual views, based on the much more extensive use of AJAX in the new web-code. Examples are the genetree view (B) which allows nodes to be expanded or collapsed interactively, making the view much more usable for large gene families; the substantially redesigned supporting evidence views (C) and the page configuration options on many views (e.g. A) which are much more intuitive than before and have a much greater range of display options.
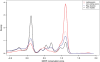
Figure 2.
Figure shows a smoothed density plot of the GERP conservation scores (30) calculated from the 9-way EPO mammalian genome alignment corresponding to human chromosome X (Ensembl release 51). Four different types of genomic features are plotted: coding exons (red), non-coding exons (pink), regulatory features (blue) and ancestral repeats (black). A GERP score of 0 indicates no evidence of selective constraint, whereas high GERP scores shows evidence of selective constraint. Non-coding exons include all non-coding positions of protein-coding genes. Regulatory features include all regulatory features defined by the Ensembl regulatory build (‘Gene Associated’, ‘Non-Gene Associated’, ‘Promoter Associated’ and ‘Unclassified’). Ancestral repeats include MER type II transposons only, as defined by RepeatMasker. Conserved features, such as exons and regulatory features, are clearly distinguished from repeats, a good indication of the quality of the EPO alignments.
Similar articles
- Ensembl 2008.
Flicek P, Aken BL, Beal K, Ballester B, Caccamo M, Chen Y, Clarke L, Coates G, Cunningham F, Cutts T, Down T, Dyer SC, Eyre T, Fitzgerald S, Fernandez-Banet J, Gräf S, Haider S, Hammond M, Holland R, Howe KL, Howe K, Johnson N, Jenkinson A, Kähäri A, Keefe D, Kokocinski F, Kulesha E, Lawson D, Longden I, Megy K, Meidl P, Overduin B, Parker A, Pritchard B, Prlic A, Rice S, Rios D, Schuster M, Sealy I, Slater G, Smedley D, Spudich G, Trevanion S, Vilella AJ, Vogel J, White S, Wood M, Birney E, Cox T, Curwen V, Durbin R, Fernandez-Suarez XM, Herrero J, Hubbard TJ, Kasprzyk A, Proctor G, Smith J, Ureta-Vidal A, Searle S. Flicek P, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D707-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm988. Epub 2007 Nov 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18000006 Free PMC article. - Ensembl 2012.
Flicek P, Amode MR, Barrell D, Beal K, Brent S, Carvalho-Silva D, Clapham P, Coates G, Fairley S, Fitzgerald S, Gil L, Gordon L, Hendrix M, Hourlier T, Johnson N, Kähäri AK, Keefe D, Keenan S, Kinsella R, Komorowska M, Koscielny G, Kulesha E, Larsson P, Longden I, McLaren W, Muffato M, Overduin B, Pignatelli M, Pritchard B, Riat HS, Ritchie GR, Ruffier M, Schuster M, Sobral D, Tang YA, Taylor K, Trevanion S, Vandrovcova J, White S, Wilson M, Wilder SP, Aken BL, Birney E, Cunningham F, Dunham I, Durbin R, Fernández-Suarez XM, Harrow J, Herrero J, Hubbard TJ, Parker A, Proctor G, Spudich G, Vogel J, Yates A, Zadissa A, Searle SM. Flicek P, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(Database issue):D84-90. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr991. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22086963 Free PMC article. - Ensembl's 10th year.
Flicek P, Aken BL, Ballester B, Beal K, Bragin E, Brent S, Chen Y, Clapham P, Coates G, Fairley S, Fitzgerald S, Fernandez-Banet J, Gordon L, Gräf S, Haider S, Hammond M, Howe K, Jenkinson A, Johnson N, Kähäri A, Keefe D, Keenan S, Kinsella R, Kokocinski F, Koscielny G, Kulesha E, Lawson D, Longden I, Massingham T, McLaren W, Megy K, Overduin B, Pritchard B, Rios D, Ruffier M, Schuster M, Slater G, Smedley D, Spudich G, Tang YA, Trevanion S, Vilella A, Vogel J, White S, Wilder SP, Zadissa A, Birney E, Cunningham F, Dunham I, Durbin R, Fernández-Suarez XM, Herrero J, Hubbard TJ, Parker A, Proctor G, Smith J, Searle SM. Flicek P, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jan;38(Database issue):D557-62. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp972. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 19906699 Free PMC article. - Genome information resources - developments at Ensembl.
Hammond MP, Birney E. Hammond MP, et al. Trends Genet. 2004 Jun;20(6):268-72. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2004.04.002. Trends Genet. 2004. PMID: 15145580 Review. - An overview of Ensembl.
Birney E, Andrews TD, Bevan P, Caccamo M, Chen Y, Clarke L, Coates G, Cuff J, Curwen V, Cutts T, Down T, Eyras E, Fernandez-Suarez XM, Gane P, Gibbins B, Gilbert J, Hammond M, Hotz HR, Iyer V, Jekosch K, Kahari A, Kasprzyk A, Keefe D, Keenan S, Lehvaslaiho H, McVicker G, Melsopp C, Meidl P, Mongin E, Pettett R, Potter S, Proctor G, Rae M, Searle S, Slater G, Smedley D, Smith J, Spooner W, Stabenau A, Stalker J, Storey R, Ureta-Vidal A, Woodwark KC, Cameron G, Durbin R, Cox A, Hubbard T, Clamp M. Birney E, et al. Genome Res. 2004 May;14(5):925-8. doi: 10.1101/gr.1860604. Epub 2004 Apr 12. Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15078858 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Comparative genomics of odorant binding proteins in Anopheles gambiae, Aedes aegypti, and Culex quinquefasciatus.
Manoharan M, Ng Fuk Chong M, Vaïtinadapoulé A, Frumence E, Sowdhamini R, Offmann B. Manoharan M, et al. Genome Biol Evol. 2013;5(1):163-80. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evs131. Genome Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23292137 Free PMC article. - The Evolution of Bony Vertebrate Enhancers at Odds with Their Coding Sequence Landscape.
Yousaf A, Sohail Raza M, Ali Abbasi A. Yousaf A, et al. Genome Biol Evol. 2015 Aug 6;7(8):2333-43. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv146. Genome Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 26253316 Free PMC article. - A zebrafish Notum homolog specifically blocks the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Flowers GP, Topczewska JM, Topczewski J. Flowers GP, et al. Development. 2012 Jul;139(13):2416-25. doi: 10.1242/dev.063206. Development. 2012. PMID: 22669824 Free PMC article. - A post-assembly genome-improvement toolkit (PAGIT) to obtain annotated genomes from contigs.
Swain MT, Tsai IJ, Assefa SA, Newbold C, Berriman M, Otto TD. Swain MT, et al. Nat Protoc. 2012 Jun 7;7(7):1260-84. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.068. Nat Protoc. 2012. PMID: 22678431 Free PMC article. - An Alu-based phylogeny of gibbons (hylobatidae).
Meyer TJ, McLain AT, Oldenburg JM, Faulk C, Bourgeois MG, Conlin EM, Mootnick AR, de Jong PJ, Roos C, Carbone L, Batzer MA. Meyer TJ, et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2012 Nov;29(11):3441-50. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss149. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Mol Biol Evol. 2012. PMID: 22683814 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- BBS/B/13462/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBE0116401/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 077198/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BBS/B/13438/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/E010768/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 062023/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/E011640/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous