Extracytoplasmic function sigma factors regulate expression of the Bacillus subtilis yabE gene via a cis-acting antisense RNA - PubMed (original) (raw)
Extracytoplasmic function sigma factors regulate expression of the Bacillus subtilis yabE gene via a cis-acting antisense RNA
Warawan Eiamphungporn et al. J Bacteriol. 2009 Feb.
Abstract
Bacillus subtilis yabE encodes a predicted resuscitation-promoting factor/stationary-phase survival (Rpf/Sps) family autolysin. Here, we demonstrate that yabE is negatively regulated by a cis-acting antisense RNA which, in turn, is regulated by two extracytoplasmic function sigma factors: sigma(X) and sigma(M).
Figures
FIG. 1.
(A) Organization of yabE and the downstream PECF element. Promoter sites are indicated by bent arrows with a subscript to indicate the relevant holoenzyme(s). A putative transcription terminator downstream of yabE is indicated by an oval. RnmV is an RNase M5/primase-related protein involved in the maturation of the 5S rRNA (6). (B) Alignment of PECF elements from various bacilli. The intergenic region between yabE and rnmV of B. subtilis (Bsu) was aligned with the corresponding sequences from B. amyloliquefaciens (Bam) and B. licheniformis (Bli) by using the ClustalW2 program (
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/clustalw2/index.html
). The putative −10 and −35 regions are indicated. The run of seven A residues near the end of the sequence shown corresponds to the run of U residues in the yabE transcription terminator.
FIG. 2.
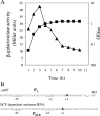
(A) Growth phase regulation of PECF. The β-galactosidase activity of the PECF_-lacZ_ fusion in the wild type (CU1065) was assayed during growth in LB medium, with samples taken every 1 h for the measurement of the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) and the β-galactosidase activity. Solid squares represent growth at an optical density at 600 nm, while solid triangles represent β-galactosidase activity. (B) Mapping of the transcriptional start sites of yabE and ECF-directed antisense transcripts by the rapid amplification of cDNA 5′ ends. The putative −10 and −35 regions are underlined. The transcription start sites are in bold, and the translation start site is italicized. PA is the promoter corresponding to σA. Met indicates the start codon (methionine).
FIG. 3.
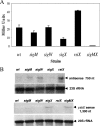
(A) PECF-directed antisense expression is dependent on σX and σM. The β-galactosidase activity of the PECF-lacZ fusion was assayed in various ECF deletion strains indicated by the relevant gene. Cultures were grown in LB medium, and samples were taken when cells reached late log phase. Data are expressed as averages ± standard deviations of results for triplicate samples. wt, wild type. (B) Regulation of yabE by an antisense RNA. Total RNA (15-μg) samples prepared from late-log-phase cultures of various deletion strains after growth in LB medium were analyzed by Northern blotting. RNA was separated, blotted, and hybridized with [γ-32P]ATP-labeled strand-specific probes for the yabE and the antisense RNA transcripts (indicated with arrowheads). The level of 23S rRNA is shown underneath as a loading control (2 μg of RNA was loaded). nt, nucleotides.
Similar articles
- Regulation of sigma D expression and activity by spo0, abrB, and sin gene products in Bacillus subtilis.
Márquez-Magaña LM, Mirel DB, Chamberlin MJ. Márquez-Magaña LM, et al. J Bacteriol. 1994 Apr;176(8):2435-8. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.8.2435-2438.1994. J Bacteriol. 1994. PMID: 8157613 Free PMC article. - Interaction of Bacillus subtilis extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors with the N-terminal regions of their potential anti-sigma factors.
Yoshimura M, Asai K, Sadaie Y, Yoshikawa H. Yoshimura M, et al. Microbiology (Reading). 2004 Mar;150(Pt 3):591-599. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26712-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2004. PMID: 14993308 - A σD-dependent antisense transcript modulates expression of the cyclic-di-AMP hydrolase GdpP in Bacillus subtilis.
Luo Y, Helmann JD. Luo Y, et al. Microbiology (Reading). 2012 Nov;158(Pt 11):2732-2741. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.062174-0. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Microbiology (Reading). 2012. PMID: 22956758 Free PMC article. - The extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors.
Helmann JD. Helmann JD. Adv Microb Physiol. 2002;46:47-110. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(02)46002-x. Adv Microb Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12073657 Review. - Bacillus subtilis extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors and defense of the cell envelope.
Helmann JD. Helmann JD. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Apr;30:122-132. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2016.02.002. Epub 2016 Feb 20. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26901131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Antisense RNA regulation and application in the development of novel antibiotics to combat multidrug resistant bacteria.
Ji Y, Lei T. Ji Y, et al. Sci Prog. 2013;96(Pt 1):43-60. doi: 10.3184/003685013X13617194309028. Sci Prog. 2013. PMID: 23738437 Free PMC article. Review. - Modulation of extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factor promoter selectivity by spacer region sequence.
Gaballa A, Guariglia-Oropeza V, Dürr F, Butcher BG, Chen AY, Chandrangsu P, Helmann JD. Gaballa A, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 9;46(1):134-145. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx953. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29069433 Free PMC article. - Mfd regulates RNA polymerase association with hard-to-transcribe regions in vivo, especially those with structured RNAs.
Ragheb MN, Merrikh C, Browning K, Merrikh H. Ragheb MN, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 5;118(1):e2008498118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008498118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33443179 Free PMC article. - Transcriptome analysis of Pseudomonas syringae identifies new genes, noncoding RNAs, and antisense activity.
Filiatrault MJ, Stodghill PV, Bronstein PA, Moll S, Lindeberg M, Grills G, Schweitzer P, Wang W, Schroth GP, Luo S, Khrebtukova I, Yang Y, Thannhauser T, Butcher BG, Cartinhour S, Schneider DJ. Filiatrault MJ, et al. J Bacteriol. 2010 May;192(9):2359-72. doi: 10.1128/JB.01445-09. Epub 2010 Feb 26. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20190049 Free PMC article.
References
- Cao, M., P. A. Kobel, M. M. Morshedi, M. F. Wu, C. Paddon, and J. D. Helmann. 2002. Defining the Bacillus subtilis σW regulon: a comparative analysis of promoter consensus search, run-off transcription/macroarray analysis (ROMA), and transcriptional profiling approaches. J. Mol. Biol. 316443-457. - PubMed
- Cao, M., T. Wang, R. Ye, and J. D. Helmann. 2002. Antibiotics that inhibit cell wall biosynthesis induce expression of the Bacillus subtilis σW and σM regulons. Mol. Microbiol. 451267-1276. - PubMed
- Cohen-Gonsaud, M., P. Barthe, C. Bagneris, B. Henderson, J. Ward, C. Roumestand, and N. H. Keep. 2005. The structure of a resuscitation-promoting factor domain from Mycobacterium tuberculosis shows homology to lysozymes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12270-273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases