Effect of extended-release naltrexone (XR-NTX) on quality of life in alcohol-dependent patients - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
Effect of extended-release naltrexone (XR-NTX) on quality of life in alcohol-dependent patients
Helen M Pettinati et al. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009 Feb.
Abstract
Background: Extended-release naltrexone (XR-NTX) is a once-a-month injectable formulation for the treatment of alcohol dependence previously shown to reduce drinking and heavy drinking relative to placebo (Garbutt et al., 2005). A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study established the efficacy and safety of XR-NTX in this patient population. In this report, the effect of XR-NTX on quality of life (QOL) was examined.
Methods: Alcohol-dependent patients were randomly assigned to receive XR-NTX 380 mg (N = 205), XR-NTX 190 mg (N = 210), or placebo (N = 209), combined with a standardized psychosocial intervention. QOL was assessed using the Medical Outcomes Study 36-item short-form health survey, administered at baseline and at 4-week intervals during 24 weeks of treatment.
Results: Compared with U.S. population norms, patients showed initial impairment in the health-related QOL domains of mental health, social functioning, and problems with work or other daily activities due to emotional problems. Adherence to all 6 injections was 65% for XR-NTX 190 mg, 63% for XR-NTX 380 mg, and 64% for placebo. Generalized estimating equations analyses using an intention-to-treat sample revealed that XR-NTX 380 mg was associated with significantly greater improvements from baseline in mental health (p = 0.0496), social functioning (p = 0.010), general health (p = 0.048), and physical functioning (p = 0.028), compared with placebo. Linear regression analyses revealed that reductions from baseline in drinking (percentage of drinking days and percentage of heavy drinking days in the last 30 days) were significantly (p < 0.05) correlated with improvements in quality of life.
Conclusion: Extended-release naltrexone 380 mg in combination with psychosocial intervention was associated with improvements in QOL, specifically in the domains of mental health, social functioning, general health, and physical functioning.
Figures
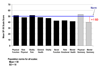
Figure 1
Mean SF-36 Normalized Scores for Alcohol-Dependent Patients (_N_=622) at Baseline.
Similar articles
- Combining behavioral harm-reduction treatment and extended-release naltrexone for people experiencing homelessness and alcohol use disorder in the USA: a randomised clinical trial.
Collins SE, Duncan MH, Saxon AJ, Taylor EM, Mayberry N, Merrill JO, Hoffmann GE, Clifasefi SL, Ries RK. Collins SE, et al. Lancet Psychiatry. 2021 Apr;8(4):287-300. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30489-2. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Lancet Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33713622 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Efficacy of extended-release naltrexone in patients with relatively higher severity of alcohol dependence.
Pettinati HM, Silverman BL, Battisti JJ, Forman R, Schweizer E, Gastfriend DR. Pettinati HM, et al. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 Oct;35(10):1804-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01524.x. Epub 2011 May 16. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21575016 Clinical Trial. - Early treatment response in alcohol dependence with extended-release naltrexone.
Ciraulo DA, Dong Q, Silverman BL, Gastfriend DR, Pettinati HM. Ciraulo DA, et al. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008 Feb;69(2):190-5. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v69n0204. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18348601 Clinical Trial. - Intramuscular extended-release naltrexone: current evidence.
Gastfriend DR. Gastfriend DR. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011 Jan;1216:144-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05900.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011. PMID: 21272018 Review.
Cited by
- The Effects of as-Needed Nalmefene on Patient-Reported Outcomes and Quality of Life in Relation to a Reduction in Alcohol Consumption in Alcohol-Dependent Patients.
François C, Rahhali N, Chalem Y, Sørensen P, Luquiens A, Aubin HJ. François C, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Jun 8;10(6):e0129289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129289. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26053024 Free PMC article. - The opioid receptors as targets for drug abuse medication.
Noble F, Lenoir M, Marie N. Noble F, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Aug;172(16):3964-79. doi: 10.1111/bph.13190. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25988826 Free PMC article. Review. - Hazardous drinking and alcohol use disorders.
MacKillop J, Agabio R, Feldstein Ewing SW, Heilig M, Kelly JF, Leggio L, Lingford-Hughes A, Palmer AA, Parry CD, Ray L, Rehm J. MacKillop J, et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022 Dec 22;8(1):80. doi: 10.1038/s41572-022-00406-1. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022. PMID: 36550121 Free PMC article. Review. - Long-acting Preparations in Substance Abuse Management: A Review and Update.
Hegde A, Singh SM, Sarkar S. Hegde A, et al. Indian J Psychol Med. 2013 Jan;35(1):10-8. doi: 10.4103/0253-7176.112194. Indian J Psychol Med. 2013. PMID: 23833336 Free PMC article. - Using the SF-6D to measure the impact of alcohol dependence on health-related quality of life.
Nogueira JM, Rodríguez-Míguez E. Nogueira JM, et al. Eur J Health Econ. 2015 May;16(4):347-56. doi: 10.1007/s10198-014-0627-z. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Eur J Health Econ. 2015. PMID: 25193526
References
- Anton RF, O’Malley SS, Ciraulo DA, Cisler RA, Couper D, Donovan DM, Gastfriend DR, Hosking JD, Johnson BA, LoCastro JS, Longabaugh R, Mason BJ, Mattson ME, Miller WR, Pettinati HM, Randall CL, Swift R, Weiss RD, Williams LD, Zweben A. Combined pharmacotherapies and behavioral interventions for alcohol dependence. JAMA. 2006;295:2003–2017. - PubMed
- Baros AM, Latham PK, Moak DH, Voronin K, Anton RF. What role does measuring medication compliance play in evaluating the efficacy of naltrexone? Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007;31:596–603. - PubMed
- Bouza C, Angeles M, Munoz A, Amate JM. Efficacy and safety of naltrexone and acamprosate in the treatment of alcohol dependence: a systematic review. Addiction. 2004;99:811–828. - PubMed
- Daeppen JB, Krieg MA, Burnand B, Yersin B. MOS-SF-36 in evaluating health-related quality of life in alcohol-dependent patients. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 1998;24:685–694. - PubMed
- Donovan D, Mattson ME, Cisler RA, Longabaugh R, Zweben A. Quality of life as an outcome measure in alcoholism treatment research. J Stud Alcohol Suppl. 2005;15:119–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical