SNP discovery in swine by reduced representation and high throughput pyrosequencing - PubMed (original) (raw)
SNP discovery in swine by reduced representation and high throughput pyrosequencing
Ralph T Wiedmann et al. BMC Genet. 2008.
Abstract
Background: Relatively little information is available for sequence variation in the pig. We previously used a combination of short read (25 base pair) high-throughput sequencing and reduced genomic representation to discover > 60,000 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in cattle, but the current lack of complete genome sequence limits this approach in swine. Longer-read pyrosequencing-based technologies have the potential to overcome this limitation by providing sufficient flanking sequence information for assay design. Swine SNP were discovered in the present study using a reduced representation of 450 base pair (bp) porcine genomic fragments (approximately 4% of the swine genome) prepared from a pool of 26 animals relevant to current pork production, and a GS-FLX instrument producing 240 bp reads.
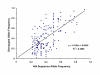
Results: Approximately 5 million sequence reads were collected and assembled into contigs having an overall observed depth of 7.65-fold coverage. The approximate minor allele frequency was estimated from the number of observations of the alternate alleles. The average coverage at the SNPs was 12.6-fold. This approach identified 115,572 SNPs in 47,830 contigs. Comparison to partial swine genome draft sequence indicated 49,879 SNP (43%) and 22,045 contigs (46%) mapped to a position on a sequenced pig chromosome and the distribution was essentially random. A sample of 176 putative SNPs was examined and 168 (95.5%) were confirmed to have segregating alleles; the correlation of the observed minor allele frequency (MAF) to that predicted from the sequence data was 0.58.
Conclusion: The process was an efficient means to identify a large number of porcine SNP having high validation rate to be used in an ongoing international collaboration to produce a highly parallel genotyping assay for swine. By using a conservative approach, a robust group of SNPs were detected with greater confidence and relatively high MAF that should be suitable for genotyping in a wide variety of commercial populations.
Figures
Figure 1
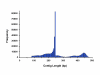
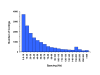
Distribution of the contig lengths showing that most of the contigs consist of reads from one end of the restriction fragments. About 25% of the contigs span the entire restriction fragment.
Figure 2
The plot shows the distribution of 115,572 SNPs by position in the contigs. The number of SNPs mirrors the profile of contig lengths.
Figure 3
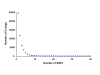
The distribution of contigs by number of SNPs.
Figure 4
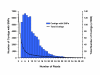
Comparison of the distribution of total contigs to contigs containing SNPs as the depth of coverage changes. The average depth of coverage where SNP were detected was 12.6.
Figure 5
Contig spacing along the sequenced pig chromosomes 1, 4, 5, 7, 11, 13 and 14.
Figure 6
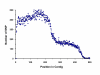
Correlation between allele frequency estimated by 454 sequencing and genotyping.
Similar articles
- Large scale single nucleotide polymorphism discovery in unsequenced genomes using second generation high throughput sequencing technology: applied to turkey.
Kerstens HH, Crooijmans RP, Veenendaal A, Dibbits BW, Chin-A-Woeng TF, den Dunnen JT, Groenen MA. Kerstens HH, et al. BMC Genomics. 2009 Oct 16;10:479. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-479. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19835600 Free PMC article. - Application of massive parallel sequencing to whole genome SNP discovery in the porcine genome.
Amaral AJ, Megens HJ, Kerstens HH, Heuven HC, Dibbits B, Crooijmans RP, den Dunnen JT, Groenen MA. Amaral AJ, et al. BMC Genomics. 2009 Aug 12;10:374. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-374. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19674453 Free PMC article. - The development and characterization of a 60K SNP chip for chicken.
Groenen MA, Megens HJ, Zare Y, Warren WC, Hillier LW, Crooijmans RP, Vereijken A, Okimoto R, Muir WM, Cheng HH. Groenen MA, et al. BMC Genomics. 2011 May 31;12(1):274. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-274. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21627800 Free PMC article. - Genome Wide Sampling Sequencing for SNP Genotyping: Methods, Challenges and Future Development.
Jiang Z, Wang H, Michal JJ, Zhou X, Liu B, Woods LC, Fuchs RA. Jiang Z, et al. Int J Biol Sci. 2016 Jan 1;12(1):100-8. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.13498. eCollection 2016. Int J Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26722221 Free PMC article. Review. - Detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Kwok PY, Chen X. Kwok PY, et al. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2003 Apr;5(2):43-60. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12793528 Review.
Cited by
- Reduced Representation Libraries from DNA Pools Analysed with Next Generation Semiconductor Based-Sequencing to Identify SNPs in Extreme and Divergent Pigs for Back Fat Thickness.
Bovo S, Bertolini F, Schiavo G, Mazzoni G, Dall'Olio S, Fontanesi L. Bovo S, et al. Int J Genomics. 2015;2015:950737. doi: 10.1155/2015/950737. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Int J Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25821781 Free PMC article. - Discovery of pod shatter-resistant associated SNPs by deep sequencing of a representative library followed by bulk segregant analysis in rapeseed.
Hu Z, Hua W, Huang S, Yang H, Zhan G, Wang X, Liu G, Wang H. Hu Z, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034253. Epub 2012 Apr 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22529909 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide linkage mapping of yield-related traits in three Chinese bread wheat populations using high-density SNP markers.
Li F, Wen W, He Z, Liu J, Jin H, Cao S, Geng H, Yan J, Zhang P, Wan Y, Xia X. Li F, et al. Theor Appl Genet. 2018 Sep;131(9):1903-1924. doi: 10.1007/s00122-018-3122-6. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Theor Appl Genet. 2018. PMID: 29858949 - Single nucleotide polymorphism discovery in rainbow trout by deep sequencing of a reduced representation library.
Sánchez CC, Smith TP, Wiedmann RT, Vallejo RL, Salem M, Yao J, Rexroad CE 3rd. Sánchez CC, et al. BMC Genomics. 2009 Nov 25;10:559. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-559. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19939274 Free PMC article. - Two different high throughput sequencing approaches identify thousands of de novo genomic markers for the genetically depleted Bornean elephant.
Sharma R, Goossens B, Kun-Rodrigues C, Teixeira T, Othman N, Boone JQ, Jue NK, Obergfell C, O'Neill RJ, Chikhi L. Sharma R, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049533. Epub 2012 Nov 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23185354 Free PMC article.
References
- McKay SD, Schnabel RD, Murdoch BM, Matukumalli LK, Aerts J, Coppieters W, Crews D, Dias Neto E, Gill CA, Gao C, Mannen H, Stothard P, Wang Z, Van Tassell CP, Williams JL, Taylor JF, Moore SS. Whole genome linkage disequilibrium maps in cattle. BMC Genet. 2007;8:74. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-8-74. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources