Elevated expressions of 15-lipoxygenase and lipoxin A4 in children with acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Elevated expressions of 15-lipoxygenase and lipoxin A4 in children with acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
Sheng-Hua Wu et al. Am J Pathol. 2009 Jan.
Abstract
Anti-inflammatory effects of the 15-lipoxygenase (15-LO) derivatives lipoxin A(4) (LXA(4)) and 15-S-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (15-S-HETE) have been documented in many experimental models of acute inflammation. However, the expression levels of 15-LO and its products in human renal diseases remain unknown. This study investigated the expression levels of LXA(4), leukotriene B(4) (LTB(4)), and 15-LO in leukocytes and glomeruli obtained from 22 children with acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (APSGN), and determined the modulatory effects of both 15-S-HETE and LXA(4) on LTB(4) synthesis in leukocytes and LTB(4)-evoked chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) obtained from children during the first 3 days after onset of APSGN. Expression levels of both LXA(4) and 15-LO in leukocytes and glomeruli were up-regulated during the acute phase of disease, further peaking between days 10 and 14, and remained increased after 6 to 8 weeks of APSGN onset. In contrast, blood and urinary levels of LTB(4) as well as the number of glomerular PMNs peaked during the acute phase of disease and then decreased during the resolution phase. Administration of both 15-S-HETE and LXA(4) in vitro inhibited LTB(4)-induced chemotaxis of PMNs and production of LTB(4) from leukocytes obtained from patients with APSGN. The current study provides further support for an anti-inflammatory role for 15-LO products in human nephritis through both antagonism and inhibition of leukotriene synthesis and its biological activity.
Figures
Figure 1
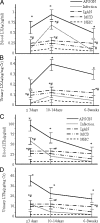
Temporal changes of whole blood and urinary LXA4 and LTB4. The samples were obtained from 22 children with APSGN, 12 children with acute pharyngeal infections by streptococci (infection), 4 patients with IgA nephropathy (IgAN), and 6 children with MCD in the first 3 days, 10 to 14 days, and 6 to 8 weeks after the onset of the diseases, or from 22 NHC who served as controls. The extraction methods were performed as described in the Materials and Methods; whole blood and urinary LXA4 and LTB4 were assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay following the manufacturer’s instructions. *P < 0.05 as compared to the same kind of eicosanoid levels of NHC at the same time point. #P < 0.05 as compared to the same kind of eicosanoid levels of APSGN at the same time point.
Figure 2
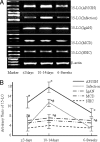
Expression of 15-LO mRNA was assessed by RT-PCR in leukocytes. mRNA was derived from leukocytes obtained from eight children with APSGN, four children with acute pharyngeal infection by streptococci (infection), four patients with IgA nephropathy (IgAN), and four children with MCD in the first 3 days, 10 to 14 days, and 6 to 8 weeks after the onset of the diseases, or from eight NHC who served as controls. A: RT-PCR for 15-LO mRNA expression; β-actin served as an internal control. B: Data of semiquantitative analysis using UVP-gel densitometry are shown. Arbitrary units = (A15-LO/Aβ-actin) × 100%. *P < 0.05 as compared to eicosanoid levels of NHC at the same time point. #P < 0.05 as compared to eicosanoid levels of APSGN at the same time point.
Figure 3
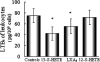
Production of LTB4 in leukocytes. The leukocytes were obtained from eight children in the first 3 days (acute phase) after the onset of APSGN, and exposed to the calcium ionophore A23187 (2 μmol/L) plus vehicle, served as controls, or A23187 plus 15-S-HETE (30 nmol/L), or A23187 plus LXA4 (30 nmol/L), or A23187 plus 12-S-HETE (30 nmol/L) 37°C for 45 minutes, respectively. Release of LTB4 in supernatants was assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay following the manufacturer’s instructions. *P < 0.05 as compared to levels of controls.
Figure 4
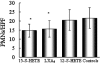
Chemotactic assays of PMNs in response to LTB4. PMNs were obtained from eight children with APSGN. LTB4 (10 nmol/L) was placed in the lower chamber of Transwell cluster plates. The leukocytes were pretreated with the vehicle (1% ethanol as a control), 15-S-HETE (30 nmol/L), LXA4 (30 nmol/L), or 12-S-HETE (30 nmol/L) for 20 minutes and then added to the upper chamber and incubated at 37 C for 30 minutes. The membrane filters were fixed and stained with H&E. PMNs that migrated from the upper chamber were counted in duplicate per ×400 high-power field with a light microscope. *P < 0.05 as compared to levels of controls.
Figure 5
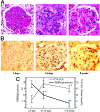
Glomerular PMN counts and 15-LO expression. The glomeruli were obtained from children with APSGN in the first 3 days (22 patients, acute phase), 10 to 14 days (6 patients, early resolution phase), and 6 to 8 weeks (4 patients, late resolution phase) after the onset of the disease. A and C: Infiltrating PMNs from three to six glomeruli per patient were counted in duplicate H&E-stained sections per ×1000 high-power field with a light microscope. B: Glomerular 15-LO expressions were determined by immunohistochemical staining. Methyl green was used for counterstaining. C: The mean ratio of the 15-LO-positive cellular area (deep brown, not green) to the single glomerulus was assessed by a JD-801 computer-aided image analyzer under high-power magnification (×1000). *P < 0.05 as compared to eicosanoid levels in the acute phase of APSGN.
Similar articles
- Inverse temporal changes of lipoxin A4 and leukotrienes in children with Henoch-Schönlein purpura.
Wu SH, Liao PY, Yin PL, Zhang YM, Dong L. Wu SH, et al. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2009 Apr;80(4):177-83. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2009.01.008. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2009. PMID: 19264468 - 15(S)-HETE modulates LTB(4) production and neutrophil chemotaxis in chronic bronchitis.
Profita M, Sala A, Riccobono L, Pace E, Paternò A, Zarini S, Siena L, Mirabella A, Bonsignore G, Vignola AM. Profita M, et al. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2000 Oct;279(4):C1249-58. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2000.279.4.C1249. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11003605 Clinical Trial. - 15-Lipoxygenase products as leukotriene antagonists: therapeutic potential in glomerulonephritis.
Badr KF. Badr KF. Kidney Int Suppl. 1992 Oct;38:S101-8. Kidney Int Suppl. 1992. PMID: 1405359 Review. - Reduced inflammation and tissue damage in transgenic rabbits overexpressing 15-lipoxygenase and endogenous anti-inflammatory lipid mediators.
Serhan CN, Jain A, Marleau S, Clish C, Kantarci A, Behbehani B, Colgan SP, Stahl GL, Merched A, Petasis NA, Chan L, Van Dyke TE. Serhan CN, et al. J Immunol. 2003 Dec 15;171(12):6856-65. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.12.6856. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14662892 - Role of leukotrienes and lipoxygenases in glomerular injury.
Nassar GM, Badr KF. Nassar GM, et al. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1995;21(4-5):262-70. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1995. PMID: 7565475 Review.
Cited by
- Pro-resolving actions and stereoselective biosynthesis of 18S E-series resolvins in human leukocytes and murine inflammation.
Oh SF, Pillai PS, Recchiuti A, Yang R, Serhan CN. Oh SF, et al. J Clin Invest. 2011 Feb;121(2):569-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI42545. Epub 2011 Jan 4. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21206090 Free PMC article. - Lipid mediators in the resolution of inflammation.
Serhan CN, Chiang N, Dalli J, Levy BD. Serhan CN, et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Oct 30;7(2):a016311. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016311. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 25359497 Free PMC article. Review. - Lipoxin A4 Regulates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced BV2 Microglial Activation and Differentiation via the Notch Signaling Pathway.
Wu J, Ding DH, Li QQ, Wang XY, Sun YY, Li LJ. Wu J, et al. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Feb 4;13:19. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00019. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30778288 Free PMC article. - Resolvin D1 limits polymorphonuclear leukocyte recruitment to inflammatory loci: receptor-dependent actions.
Norling LV, Dalli J, Flower RJ, Serhan CN, Perretti M. Norling LV, et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Aug;32(8):1970-8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.249508. Epub 2012 Apr 12. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22499990 Free PMC article.
References
- Kobrin SM, Madaio MP. Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis and other bacterial infection-related glomerulonephritis. Schrier RW, editor. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,; Diseases of the Kidney and Urinary Tract. (ed 7) 2001:pp 1617–1624.
- Falk RJ, Jennette JC, Nachman PH. Primary glomerular disease. Brenner BM, editor. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders,; The Kidney. (ed 7) 2004:pp 1327–1332.
- O'Meara YM, Brady HR. Lipoxins, leukocyte recruitment and the resolution phase of acute glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1997;51:S56–S61. - PubMed
- Kieran NE, Maderna P, Godson C. Lipoxins: potential anti-inflammatory, proresolution, and antifibrotic mediators in renal disease. Kidney Int. 2004;65:1145–1154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical