Update on worldwide efforts to prevent type 1 diabetes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Update on worldwide efforts to prevent type 1 diabetes
Jay S Skyler et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008 Dec.
Abstract
This paper reviews worldwide efforts to interdict the type 1 diabetes (T1D) disease process, during the stage of evolution of the disease prior to the time of disease onset. The goal of intervention before disease onset is to arrest immune destruction and thus prevent or delay clinical disease. In this regard, there have been several large-scale multicenter randomized controlled clinical trials designed to prevent T1D. These have tested nicotinamide, parenteral insulin, oral insulin, nasal insulin, and the elimination of cow's milk from infant feeding.
Figures
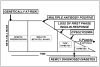
Figure 1
Schematic depiction of potential timing of interventions to interdict the type 1 diabetes disease process. This can be in genetically at-risk newborns or young children prior to detection of autoimmunity, in individuals with diabetes autoantibodies, in those with autoantibodies plus a metabolic defect -either loss of first phase insulin response to intravenous glucose or the presence of dysglycemia on an oral glucose tolerance test; or at the time of diagnosis of type 1 diabetes (or shortly thereafter).
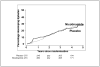
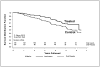
Figure 2
Cumulative incidence of type 1 diabetes in the nicotinamide and placebo arms of the ENDIT study. Adapted from Lancet 2003; 363: 925–931.
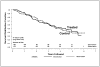
Figure 3
Life-table depicting time to diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in the DPT-1 parenteral insulin trial. Adapted from New Engl J Med 2002; 346:1685–91.
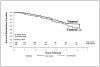
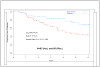
Figure 4
Life-table depicting time to diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in the DPT-1 oral insulin trial. Adapted from Diabetes Care 2005; 28:1068–76.
Figure 5
Life-table depicting time to diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in the DPT-1 oral insulin trial, for the subset of subjects with baseline confirmed insulin autoantibody level of 80 nU/ml or above. Adapted from Diabetes Care 2005; 28:1068–76.
Figure 6
Life-table depicting time to diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in the DPT-1 oral insulin trial, for the subset of subjects with baseline confirmed insulin autoantibody level of 300 nU/ml or above. From an analysis by Todd MacKenzie PhD, Dartmouth University, conducted for NIDDK.
Similar articles
- Primary and secondary prevention of Type 1 diabetes.
Skyler JS. Skyler JS. Diabet Med. 2013 Feb;30(2):161-9. doi: 10.1111/dme.12100. Diabet Med. 2013. PMID: 23231526 Free PMC article. Review. - The Deutsche Nicotinamide Intervention Study: an attempt to prevent type 1 diabetes. DENIS Group.
Lampeter EF, Klinghammer A, Scherbaum WA, Heinze E, Haastert B, Giani G, Kolb H. Lampeter EF, et al. Diabetes. 1998 Jun;47(6):980-4. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.47.6.980. Diabetes. 1998. PMID: 9604880 Clinical Trial. - Prevention of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus 1998.
Pozzilli P. Pozzilli P. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1998 Mar;14(1):69-84. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-0895(199803)14:1<69::aid-dmr203>3.0.co;2-e. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1998. PMID: 9605630 Review. - Update on major trials for the prevention of type 1 diabetes mellitus: the American Diabetes Prevention Trial (DPT-1) and the European Nicotinamide Diabetes Intervention Trial (ENDIT).
Schatz DA, Bingley PJ. Schatz DA, et al. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2001;14 Suppl 1:619-22. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2001.14.s1.619. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2001. PMID: 11393553 Review. - Immunotherapeutic approaches to prevent, ameliorate, and cure type 1 diabetes.
Aly T, Devendra D, Eisenbarth GS. Aly T, et al. Am J Ther. 2005 Nov-Dec;12(6):481-90. doi: 10.1097/01.mjt.0000178782.97413.79. Am J Ther. 2005. PMID: 16280641 Review.
Cited by
- Disease-Modifying Therapies in Type 1 Diabetes: A Look into the Future of Diabetes Practice.
Greenbaum C, VanBuecken D, Lord S. Greenbaum C, et al. Drugs. 2019 Jan;79(1):43-61. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-1035-y. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30612319 Free PMC article. Review. - Altered Function of Antigen-Presenting Cells in Type 1 Diabetes: A Challenge for Antigen-Specific Immunotherapy?
Creusot RJ, Postigo-Fernandez J, Teteloshvili N. Creusot RJ, et al. Diabetes. 2018 Aug;67(8):1481-1494. doi: 10.2337/db17-1564. Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 30030289 Free PMC article. Review. - Immune intervention in type 1 diabetes.
Michels AW, Eisenbarth GS. Michels AW, et al. Semin Immunol. 2011 Jun;23(3):214-9. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2011.07.003. Epub 2011 Aug 17. Semin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21852151 Free PMC article. Review. - Oral tolerance.
Faria AM, Weiner HL. Faria AM, et al. Immunol Rev. 2005 Aug;206:232-59. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00280.x. Immunol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16048553 Free PMC article. Review. - Insulin as a key autoantigen in the development of type 1 diabetes.
Nakayama M. Nakayama M. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2011 Nov;27(8):773-7. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.1250. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2011. PMID: 22069258 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Williams AJK, Bingley PJ, Moore WPM, Gale EAM the ENDIT screening group. Islet autoantibodies, nationality and gender: a multinational screening study in first-degree relatives of patients with Type I diabetes. Diabetologia. 2002;45:217–223. - PubMed
- European Nicotinamide Diabetes Intervention Trial (ENDIT) Group. Gale EAM. Intervening before the onset of Type 1 diabetes: baseline data from the European Nicotinamide Diabetes Intervention Trial (ENDIT) Diabetologia. 2003;46:339–346. - PubMed
- European Nicotinamide Diabetes Intervention Trial (ENDIT) Group. European Nicotinamide Diabetes Intervention Trial (ENDIT): A randomized controlled trial of intervention before the onset of type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 2004;363:925–931. - PubMed
- Diabetes Prevention Trial – Type 1 Study Group. Effects of Insulin in Relatives of Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine. 2002;346:1685–1691. - PubMed
- Diabetes Prevention Trial -Type 1 Diabetes Study Group. Effects of Oral Insulin in Relatives of Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1068–1076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical