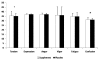Thermogenic effect of an acute ingestion of a weight loss supplement - PubMed (original) (raw)
Thermogenic effect of an acute ingestion of a weight loss supplement
Jay R Hoffman et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009.
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to examine the acute effects of a weight loss supplement on resting oxygen uptake (VO2), respiratory quotient (RQ), caloric expenditure (kcal), heart rate (HR), and blood pressure (BP) in healthy and physically active individuals.
Methods: Ten subjects (5 male, 5 female; 20.2 +/- 1.2 y; 172.2 +/- 8.9 cm; 71.5 +/- 17.2 kg; 17.3 +/- 2.6% body fat) underwent two testing sessions administered in a randomized and double-blind fashion. During each session, subjects reported to the Human Performance Laboratory after at least 3-h post-absorptive state and were provided either 3 capsules of the weight loss supplement (SUP), commercially marketed as Meltdown(R) or 3 capsules of a placebo (P). Subjects then rested in a semi-recumbent position for three hours. VO2 and HR were determined every 5 min during the first 30 min and every 10 min during the next 150 min. BP was determined every 15 min during the first 30 min and every 30 min thereafter. The profile of mood states was assessed every 30 min.
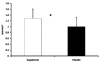
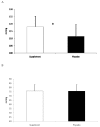
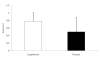
Results: Area under the curve analysis revealed a significant 28.9% difference in VO2 between SUP and P for the three hour study period. In addition, a significant difference in energy expenditure was also seen between SUP (1.28 +/- 0.33 kcal.min-1) and P (1.00 +/- 0.32 kcal.min-1). A trend (p = 0.06) towards a greater utilization of stored fat as an energy source was also demonstrated (0.78 +/- 0.23 kcal.min-1 and 0.50 +/- 0.38 kcal.min-1 in P and SUP, respectively). Significant elevations in HR were seen during hours two and three of the study, and significantly higher average systolic BP was observed between SUP (118.0 +/- 7.3 mmHg) and P (111.4 +/- 8.2 mmHg). No significant differences were seen in diastolic blood pressure at any time point. Significant increases in tension and confusion were seen in SUP.
Conclusion: Results indicate a significant increase in energy expenditure in young, healthy individuals following an acute ingestion of a weight loss supplement. In addition, ingestion of this supplement appears modify mood and elevate HR and systolic BP following ingestion.
Figures
Figure 1
Average 3-Hour Energy Expenditure. * = Supplement significantly (p < 0.05) different than Placebo: Data are reported mean ± SD.
Figure 2
a: Average 3-Hour Systolic Blood Pressure. * = Supplement significantly (p < 0.05) different than Placebo: 2b: Average 3-Hour Diastolic Blood Pressure. Data are reported mean ± SD.
Figure 3
Average 3-Hour Fat Utilization. Data are reported mean ± SD.
Figure 4
Average Profile of Mood States. * = Supplement significantly (p < 0.05) different than Placebo. Data are reported mean ± SD.
Similar articles
- Thermogenic effect of meltdown RTD energy drink in young healthy women: a double blind, cross-over design study.
Rashti SL, Ratamess NA, Kang J, Faigenbaum AD, Chilakos A, Hoffman JR. Rashti SL, et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2009 Dec 17;8:57. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-8-57. Lipids Health Dis. 2009. PMID: 20017916 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Thermogenic effect from nutritionally enriched coffee consumption.
Hoffman JR, Kang J, Ratamess NA, Jennings PF, Mangine G, Faigenbaum AD. Hoffman JR, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2006 Jun 5;3(1):35-41. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-3-1-35. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2006. PMID: 18500961 Free PMC article. - The effects of a fat loss supplement on resting metabolic rate and hemodynamic variables in resistance trained males: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial.
Campbell BI, Colquhoun RJ, Zito G, Martinez N, Kendall K, Buchanan L, Lehn M, Johnson M, St Louis C, Smith Y, Cloer B. Campbell BI, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2016 Apr 1;13:14. doi: 10.1186/s12970-016-0125-z. eCollection 2016. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27042166 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The acute effects of the thermogenic supplement Meltdown on energy expenditure, fat oxidation, and hemodynamic responses in young, healthy males.
Jitomir J, Nassar E, Culbertson J, Moreillon J, Buford T, Hudson G, Cooke M, Kreider R, Willoughby DS. Jitomir J, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008 Dec 16;5:23. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-5-23. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2008. PMID: 19087290 Free PMC article. - Effects of commercially available dietary supplements on resting energy expenditure: a brief report.
Vaughan RA, Conn CA, Mermier CM. Vaughan RA, et al. ISRN Nutr. 2014 Jan 2;2014:650264. doi: 10.1155/2014/650264. eCollection 2014. ISRN Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24967272 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Thermogenic effect of meltdown RTD energy drink in young healthy women: a double blind, cross-over design study.
Rashti SL, Ratamess NA, Kang J, Faigenbaum AD, Chilakos A, Hoffman JR. Rashti SL, et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2009 Dec 17;8:57. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-8-57. Lipids Health Dis. 2009. PMID: 20017916 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The effects of supplementation with P-Synephrine alone and in combination with caffeine on resistance exercise performance.
Ratamess NA, Bush JA, Kang J, Kraemer WJ, Stohs SJ, Nocera VG, Leise MD, Diamond KB, Faigenbaum AD. Ratamess NA, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015 Sep 17;12:35. doi: 10.1186/s12970-015-0096-5. eCollection 2015. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26388707 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The effects of a thermogenic supplement on metabolic and hemodynamic variables and subjective mood states.
Prather JM, Florez CM, Vargas A, Soto B, Harrison A, Willoughby D, Tinsley G, Taylor L. Prather JM, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2023 Dec;20(1):2185538. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2023.2185538. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36862833 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Herbal medicine for sports: a review.
Sellami M, Slimeni O, Pokrywka A, Kuvačić G, D Hayes L, Milic M, Padulo J. Sellami M, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018 Mar 15;15:14. doi: 10.1186/s12970-018-0218-y. eCollection 2018. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29568244 Free PMC article. Review. - Effects of a Multi-Ingredient Preworkout Supplement Versus Caffeine on Energy Expenditure and Feelings of Fatigue during Low-Intensity Treadmill Exercise in College-Aged Males.
Lutsch DJ, Camic CL, Jagim AR, Stefan RR, Cox BJ, Tauber RN, Henert SE. Lutsch DJ, et al. Sports (Basel). 2020 Sep 25;8(10):132. doi: 10.3390/sports8100132. Sports (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32992830 Free PMC article.
References
- Hoffman JR, Faigenbaum AD, Ratamess NA, Ross R, Kang J, Tenenbaum G. Nutritional Supplementation and Anabolic Steroid Use in Adolescents. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008;40:15–24. - PubMed
- Bell A, Dorsch KD, McCreary DR, Hovey R. A look at nutritional supplement use in adolescents. J Adolesc Health. 2004;34:508–516. - PubMed
- Pittler MH, Ernst E. Dietary supplements for body-weight reduction: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79:529–536. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous