Acute exercise and oxidative stress: a 30 year history - PubMed (original) (raw)
Acute exercise and oxidative stress: a 30 year history
Kelsey Fisher-Wellman et al. Dyn Med. 2009.
Abstract
The topic of exercise-induced oxidative stress has received considerable attention in recent years, with close to 300 original investigations published since the early work of Dillard and colleagues in 1978. Single bouts of aerobic and anaerobic exercise can induce an acute state of oxidative stress. This is indicated by an increased presence of oxidized molecules in a variety of tissues. Exercise mode, intensity, and duration, as well as the subject population tested, all can impact the extent of oxidation. Moreover, the use of antioxidant supplements can impact the findings. Although a single bout of exercise often leads to an acute oxidative stress, in accordance with the principle of hormesis, such an increase appears necessary to allow for an up-regulation in endogenous antioxidant defenses. This review presents a comprehensive summary of original investigations focused on exercise-induced oxidative stress. This should provide the reader with a well-documented account of the research done within this area of science over the past 30 years.
Figures
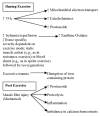
Figure 1
Potential mechanisms of increased RONS production related to an acute bout of exercise. Adapted with permission from Bloomer RJ, & Goldfarb AH. Anaerobic exercise and oxidative stress: A review. Canadian Journal of Applied Physiology, 29(3): 245–263, 2004.
Similar articles
- Effect of exercise on oxidative stress biomarkers.
Bloomer RJ. Bloomer RJ. Adv Clin Chem. 2008;46:1-50. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(08)00401-0. Adv Clin Chem. 2008. PMID: 19004186 Review. - Anaerobic exercise and oxidative stress: a review.
Bloomer RJ, Goldfarb AH. Bloomer RJ, et al. Can J Appl Physiol. 2004 Jun;29(3):245-63. doi: 10.1139/h04-017. Can J Appl Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15199226 Review. - Exercise and oxidative stress: potential effects of antioxidant dietary strategies in sports.
Pingitore A, Lima GP, Mastorci F, Quinones A, Iervasi G, Vassalle C. Pingitore A, et al. Nutrition. 2015 Jul-Aug;31(7-8):916-22. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Nutrition. 2015. PMID: 26059364 Review. - Effects of Aerobic-, Anaerobic- and Combined-Based Exercises on Plasma Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Healthy Untrained Young Adults.
Ammar A, Trabelsi K, Boukhris O, Glenn JM, Bott N, Masmoudi L, Hakim A, Chtourou H, Driss T, Hoekelmann A, El Abed K. Ammar A, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Apr 10;17(7):2601. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17072601. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32290148 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Influence of acute exercise of varying intensity and duration on postprandial oxidative stress.
Canale RE, Farney TM, McCarthy CG, Bloomer RJ. Canale RE, et al. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2014 Sep;114(9):1913-24. doi: 10.1007/s00421-014-2912-z. Epub 2014 Jun 8. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24907974
Cited by
- Effect of eccentric training on mitochondrial function and oxidative stress in the skeletal muscle of rats.
Silva LA, Bom KF, Tromm CB, Rosa GL, Mariano I, Pozzi BG, Tuon T, Stresck EL, Souza CT, Pinho RA. Silva LA, et al. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2013 Jan;46(1):14-20. doi: 10.1590/1414-431x20121956. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2013. PMID: 23314343 Free PMC article. - Does Multi-Strain Probiotic Supplementation Impact the Effort Capacity of Competitive Road Cyclists?
Mazur-Kurach P, Frączek B, Klimek AT. Mazur-Kurach P, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 26;19(19):12205. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912205. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231510 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Hepatoprotective effects of Berberis vulgaris leaf extract on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.
Tahmasebi M, Sadeghi H, Nazem H, Kokhdan EP, Omidifar N. Tahmasebi M, et al. J Educ Health Promot. 2018 Nov 27;7:147. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_48_17. eCollection 2018. J Educ Health Promot. 2018. PMID: 30596119 Free PMC article. - From phenoloxidase to fecundity: food availability does not influence the costs of oxidative challenge in a wing-dimorphic cricket.
Stahlschmidt ZR, Jeong N, Johnson D, Meckfessel N. Stahlschmidt ZR, et al. J Comp Physiol B. 2020 Jan;190(1):17-26. doi: 10.1007/s00360-019-01244-6. Epub 2019 Nov 13. J Comp Physiol B. 2020. PMID: 31720761 - Dark Chocolate Intake Positively Modulates Redox Status and Markers of Muscular Damage in Elite Football Athletes: A Randomized Controlled Study.
Cavarretta E, Peruzzi M, Del Vescovo R, Di Pilla F, Gobbi G, Serdoz A, Ferrara R, Schirone L, Sciarretta S, Nocella C, De Falco E, Schiavon S, Biondi-Zoccai G, Frati G, Carnevale R. Cavarretta E, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Nov 21;2018:4061901. doi: 10.1155/2018/4061901. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30584461 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Halliwell B. Reactive oxygen species in living systems: source, biochemistry, and role in human disease. Am J Med. 1991;91:14S–22S. - PubMed
- Miller DM, Buettner GR, Aust SD. Transition metals as catalysts of "autoxidation" reactions. Free Radic Biol Med. 1990;8:95–108. - PubMed
- Bogdan C, Rollinghoff M, Diefenbach A. Reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen intermediates in innate and specific immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2000;12:64–76. - PubMed
- Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39:44–84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous