A polymorphism in npr-1 is a behavioral determinant of pathogen susceptibility in C. elegans - PubMed (original) (raw)
A polymorphism in npr-1 is a behavioral determinant of pathogen susceptibility in C. elegans
Kirthi C Reddy et al. Science. 2009.
Abstract
The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans responds to pathogenic bacteria with conserved innate immune responses and pathogen avoidance behaviors. We investigated natural variation in C. elegans resistance to pathogen infection. With the use of quantitative genetic analysis, we determined that the pathogen susceptibility difference between the laboratory wild-type strain N2 and the wild isolate CB4856 is caused by a polymorphism in the npr-1 gene, which encodes a homolog of the mammalian neuropeptide Y receptor. We show that the mechanism of NPR-1-mediated pathogen resistance is through oxygen-dependent behavioral avoidance rather than direct regulation of innate immunity. For C. elegans, bacteria represent food but also a potential source of infection. Our data underscore the importance of behavioral responses to oxygen levels in finding an optimal balance between these potentially conflicting cues.
Figures
Fig. 1
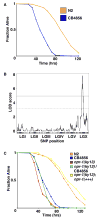
The enhanced pathogen susceptibility of CB4856 is caused by the 215F allele of npr-1. A. Fraction alive versus time for N2 (orange) and CB4856 (blue) fed PA14 using standard assays (18). Means from 27 independent experiments for each strain are shown. B. Logarithm of the odds ratio (LOD) score for linkage between LT50 and 1454 single nucleotide polymorphims (SNPs) in 126 recombinant inbred lines showing one major quantitative trait locus on LGX. Dotted and solid lines show 5 and 0.1% genome-wide significance levels, respectively, determined from 1000 permutations. C. Fraction alive versus time for N2 (orange), CB4856 (blue), the npr-1 loss-of-function mutant ky13 (red), a complementation test between npr-1(ky13) derived from the N2 background and npr-1 derived from the CB4856 background (green), and rescue of the npr-1(ky13) allele (yellow).
Fig. 2
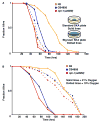
_npr-1_-mediated behaviors determine the susceptibility of C. elegans to PA14. A. Fraction alive versus time for N2 (orange) and CB4856 (blue) fed PA14 on standard plates (solid lines) and big lawn plates (dotted lines). B. Fraction alive versus time for N2 (orange), CB4856 (blue), and the npr-1 loss-of-function allele ad609 (red) at 21% oxygen (solid lines) and 10% oxygen (dotted lines).
Fig. 3
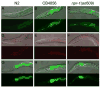
_npr-1_-mediated behaviors cause increased exposure to bacteria. Differential interference contrast and fluorescence microscopy of N2, CB4856, and npr-1(ad609) animals fed GFP-labeled PA14 for 24 hours on a standard lawn (A to C) or fed a 50:1 mixture of unlabeled PA14 and 0.2 μm fluorescent beads (D to F) or on a big lawn of GFP-labeled PA14 (G to I).
Similar articles
- Natural Genetic Variation in the Caenorhabditis elegans Response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Martin N, Singh J, Aballay A. Martin N, et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Apr 3;7(4):1137-1147. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.039057. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28179390 Free PMC article. - Contrasting invertebrate immune defense behaviors caused by a single gene, the Caenorhabditis elegans neuropeptide receptor gene npr-1.
Nakad R, Snoek LB, Yang W, Ellendt S, Schneider F, Mohr TG, Rösingh L, Masche AC, Rosenstiel PC, Dierking K, Kammenga JE, Schulenburg H. Nakad R, et al. BMC Genomics. 2016 Apr 11;17:280. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2603-8. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27066825 Free PMC article. - Caenorhabditis elegans NPR-1-mediated behaviors are suppressed in the presence of mucoid bacteria.
Reddy KC, Hunter RC, Bhatla N, Newman DK, Kim DH. Reddy KC, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 2;108(31):12887-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1108265108. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21768378 Free PMC article. - Host-microbe interactions and the behavior of Caenorhabditis elegans.
Kim DH, Flavell SW. Kim DH, et al. J Neurogenet. 2020 Sep-Dec;34(3-4):500-509. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2020.1802724. Epub 2020 Aug 12. J Neurogenet. 2020. PMID: 32781873 Free PMC article. Review. - Behavioral genetics: guanylyl cyclase prompts worms to party.
Riedl CA, Sokolowski MB. Riedl CA, et al. Curr Biol. 2004 Aug 24;14(16):R657-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.08.011. Curr Biol. 2004. PMID: 15324682 Review.
Cited by
- WormQTL--public archive and analysis web portal for natural variation data in Caenorhabditis spp.
Snoek LB, Van der Velde KJ, Arends D, Li Y, Beyer A, Elvin M, Fisher J, Hajnal A, Hengartner MO, Poulin GB, Rodriguez M, Schmid T, Schrimpf S, Xue F, Jansen RC, Kammenga JE, Swertz MA. Snoek LB, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(Database issue):D738-43. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1124. Epub 2012 Nov 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23180786 Free PMC article. - Peptide neuromodulation in invertebrate model systems.
Taghert PH, Nitabach MN. Taghert PH, et al. Neuron. 2012 Oct 4;76(1):82-97. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.08.035. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 23040808 Free PMC article. Review. - The laboratory domestication of Caenorhabditis elegans.
Sterken MG, Snoek LB, Kammenga JE, Andersen EC. Sterken MG, et al. Trends Genet. 2015 May;31(5):224-31. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2015.02.009. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Trends Genet. 2015. PMID: 25804345 Free PMC article. Review. - Phosphorylation of the conserved transcription factor ATF-7 by PMK-1 p38 MAPK regulates innate immunity in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Shivers RP, Pagano DJ, Kooistra T, Richardson CE, Reddy KC, Whitney JK, Kamanzi O, Matsumoto K, Hisamoto N, Kim DH. Shivers RP, et al. PLoS Genet. 2010 Apr 1;6(4):e1000892. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000892. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20369020 Free PMC article. - Caenorhabditis elegans as a Model Host to Monitor the Candida Infection Processes.
Elkabti AB, Issi L, Rao RP. Elkabti AB, et al. J Fungi (Basel). 2018 Nov 7;4(4):123. doi: 10.3390/jof4040123. J Fungi (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30405043 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Sawin ER, Ranganathan R, Horvitz HR. Neuron. 2000 Jun;26:619. - PubMed
- Gray JM, et al. Nature. 2004 Jul 15;430:317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HG004321/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM084477/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 GM084477-02/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM071508/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM084477/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM089007/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM071508/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004321-02/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004321/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous