Genetic variation in 5HTTLPR is associated with emotional resilience - PubMed (original) (raw)
Genetic variation in 5HTTLPR is associated with emotional resilience
Murray B Stein et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2009.
Abstract
Emotional resilience can be defined as the ability to maintain healthy and stable levels of psychological functioning in the wake of stress and trauma. Although genes that contribute to psychopathology (often in interaction with environmental stressors) are being detected with increasing consistency, genes that influence resilience to stress have been less studied. In this study, 423 undergraduate college students completed a psychometrically sound 10-item self-report measure of resilience (CDRISC-10) and provided blood for DNA. Linear and logistic regression analyses were used to model relationships between the serotonin transporter promoter polymorphism (5HTTLPR) and CDRISC-10 scores and categories, respectively. CDRISC-10 scores were normally distributed (mean 26.17, SD 5.88 [range 5-40]). In models adjusting for ancestry proportion scores (to mitigate confounding by population stratification) and other covariates, each copy of the "s" allele of 5HTTLPR was associated with approximately 1-point lower CDRISC-10 score. Each copy of the "s" allele was associated with increased (adjusted OR = 1.53, 95% CI 1.06-2.21, P = 0.024) odds of being in the low resilient category (>1 SD below the mean), compared to being homozygous for the "l" allele. These findings suggest that variation in 5HTTLPR is associated with individual differences in emotional resilience, defined as an individual's ability to withstand and bounce back from stress. This relationship may explain the frequently observed interaction between 5HTTLPR and life stressors in predicting adverse mental health outcomes (e.g., depressive symptoms). Replication is needed, in concert with identification of other genes that influence emotional resilience and related phenotypes.
(c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
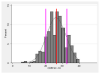
FIGURE 1. Distribution of CDRISC-10 Scores in the Sample (N=423)
Distribution of CDRISC-10 scores in the sample of N = 423 subject. The red bar shows the mean value for the sample with the pink bars showing 1 standard deviation (SD) below and above the mean, respectively.
Similar articles
- The integrated model of serotonin transporter gene variation (5HTTLPR) and the glial cell transporter in stress vulnerability and depression.
Shinozaki G. Shinozaki G. Med Hypotheses. 2012 Mar;78(3):410-4. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2011.10.043. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Med Hypotheses. 2012. PMID: 22236459 - Do 5HTTLPR and stress interact in risk for depression and suicidality? Item response analyses of a large sample.
Coventry WL, James MR, Eaves LJ, Gordon SD, Gillespie NA, Ryan L, Heath AC, Montgomery GW, Martin NG, Wray NR. Coventry WL, et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2010 Apr 5;153B(3):757-65. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.31044. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2010. PMID: 19911410 Free PMC article. - Genetic and environmental modulation of neurotrophic and anabolic stress response: Counterbalancing forces.
Taylor MK, Carpenter J, Stone M, Hernandez LM, Rauh MJ, Laurent HK, Granger DA. Taylor MK, et al. Physiol Behav. 2015 Nov 1;151:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.06.027. Epub 2015 Jun 28. Physiol Behav. 2015. PMID: 26136163 - Associations of 5HTTLPR polymorphism with major depressive disorder and alcohol dependence: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Oo KZ, Aung YK, Jenkins MA, Win AK. Oo KZ, et al. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2016 Sep;50(9):842-57. doi: 10.1177/0004867416637920. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26979101 Review.
Cited by
- Psychometric properties of the 10-item Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale in Chinese military personnel.
Tu Z, He J, Wang Z, Song M, Tian J, Wang C, Ba J, Shen X. Tu Z, et al. Front Psychol. 2023 Aug 4;14:1163382. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1163382. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37599761 Free PMC article. - The Individual and Societal Burden of Treatment-Resistant Depression: An Overview.
Baig-Ward KM, Jha MK, Trivedi MH. Baig-Ward KM, et al. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2023 Jun;46(2):211-226. doi: 10.1016/j.psc.2023.02.001. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2023. PMID: 37149341 Free PMC article. Review. - Genetic Variants Associated With Resilience in Human and Animal Studies.
Cahill S, Chandola T, Hager R. Cahill S, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2022 May 20;13:840120. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.840120. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35669264 Free PMC article. - The study on psychological resilience of tinnitus and associated influencing factors.
Xin F, Li Q, Guan F, Suo M, Yang J, Li D, Zhao C. Xin F, et al. J Otol. 2022 Jan;17(1):13-17. doi: 10.1016/j.joto.2021.08.001. Epub 2021 Aug 28. J Otol. 2022. PMID: 35140754 Free PMC article. - Depressive Symptoms among Middle-Aged Women-Understanding the Cause.
Cybulska AM, Szkup M, Schneider-Matyka D, Skonieczna-Żydecka K, Kaczmarczyk M, Jurczak A, Wieder-Huszla S, Karakiewicz B, Grochans E. Cybulska AM, et al. Brain Sci. 2020 Dec 28;11(1):26. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11010026. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33379297 Free PMC article.
References
- Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1961;4:561–571. - PubMed
- Bernstein DP, Fink L, Handelsman L, Lovejoy M, Wenzel K, Sapareto E, Ruggiero J. Initial reliability and validity of a new retrospective measure of child abuse and neglect. Am J Psychiatry. 1994;151:1132–1136. - PubMed
- Bertolino A, Arciero G, Rubino V, Latorre V, De Candia M, Mazzola V, Blasi G, Caforio G, Hariri A, Kolachana B, Nardini M, Weinberger DR, Scarabino T. Variation of human amygdala response during threatening stimuli as a function of 5′HTTLPR genotype and personality style. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;57:1517–1525. - PubMed
- Binder EB, Bradley RG, Liu W, Epstein MP, Deveau TC, Mercer KB, Tang Y, Gillespie CF, Heim CM, Nemeroff CB, Schwartz AC, Cubells JF, Ressler KJ. Association of FKBP5 polymorphisms and childhood abuse with risk of posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms in adults. JAMA. 2008;299:1291–1305. - PMC - PubMed
- Bonanno GA. Loss, trauma, and human resilience - Have we underestimated the human capacity to thrive after extremely aversive events? American Psychologist. 2004;59:20–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DA012690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DA015105/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 MH064122/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K24 MH064122-09/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA12849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AA11330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DA12690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH64122/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DA15105/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources