A critical role for IL-21 receptor signaling in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus in BXSB-Yaa mice - PubMed (original) (raw)
A critical role for IL-21 receptor signaling in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus in BXSB-Yaa mice
Jason A Bubier et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009.
Abstract
Interleukin 21 (IL-21) is a pleiotropic cytokine produced by CD4 T cells that affects the differentiation and function of T, B, and NK cells by binding to a receptor consisting of the common cytokine receptor gamma chain and the IL-21 receptor (IL-21R). IL-21, a product associated with IL-17-producing CD4 T cells (T(H)17) and follicular CD4 T helper cells (T(FH)), has been implicated in autoimmune disorders including the severe systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)-like disease characteristic of BXSB-Yaa mice. To determine whether IL-21 plays a significant role in this disease, we compared IL-21R-deficient and -competent BXSB-Yaa mice for multiple parameters of SLE. The deficient mice showed none of the abnormalities characteristic of SLE in IL-21R-competent Yaa mice, including hypergammaglobulinemia, autoantibody production, reduced frequencies of marginal zone B cells and monocytosis, renal disease, and premature morbidity. IL-21 production associated with this autoimmune disease was not a product of T(H)17 cells and was not limited to conventional CXCR5(+) T(FH) but instead was produced broadly by ICOS(+) CD4(+) splenic T cells. IL-21 arising from an abnormal population of CD4 T cells is thus central to the development of this lethal disease, and, more generally, could play an important role in human SLE and related autoimmune disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors are listed as co-inventors on applications for and/or issued patents related to IL-21.
Figures
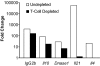
Fig. 1.
IL-21 is the product of T cells. Fold change computations were based on the mean CT (cycle threshold) values normalized to 18S RNA from spleen cells pooled from 2 21-week-old BXSB-Yaa and 2 BXSB-wt mice, depleted of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells or left intact.
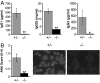
Fig. 2.
IL-21R deficiency prevents humoral components of the BXSB-Yaa autoimmune disease. (A) ELISA analysis of Ig subclass levels in plasma from 10 Yaa/Il21r+/− (gray bars) and 10 _Yaa/Il21_−/− (black bars) 16-week-old mice. (B) Anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) from Yaa/Il21r+/− mice compared with _Yaa/Il21_−/− mice detected by staining of Hep-2 cell slides (Right) with quantitation by ImageJ (Left). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.002.
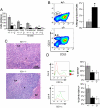
Fig. 3.
IL-21R deficiency prevents the abnormal leukocyte populations characteristic of BXSB-Yaa mice. (A) Spleens of _Yaa/Il21_−/− mice exhibit greatly reduced cellularity compared with spleens of Yaa/Il21r+/− mice. Yaa/Il21r+/− mice have high numbers of total B cells, and immature and mature B cells; this phenotype was abolished in _Yaa/Il21_−/− mice. (B) The frequencies of splenic MZ B cells (CD19+ CD21hi CD23lo) typically depleted in Yaa/Il21r+/− mice are restored in _Yaa/Il21_−/− mice. (C) Yaa/Il21r+/− but not _Yaa/Il21_−/− spleens lack an obvious MZ and show expansion in red pulp with monocytosis and accumulations of plasma cells resulting in compression of the white pulp. Central arteriole (CA), follicle (F) of H&E-stained sections. (D) _Yaa/Il21_−/− mice do not develop spleen cell monocytosis as measured by CD11b expression and have fewer CD11c-positive dendritic cells compared with Yaa/Il21r+/− littermate controls. Data are representative of spleens from 16-week-old mice. Data from BXSB female mice thus lacking Yaa of the same age are included for comparison.
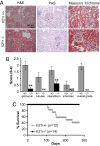
Fig. 4.
IL-21R deficiency prevents renal disease and mortality characteristic of BXSB-Yaa mice. (A and B) Kidney sections from 16-week-old Yaa/Il21r+/− and _Yaa/Il21_−/− mice were stained with H&E, periodic acid/Schiff reagent (PAS), or Masson's trichrome. (A) Representative sections. (B) Kidneys were graded for severity of changes. N.S., not significant at P ≤ 0.05. (C) Kaplan–Meier lifespan analysis indicated a significant Wilcoxon P value of 0.0017 for survival differences.
Fig. 5.
IL-21R deficiency decreases numbers of TFH cells. Splenic CD4 T cells from 16-week-old _Yaa/Il21_−/−, Yaa, and Yaa/Il21r+/− mice were analyzed for ICOS and CXCR5 expression by flow cytometry analysis. (A) Representative data. (B) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) and percent ICOShi splenic CD4 T cells; there were 10 mice per group. (C) Correlation of total mononuclear spleen cell numbers with MFI of ICOS (Upper) or CXCR5 (Lower) on CD4 T cells of individual 16-week-old Yaa/Il21r+/− and _Yaa/Il21_−/− mice. (D) Gene expression comparison of flow cytometry-sorted ICOShi and ICOSlo splenic CD4 T cells (Upper) and ICOShi CXCR5hi and CXCR5lo splenic CD4 T cells (Lower) from BXSB-Yaa mice. See
Fig. S4
for flow cytometric gates.
Similar articles
- IL-21 is a double-edged sword in the systemic lupus erythematosus-like disease of BXSB.Yaa mice.
McPhee CG, Bubier JA, Sproule TJ, Park G, Steinbuck MP, Schott WH, Christianson GJ, Morse HC 3rd, Roopenian DC. McPhee CG, et al. J Immunol. 2013 Nov 1;191(9):4581-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300439. Epub 2013 Sep 27. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24078696 Free PMC article. - Treatment of BXSB-Yaa mice with IL-21R-Fc fusion protein minimally attenuates systemic lupus erythematosus.
Bubier JA, Bennett SM, Sproule TJ, Lyons BL, Olland S, Young DA, Roopenian DC. Bubier JA, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Sep;1110:590-601. doi: 10.1196/annals.1423.063. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17911475 - Elevated production of B cell chemokine CXCL13 is correlated with systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity.
Wong CK, Wong PT, Tam LS, Li EK, Chen DP, Lam CW. Wong CK, et al. J Clin Immunol. 2010 Jan;30(1):45-52. doi: 10.1007/s10875-009-9325-5. Epub 2009 Sep 23. J Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19774453 - The role of the Yaa gene in lupus syndrome.
Izui S, Merino R, Fossati L, Iwamoto M. Izui S, et al. Int Rev Immunol. 1994;11(3):211-30. doi: 10.3109/08830189409061728. Int Rev Immunol. 1994. PMID: 7930846 Review. - T follicular helper cells, interleukin-21 and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Gensous N, Schmitt N, Richez C, Ueno H, Blanco P. Gensous N, et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017 Apr 1;56(4):516-523. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew297. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017. PMID: 27498357 Review.
Cited by
- Follicular Helper T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Why Should They Be Considered as Interesting Therapeutic Targets?
Sawaf M, Dumortier H, Monneaux F. Sawaf M, et al. J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:5767106. doi: 10.1155/2016/5767106. Epub 2016 Aug 22. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27635407 Free PMC article. Review. - Prolonged apoptotic cell accumulation in germinal centers of Mer-deficient mice causes elevated B cell and CD4+ Th cell responses leading to autoantibody production.
Khan TN, Wong EB, Soni C, Rahman ZS. Khan TN, et al. J Immunol. 2013 Feb 15;190(4):1433-46. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200824. Epub 2013 Jan 14. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23319738 Free PMC article. - Insights Into the Molecular Mechanisms of T Follicular Helper-Mediated Immunity and Pathology.
Qin L, Waseem TC, Sahoo A, Bieerkehazhi S, Zhou H, Galkina EV, Nurieva R. Qin L, et al. Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 15;9:1884. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01884. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30158933 Free PMC article. Review. - Immunoglobulin genes, reproductive isolation and vertebrate speciation.
Collins AM, Watson CT, Breden F. Collins AM, et al. Immunol Cell Biol. 2022 Aug;100(7):497-506. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12567. Epub 2022 Jul 4. Immunol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35781330 Free PMC article. - Interleukin 17 acts in synergy with B cell-activating factor to influence B cell biology and the pathophysiology of systemic lupus erythematosus.
Doreau A, Belot A, Bastid J, Riche B, Trescol-Biemont MC, Ranchin B, Fabien N, Cochat P, Pouteil-Noble C, Trolliet P, Durieu I, Tebib J, Kassai B, Ansieau S, Puisieux A, Eliaou JF, Bonnefoy-Bérard N. Doreau A, et al. Nat Immunol. 2009 Jul;10(7):778-85. doi: 10.1038/ni.1741. Epub 2009 May 31. Nat Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19483719 Retracted.
References
- Murphy ED, Roths JB. A Y chromosome associated factor in strain BXSB producing accelerated autoimmunity and lymphoproliferation. Arthritis Rheum. 1979;22:1188–1194. - PubMed
- Pisitkun P, et al. Autoreactive B cell responses to RNA-related antigens due to TLR7 gene duplication. Science. 2006;312:1669–1672. - PubMed
- Parrish-Novak J, et al. Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature. 2000;408:57–63. - PubMed
- Spolski R, Leonard WJ. Interleukin-21: Basic biology and implications for cancer and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:57–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous