Significant vitamin D deficiency in youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus - PubMed (original) (raw)
Significant vitamin D deficiency in youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Britta M Svoren et al. J Pediatr. 2009 Jan.
Abstract
Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D was measured in 128 youth with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Less than 25% of the patients were vitamin D sufficient. Because individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus possess multiple risk factors for skeletal fragility, ensuring vitamin D sufficiency throughout childhood and adolescence in this population seems especially warranted.
Figures
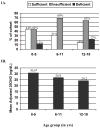
Figure 1
Figure 1A Vitamin D status. Among 0–5, 6–11, and 12–18 year olds, the percentage of participants with either vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency was 56%, 69%, and 85%, respectively. B, Adjusted 25OHD levels. A mean adjusted 25OHD value was calculated for each age group controlling for patient ethnicity, visit season, sex, z-BMI, A1c, and diabetes duration. The 12–18 year olds had significantly lower 25OHD levels compared with 0–5 year olds (<0.01).
Comment in
- Overall health in youth with type 1 diabetes.
Daniels SR. Daniels SR. J Pediatr. 2009 Jan;154(1):A2. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.11.019. J Pediatr. 2009. PMID: 19187721 No abstract available. - They're still kids.
Zeitler PS, Klingensmith GJ. Zeitler PS, et al. J Pediatr. 2009 Jan;154(1):7-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.09.028. J Pediatr. 2009. PMID: 19187730 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Free vitamin D levels in steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome and healthy controls.
Banerjee S, Basu S, Akhtar S, Sinha R, Sen A, Sengupta J. Banerjee S, et al. Pediatr Nephrol. 2020 Mar;35(3):447-454. doi: 10.1007/s00467-019-04433-1. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Pediatr Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31845055 - Treating vitamin D deficiency in children with type I diabetes could improve their glycaemic control.
Giri D, Pintus D, Burnside G, Ghatak A, Mehta F, Paul P, Senniappan S. Giri D, et al. BMC Res Notes. 2017 Sep 7;10(1):465. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-2794-3. BMC Res Notes. 2017. PMID: 28882195 Free PMC article. - Assessment Of Serum Vitamin D Level In Children With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study.
Bayan AS, El-Aziz Nosair NA, Salamah AM. Bayan AS, et al. J Pak Med Assoc. 2023 Apr;73(Suppl 4)(4):S317-S321. doi: 10.47391/JPMA.EGY-S4-61. J Pak Med Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37482879 - [Vitamin D deficiency in Spanish population. Importance of egg on nutritional improvement].
Rodríguez-Rodríguez E, Aparicio Vizuete A, Sánchez-Rodríguez P, Lorenzo Mora AM, López-Sobaler AM, Ortega RM. Rodríguez-Rodríguez E, et al. Nutr Hosp. 2019 Aug 27;36(Spec No3):3-7. doi: 10.20960/nh.02798. Nutr Hosp. 2019. PMID: 31368328 Review. Spanish. - Clinical practice guidelines for vitamin D in the United Arab Emirates.
Haq A, Wimalawansa SJ, Pludowski P, Anouti FA. Haq A, et al. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Jan;175:4-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.09.021. Epub 2016 Sep 28. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 27693095 Review.
Cited by
- Does vitamin D supplementation benefit patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus who are vitamin D deficient? A study was performed at the Sudan Childhood Diabetes Center from 2019 to 2022.
Suliman HA, Elkhawad AO, Babiker OO, Alhaj YM, Eltom KH, Elnour AA. Suliman HA, et al. SAGE Open Med. 2024 May 6;12:20503121241242931. doi: 10.1177/20503121241242931. eCollection 2024. SAGE Open Med. 2024. PMID: 38711469 Free PMC article. - Proportion of vitamin D deficiency in children/adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Yang X, Chai M, Lin M. Yang X, et al. BMC Pediatr. 2024 Mar 16;24(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-04683-5. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38493103 Free PMC article. - 25OHVitamin D Levels in a Canarian Pediatric Population with and without Type 1 Diabetes: The Role of Acidosis.
Nóvoa-Medina Y, Barreiro-Bautista M, Perdomo-Quinteiro M, González-Martín JM, Quinteiro-González S, Domínguez Á, Cabrera M, López S, Pavlovic S, Wägner AM. Nóvoa-Medina Y, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Jul 7;15(13):3067. doi: 10.3390/nu15133067. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447392 Free PMC article. - Vitamin D Status in Diabetic Moroccan Children And Adolescents: a Case-control Study.
Bouichrat N, Benyakhef S, Assarrar I, Draoui N, Lazreg Y, Abda N, Rouf S, Latrech H. Bouichrat N, et al. Rev Diabet Stud. 2023 Mar 31;19(1):1-7. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2023.19.1. Rev Diabet Stud. 2023. PMID: 37185054 Free PMC article. - Vitamin D Status in Osteoporotic and Diabetic Patients and Athletic Healthy Individuals from Northern Greece.
Anetakis C, Mitka S, Chatzidimitriou M, Anagnostopoulos K, Eleftheriou P, Lialiaris T. Anetakis C, et al. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2023 Jan;11(4):565-576. doi: 10.52547/rbmb.11.4.565. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37131899 Free PMC article.
References
- Holick MF. High prevalence of vitamin D inadequacy and implications for health. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006;81:353–73. - PubMed
- El Hajj FG, Nabulsi M, Choucair M, Salamoun M, Hajj SC, Kizirian A, et al. Hypovitaminosis D in healthy schoolchildren. Pediatrics. 2001;107:E53. - PubMed
- Tuominen JT, Impivaara O, Puukka P, Ronnemaa T. Bone mineral density in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:1196–200. - PubMed
- Miazgowski T, Czekalski S. A 2-year follow-up study on bone mineral density and markers of bone turnover in patients with long-standing insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Osteoporos Int. 1998;8:399–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K12DK63696/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK046887/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K12 DK063696/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- L40 DK068871-02/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK046887/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical