Statistical hypothesis testing in intraspecific phylogeography: nested clade phylogeographical analysis vs. approximate Bayesian computation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Statistical hypothesis testing in intraspecific phylogeography: nested clade phylogeographical analysis vs. approximate Bayesian computation
Alan R Templeton. Mol Ecol. 2009 Jan.
Abstract
Nested clade phylogeographical analysis (NCPA) and approximate Bayesian computation (ABC) have been used to test phylogeographical hypotheses. Multilocus NCPA tests null hypotheses, whereas ABC discriminates among a finite set of alternatives. The interpretive criteria of NCPA are explicit and allow complex models to be built from simple components. The interpretive criteria of ABC are ad hoc and require the specification of a complete phylogeographical model. The conclusions from ABC are often influenced by implicit assumptions arising from the many parameters needed to specify a complex model. These complex models confound many assumptions so that biological interpretations are difficult. Sampling error is accounted for in NCPA, but ABC ignores important sources of sampling error that creates pseudo-statistical power. NCPA generates the full sampling distribution of its statistics, but ABC only yields local probabilities, which in turn make it impossible to distinguish between a good fitting model, a non-informative model, and an over-determined model. Both NCPA and ABC use approximations, but convergences of the approximations used in NCPA are well defined whereas those in ABC are not. NCPA can analyse a large number of locations, but ABC cannot. Finally, the dimensionality of tested hypothesis is known in NCPA, but not for ABC. As a consequence, the 'probabilities' generated by ABC are not true probabilities and are statistically non-interpretable. Accordingly, ABC should not be used for hypothesis testing, but simulation approaches are valuable when used in conjunction with NCPA or other methods that do not rely on highly parameterized models.
Figures
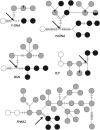
Figure 1
Five haplotype trees estimated from samples of African savanna elephants (black), African forest elephants (grey), and Asian elephants as an outgroup (white circles) by Roca et al. (2005). A black arrow shows the points in the haplotype trees at which a significant fragmentation event was inferred by NCPA that primarily separates the forested and savanna areas of Africa.
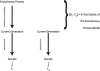
Figure 2
A diagram of the sampling considerations made explicit by Ewens (1983) for long-term statistics (Slt) and current generation statistics (Scg). A contrast of these two types of statistics will focus its power on the evolutionary model used to generate the long-term statistic only if both types of statistics include the impact of sampling error from the current generation.
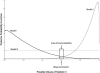
Figure 3
Hypothetical posterior distributions for three models for a univariate statistic and an area around the observed value of statistic where local probabilities are evaluated.
Similar articles
- Statistical phylogeography: methods of evaluating and minimizing inference errors.
Templeton AR. Templeton AR. Mol Ecol. 2004 Apr;13(4):789-809. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294x.2003.02041.x. Mol Ecol. 2004. PMID: 15012756 - Evaluating nested clade phylogeographic analysis under models of restricted gene flow.
Panchal M, Beaumont MA. Panchal M, et al. Syst Biol. 2010 Jul;59(4):415-32. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syq022. Epub 2010 May 24. Syst Biol. 2010. PMID: 20547778 - The automation and evaluation of nested clade phylogeographic analysis.
Panchal M, Beaumont MA. Panchal M, et al. Evolution. 2007 Jun;61(6):1466-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00124.x. Evolution. 2007. PMID: 17542853 - Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC) in practice.
Csilléry K, Blum MG, Gaggiotti OE, François O. Csilléry K, et al. Trends Ecol Evol. 2010 Jul;25(7):410-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2010.04.001. Epub 2010 May 18. Trends Ecol Evol. 2010. PMID: 20488578 Review. - Phylogeography's past, present, and future: 10 years after Avise, 2000.
Hickerson MJ, Carstens BC, Cavender-Bares J, Crandall KA, Graham CH, Johnson JB, Rissler L, Victoriano PF, Yoder AD. Hickerson MJ, et al. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2010 Jan;54(1):291-301. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2009.09.016. Epub 2009 Sep 13. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2010. PMID: 19755165 Review.
Cited by
- Phylogeography of Begonia luzhaiensis suggests both natural and anthropogenic causes for the marked population genetic structure.
Tseng YH, Huang HY, Xu WB, Yang HA, Peng CI, Liu Y, Chung KF. Tseng YH, et al. Bot Stud. 2019 Sep 6;60(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s40529-019-0267-9. Bot Stud. 2019. PMID: 31493093 Free PMC article. - Phylogeography of Daphnia magna Straus (Crustacea: Cladocera) in Northern Eurasia: Evidence for a deep longitudinal split between mitochondrial lineages.
Bekker EI, Karabanov DP, Galimov YR, Haag CR, Neretina TV, Kotov AA. Bekker EI, et al. PLoS One. 2018 Mar 15;13(3):e0194045. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194045. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29543844 Free PMC article. - In defence of model-based inference in phylogeography.
Beaumont MA, Nielsen R, Robert C, Hey J, Gaggiotti O, Knowles L, Estoup A, Panchal M, Corander J, Hickerson M, Sisson SA, Fagundes N, Chikhi L, Beerli P, Vitalis R, Cornuet JM, Huelsenbeck J, Foll M, Yang Z, Rousset F, Balding D, Excoffier L. Beaumont MA, et al. Mol Ecol. 2010 Feb;19(3):436-446. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04515.x. Epub 2010 Jan 11. Mol Ecol. 2010. PMID: 29284924 Free PMC article. - An efficient pipeline to generate data for studies in plastid population genomics and phylogeography.
Kohrn BF, Persinger JM, Cruzan MB. Kohrn BF, et al. Appl Plant Sci. 2017 Nov 14;5(11):apps.1700053. doi: 10.3732/apps.1700053. eCollection 2017 Nov. Appl Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 29188144 Free PMC article. - Effects of the population pedigree on genetic signatures of historical demographic events.
Wakeley J, King L, Wilton PR. Wakeley J, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jul 19;113(29):7994-8001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1601080113. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27432946 Free PMC article.
References
- Avise JC, Arnold J, Ball RM, et al. Intraspecific phylogeography: the mitochondrial DNA bridge between population genetics and systematics. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics. 1987;18:489–522.
- Beaumont MA, Panchal M. On the validity of nested clade phylogeographical analysis. Molecular Ecology. 2008;17:2563–2565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials