Community-based study on CKD subjects and the associated risk factors - PubMed (original) (raw)
Community-based study on CKD subjects and the associated risk factors
Nan Chen et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009 Jul.
Abstract
Background: The study was performed to investigate the prevalence, awareness and the risk factors of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in the community population in Shanghai, China.
Methods: A total of 2596 residents were randomly recruited from the community population in Shanghai, China. All were screened for albuminuria, haematuria, morning spot urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio and renal function. Serum creatinine, uric acid, cholesterol, triglyceride and haemoglobin were assessed. A simplified MDRD equation was used to estimate the glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). All studied subjects were screened by kidney ultrasound. Haematuria, if present in the morning spot urine dipstick test, was confirmed by microscopy. The associations among the demographic characteristics, health characteristics and indicators of kidney damage were examined.
Results: Two thousand five hundred and fifty-four residents (n = 2554), after giving informed consent and with complete data, were entered into this study. Albuminuria and haematuria were detected in 6.3% and 1.2% of all the studied subjects, respectively, whereas decreased kidney function was found in 5.8% of all studied subjects. Approximately 11.8% of subjects had at least one indicator of kidney damage. The rate of awareness of CKD was 8.2%. The logistic regression model showed that age, central obesity, hypertension, diabetes, anaemia, hyperuricaemia and nephrolithiasis each contributed to the development of CKD.
Conclusion: This is the first Shanghai community-based epidemiological study data on Chinese CKD patients. The prevalence of CKD in the community population in Shanghai is 11.8%, and the rate of awareness of CKD is 8.2%. All the factors including age, central obesity, hypertension, diabetes, anaemia, hyperuricaemia and nephrolithiasis are positively correlated with the development of CKD in our studied subjects.
Figures
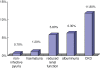
Fig. 1
Biomeasures of renal disease in the current study.
References
- US Renal Data System (USRDS) 2006. ADR (http://www.usrds.org/adr.htm. )
- Dialysis and Transplantation Registration Group The report about the registration of dialysis and transplantation in China. Chin J Nephrol. 1999;17:77–78.
- Shanghai Dialysis and Transplantation Registration Group The report about the registration of dialysis and transplantation in China. Chin J Nephrol. 1999;17:77–78.
- Garg AX, Kiberd BA, Clark WF, et al. Albuminuria and renal insufficiency prevalence guides population screening: results from the NHANES III. Kidney Int. 2002;61:2165–2175. - PubMed
- Ramirez SP, McClellan W, Port FK, et al. Risk factors for proteinuria in a large, multiracial, southeast Asian population. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:1907–1917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous