Orc1 controls centriole and centrosome copy number in human cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Orc1 controls centriole and centrosome copy number in human cells
Adriana S Hemerly et al. Science. 2009.
Abstract
Centrosomes, each containing a pair of centrioles, organize microtubules in animal cells, particularly during mitosis. DNA and centrosomes are normally duplicated once before cell division to maintain optimal genome integrity. We report a new role for the Orc1 protein, a subunit of the origin recognition complex (ORC) that is a key component of the DNA replication licensing machinery, in controlling centriole and centrosome copy number in human cells, independent of its role in DNA replication. Cyclin A promotes Orc1 localization to centrosomes where Orc1 prevents Cyclin E-dependent reduplication of both centrioles and centrosomes in a single cell division cycle. The data suggest that Orc1 is a regulator of centriole and centrosome reduplication as well as the initiation of DNA replication.
Figures
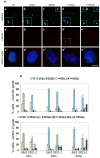
Fig. 1. Orc1 depletion causes centriole and centrosome re-duplication
(A) Human U2OS cells treated for 72 hours with Orc1-1 siRNA duplex were co-immunostained for centrioles with anti-centrin 2 (green, a to e) and centrosomes with anti--tubulin (red, a to e) antibodies. Insets are higher magnification. DNA was stained with DAPI (blue) and merged images are shown in a to e. Scale bar, 10 m. (B) Quantification of centrosome and centriole numbers by -tubulin (upper panel) and centrin 2 (Bottom panel) immunostaining, respectively. Cells were harvested at 12, 36 or 60 hours after nocodazole release. Error bars represent one standard error. 1C, one centrosome; 2C(L), two centrosomes linked; 2C(S), two centrosomes separated; >=3C(L), three or more centrosomes linked; >=3C(S), three or more centrosomes separated. 1Pair, one centriole pair; 2 Pairs (L), two centriole pairs linked; 2 Pairs (S), two centriole pairs separated; 2 Pairs (Dis.), two centriole pairs with disorganized disengaged; >=2 Pairs, more than two centriole pairs.
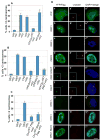
Fig. 2. Over-expression of Orc1 blocks centrosome re-duplication
U2OS asynchronous cells were transfected (or not, UNT) with the indicated constructs (see text) and treated with 16mM hydroxyurea (+ or HU). Cells were harvested at 68 hours after HU-treatment. Centrosome numbers were scored by -tubulin immunostaining in YFP or Flag positive cells. (A–C) Quantification of multiple centrosomes in HU-arrested cells. (D) Cells were immunostained for centrosomes with anti -tubulin (red, a to i); YFP expression was immunostained with anti-GFP in (A) (green, a to d) or visualized directly in (B) (e, f); and Flag expression was immunostained with anti-Flag in (C) (g to i). DNA was stained with DAPI (blue) and merged images are shown in a to i. Scale bar, 10 m. Insets are higher magnification.
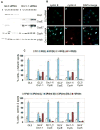
Fig. 3. Orc1 depletion causes Cdk2 and Cyclin E-dependent centriole and centrosome re-duplication
(A) and (B) Nocodazole arrested U2OS cells were transfected with control (GL3) or Orc1-1 siRNA, then released into the next cycle and re-transfected with the same siRNA duplexes. (A) Immunoblot of whole-cell extract of cells harvested at the indicated time points. Orc1, Cyclin E, Cyclin A and -tubulin levels were assessed by immunoblotting with specific antibodies. Cyclin E*, a longer exposure. (B) Cells were harvested at 12 hours after nocodazole release and co-immunostained with anti-Cyclin E (green) and anti-Cyclin A (red). DNA was stained with DAPI (blue) and merged images are shown in a and b. Scale bar, 30 m. (C) Quantification of centrosome and centriole numbers by -tubulin and centrin 2 immunostaining, respectively, of asynchronous U2OS cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs. Cells were analyzed 72 hours after the first transfection. Error bars represent one standard error.
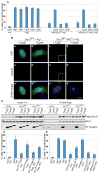
Fig. 4. Cyclin E suppresses Orc1 inhibition of centrosome re-duplication in S-phase-arrested cells
In A, B, C and D: U2OS asynchronous cells were transfected with the indicated constructs (see text) and treated with 16mM hydroxyurea (+HU). Untransfected cells were treated or not with HU (UNT +HU and UNT HU, respectively). Cells were harvested at 68 hours after transfection and HU-treatment. (A) Quantification of multiple centrosomes in transfected HU-arrested cells. Centrosome numbers were scored by -tubulin immunostaining in YFP positive cells. Error bars represent one standard error. (B) Transfected, HU-treated cells were immunostained for centrosomes with anti -tubulin (red, a to d) and YFP expression was visualized directly (green, a to d). DNA was stained with DAPI (blue) and merged images are shown in a to d. Scale bar, 10 m. (C) Immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody from whole-cell extract from HEK293 cells transiently co-expressing the indicated constructs and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Vector, full-length Orc1WT. Flag (wild type) or full-length Orc1A-A. Flag (mutant) were transiently transfected alone (); or with either T7-Cyclin E, T7-Cyclin A or T7-Cyclin Right panel: 10% of the immunoprecipitates. (D) and (E) Quantification of multiple centrosomes in transfected HU-arrested cells. Centrosome numbers were scored by -tubulin immunostaining in Flag positive cells in (D), and by -tubulin immunostaining in YFP positive cells directly visualized in (E). Error bars represent one standard error.
Similar articles
- Meier-Gorlin syndrome mutations disrupt an Orc1 CDK inhibitory domain and cause centrosome reduplication.
Hossain M, Stillman B. Hossain M, et al. Genes Dev. 2012 Aug 15;26(16):1797-810. doi: 10.1101/gad.197178.112. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22855792 Free PMC article. - The cyclin A centrosomal localization sequence recruits MCM5 and Orc1 to regulate centrosome reduplication.
Ferguson RL, Pascreau G, Maller JL. Ferguson RL, et al. J Cell Sci. 2010 Aug 15;123(Pt 16):2743-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.073098. Epub 2010 Jul 27. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 20663915 Free PMC article. - Multiple, short protein binding motifs in ORC1 and CDC6 control the initiation of DNA replication.
Hossain M, Bhalla K, Stillman B. Hossain M, et al. Mol Cell. 2021 May 6;81(9):1951-1969.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.03.003. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33761311 Free PMC article. - The centriole duplication cycle.
Fırat-Karalar EN, Stearns T. Fırat-Karalar EN, et al. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Sep 5;369(1650):20130460. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0460. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25047614 Free PMC article. Review. - The centrosome cycle: Centriole biogenesis, duplication and inherent asymmetries.
Nigg EA, Stearns T. Nigg EA, et al. Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Oct 3;13(10):1154-60. doi: 10.1038/ncb2345. Nat Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21968988 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Where and when to start: Regulating DNA replication origin activity in eukaryotic genomes.
Lee CSK, Weiβ M, Hamperl S. Lee CSK, et al. Nucleus. 2023 Dec;14(1):2229642. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2023.2229642. Nucleus. 2023. PMID: 37469113 Free PMC article. Review. - Systemic analysis of the DNA replication regulator origin recognition complex in lung adenocarcinomas identifies prognostic and expression significance.
Tang M, Chen J, Zeng T, Ye DM, Li YK, Zou J, Zhang YP. Tang M, et al. Cancer Med. 2023 Feb;12(4):5035-5054. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5238. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36205357 Free PMC article. - The consequences of differential origin licensing dynamics in distinct chromatin environments.
Mei L, Kedziora KM, Song EA, Purvis JE, Cook JG. Mei L, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Sep 23;50(17):9601-9620. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac003. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35079814 Free PMC article. - Sufu negatively regulates both initiations of centrosome duplication and DNA replication.
Zhuang T, Zhang B, Song Y, Huang F, Chi W, Xin G, Zhang Z, Cheng SY, Jiang Q, Zhang C. Zhuang T, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jul 13;118(28):e2026421118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2026421118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34260378 Free PMC article. - The γ-tubulin meshwork assists in the recruitment of PCNA to chromatin in mammalian cells.
Corvaisier M, Zhou J, Malycheva D, Cornella N, Chioureas D, Gustafsson NMS, Rosselló CA, Ayora S, Li T, Ekström-Holka K, Jirström K, Lindström L, Alvarado-Kristensson M. Corvaisier M, et al. Commun Biol. 2021 Jun 22;4(1):767. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02280-1. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34158617 Free PMC article.
References
- Nigg EA. Trends in Cell Biology. 2007;17:215. - PubMed
- Sasaki T, Gilbert DM. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2007;19:337. - PubMed
- Bettencourt-Dias M, Glover DM. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2007;8:451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA13106/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA013106-370025/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA013106-310025/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA013106-36/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA013106/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical