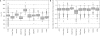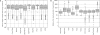An evaluation of custom microarray applications: the oligonucleotide design challenge - PubMed (original) (raw)
An evaluation of custom microarray applications: the oligonucleotide design challenge
Sophie Lemoine et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr.
Abstract
The increase in feature resolution and the availability of multipack formats from microarray providers has opened the way to various custom genomic applications. However, oligonucleotide design and selection remains a bottleneck of the microarray workflow. Several tools are available to perform this work, and choosing the best one is not an easy task, nor are the choices obvious. Here we review the oligonucleotide design field to help users make their choice. We have first performed a comparative evaluation of the available solutions based on a set of criteria including: ease of installation, user-friendly access, the number of parameters and settings available. In a second step, we chose to submit two real cases to a selection of programs. Finally, we used a set of tests for the in silico benchmark of the oligo sets obtained from each type of software. We show that the design software must be selected according to the goal of the scientist, depending on factors such as the organism used, the number of probes required and their localization on the target sequence. The present work provides keys to the choice of the most relevant software, according to the various parameters we tested.
Figures
Figure 1.
Comparison of the sensitivity of the oligonucleotides designed for the custom mouse array. For each oligonucleotide set created we plot the distribution for all oligonucleotides in the set of _T_m (A) and free energies of the most probable secondary structure (B). The name of the software used for design is displayed on the _x_-axis. AOS stands for ArrayOligoSelector.
Figure 2.
Evaluation of custom oligonucleotide specificity. (A) Duplex free energies between oligonucleotides and their best off-target hit. (B) Distribution of the distance between the 5′ of the oligonucleotide and the 3′ of the target gene sequence for each designed oligoset. The name of the software used for design is displayed on the _x_-axis. AOS stands for ArrayOligoSelector.
Figure 3.
Comparison of the sensitivity of the oligonucleotides designed for tiling array. For each oligonucleotide set created we plot the distribution for all oligonucleotides in the set of _T_m (A), GC percent (B) and free energies of the most probable secondary structure (C).
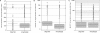
Figure 4.
Evaluation of tiling oligonucleotide specificity. (A) Distribution of the distance in base pair between oligonucleotide that follows each other on the tiling path. (B) Distribution of the number of oligonucleotide by transcript. (C) Distribution of the number of BLAST hits by oligonucleotide using the parameters described in the ‘Material and methods’ section. The _y_-axis is log scaled. To clearly display these distributions we removed all oligonucleotides with only one hit.
Similar articles
- Teolenn: an efficient and customizable workflow to design high-quality probes for microarray experiments.
Jourdren L, Duclos A, Brion C, Portnoy T, Mathis H, Margeot A, Le Crom S. Jourdren L, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jun;38(10):e117. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq110. Epub 2010 Feb 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20176570 Free PMC article. - OligoDesign: Optimal design of LNA (locked nucleic acid) oligonucleotide capture probes for gene expression profiling.
Tolstrup N, Nielsen PS, Kolberg JG, Frankel AM, Vissing H, Kauppinen S. Tolstrup N, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jul 1;31(13):3758-62. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg580. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12824412 Free PMC article. - OligoWiz 2.0--integrating sequence feature annotation into the design of microarray probes.
Wernersson R, Nielsen HB. Wernersson R, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jul 1;33(Web Server issue):W611-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki399. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15980547 Free PMC article. - [Research progress of probe design software of oligonucleotide microarrays].
Chen X, Wu Z, Liu Z. Chen X, et al. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Feb;31(1):214-21. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24804514 Review. Chinese. - Analysis and management of microarray gene expression data.
Grant GR, Manduchi E, Stoeckert CJ Jr. Grant GR, et al. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2007 Jan;Chapter 19:Unit 19.6. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb1906s77. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 18265395 Review.
Cited by
- Strain/species-specific probe design for microbial identification microarrays.
Tu Q, He Z, Deng Y, Zhou J. Tu Q, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Aug;79(16):5085-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01124-13. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23747703 Free PMC article. - PrimerBank: a resource of human and mouse PCR primer pairs for gene expression detection and quantification.
Spandidos A, Wang X, Wang H, Seed B. Spandidos A, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jan;38(Database issue):D792-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1005. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 19906719 Free PMC article. - A general framework for optimization of probes for gene expression microarray and its application to the fungus Podospora anserina.
Bidard F, Imbeaud S, Reymond N, Lespinet O, Silar P, Clavé C, Delacroix H, Berteaux-Lecellier V, Debuchy R. Bidard F, et al. BMC Res Notes. 2010 Jun 18;3:171. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-3-171. BMC Res Notes. 2010. PMID: 20565839 Free PMC article. - Cluster oligonucleotide signatures for rapid identification by sequencing.
Zahariev M, Chen W, Visagie CM, Lévesque CA. Zahariev M, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Oct 29;19(1):395. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2363-3. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 30522439 Free PMC article. - BOND: Basic OligoNucleotide Design.
Ilie L, Mohamadi H, Golding GB, Smyth WF. Ilie L, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013 Feb 27;14:69. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-69. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23444904 Free PMC article.
References
- Wang J, Li KB, Sung WK. G-PRIMER: greedy algorithm for selecting minimal primer set. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:2473–2475. - PubMed
- Raddatz G, Dehio M, Meyer TF, Dehio C. PrimeArray: genome-scale primer design for DNA-microarray construction. Bioinformatics. 2001;17:98–99. - PubMed
- Thareau V, Dehais P, Serizet C, Hilson P, Rouze P, Aubourg S. Automatic design of gene-specific sequence tags for genome-wide functional studies. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:2191–2198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources