Mapping complex disease traits with global gene expression - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Mapping complex disease traits with global gene expression
William Cookson et al. Nat Rev Genet. 2009 Mar.
Abstract
Variation in gene expression is an important mechanism underlying susceptibility to complex disease. The simultaneous genome-wide assay of gene expression and genetic variation allows the mapping of the genetic factors that underpin individual differences in quantitative levels of expression (expression QTLs; eQTLs). The availability of systematically generated eQTL information could provide immediate insight into a biological basis for disease associations identified through genome-wide association (GWA) studies, and can help to identify networks of genes involved in disease pathogenesis. Although there are limitations to current eQTL maps, understanding of disease will be enhanced with novel technologies and international efforts that extend to a wide range of new samples and tissues.
Figures
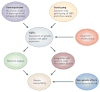
Figure 1. eQTL mapping
Expression QTL mapping begins with the measurement of gene expression in a target cell or tissue from multiple individuals. This information is the substrate for investigating the effects of DNA polymorphism (of whatever type) on the expression of individual genes. Other factors which may alter transcription, such as epigenetic CpG methylation may also be mapped. Network analyses builds upon the strong correlations that are present between transcripts, and allows the identification of modules of genes that mediate complex functions. This information can then be made available to interpret genetic associations and mapping information from the study of complex disease.
Similar articles
- Tissue specific regulation of transcription in endometrium and association with disease.
Mortlock S, Kendarsari RI, Fung JN, Gibson G, Yang F, Restuadi R, Girling JE, Holdsworth-Carson SJ, Teh WT, Lukowski SW, Healey M, Qi T, Rogers PAW, Yang J, McKinnon B, Montgomery GW. Mortlock S, et al. Hum Reprod. 2020 Feb 29;35(2):377-393. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dez279. Hum Reprod. 2020. PMID: 32103259 Free PMC article. - Cis-eQTLs in seven duck tissues identify novel candidate genes for growth and carcass traits.
Cai W, Hu J, Zhang Y, Guo Z, Zhou Z, Hou S. Cai W, et al. BMC Genomics. 2024 Apr 30;25(1):429. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10338-7. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38689208 Free PMC article. - QTL Analysis Beyond eQTLs.
Wen J, Nodzak C, Shi X. Wen J, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2082:201-210. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0026-9_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31849017 Review. - Leveraging molecular quantitative trait loci to understand the genetic architecture of diseases and complex traits.
Hormozdiari F, Gazal S, van de Geijn B, Finucane HK, Ju CJ, Loh PR, Schoech A, Reshef Y, Liu X, O'Connor L, Gusev A, Eskin E, Price AL. Hormozdiari F, et al. Nat Genet. 2018 Jul;50(7):1041-1047. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0148-2. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Nat Genet. 2018. PMID: 29942083 Free PMC article. - Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Information Improves Predictive Modeling of Disease Relevance of Non-Coding Genetic Variation.
Croteau-Chonka DC, Rogers AJ, Raj T, McGeachie MJ, Qiu W, Ziniti JP, Stubbs BJ, Liang L, Martinez FD, Strunk RC, Lemanske RF Jr, Liu AH, Stranger BE, Carey VJ, Raby BA. Croteau-Chonka DC, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Oct 16;10(10):e0140758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140758. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26474488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Identification of Potential Causal Genes for Neurodegenerative Diseases by Mitochondria-Related Genome-Wide Mendelian Randomization.
Yin KF, Chen T, Gu XJ, Jiang Z, Su WM, Duan QQ, Wen XJ, Cao B, Li JR, Chi LY, Chen YP. Yin KF, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep 30. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04528-3. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39347895 - Unsupervised pattern identification in spatial gene expression atlas reveals mouse brain regions beyond established ontology.
Cahill R, Wang Y, Xian RP, Lee AJ, Zeng H, Yu B, Tasic B, Abbasi-Asl R. Cahill R, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Sep 10;121(37):e2319804121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2319804121. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39226356 Free PMC article. - A multi-modal framework improves prediction of tissue-specific gene expression from a surrogate tissue.
Xu Y, He C, Fan J, Zhou Y, Cheng C, Meng R, Cui Y, Li W, Gamazon ER, Zhou D. Xu Y, et al. EBioMedicine. 2024 Sep;107:105305. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105305. Epub 2024 Aug 23. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39180788 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide association and expression quantitative trait loci in cattle reveals common genes regulating mammalian fertility.
Forutan M, Engle BN, Chamberlain AJ, Ross EM, Nguyen LT, D'Occhio MJ, Snr AC, Kho EA, Fordyce G, Speight S, Goddard ME, Hayes BJ. Forutan M, et al. Commun Biol. 2024 Jun 12;7(1):724. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06403-2. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38866948 Free PMC article. - Cell type-specific network analysis in Diversity Outbred mice identifies genes potentially responsible for human bone mineral density GWAS associations.
Dillard LJ, Calabrese GM, Mesner LD, Farber CR. Dillard LJ, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 21:2024.05.20.594981. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.20.594981. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38826475 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
- Hugot JP, et al. Association of NOD2 leucine-rich repeat variants with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature. 2001;411:599–603. - PubMed
- Palmer CN, et al. Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nat Genet. 2006;38:441–6. - PubMed
- Schadt EE, et al. Genetics of gene expression surveyed in maize, mouse and man. Nature. 2003;422:297–302. This paper dramatically showed the power of eQTL analysis in humans. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources