Bcl-2 inhibitors: targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Bcl-2 inhibitors: targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy
Min H Kang et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2009.
Abstract
Defects in apoptotic pathways can promote cancer cell survival and also confer resistance to antineoplastic drugs. One pathway being targeted for antineoplastic therapy is the anti-apoptotic B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) family of proteins (Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, Bcl-w, Mcl-1, Bfl1/A-1, and Bcl-B) that bind to and inactivate BH3-domain pro-apoptotic proteins. Signals transmitted by cellular damage (including antineoplastic drugs) or cytokine deprivation can initiate apoptosis via the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. It is controversial whether some BH3-domain proteins (Bim or tBid) directly activate multidomain pro-apoptotic proteins (e.g., Bax and Bak) or act via inhibition of those anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins (Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, Bcl-w, Mcl-1, Bfl1/A-1, and Bcl-B) that stabilize pro-apoptotic proteins. Overexpression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members has been associated with chemotherapy resistance in various human cancers, and preclinical studies have shown that agents targeting anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members have preclinical activity as single agents and in combination with other antineoplastic agents. Clinical trials of several investigational drugs targeting the Bcl-2 family (oblimersen sodium, AT-101, ABT-263, GX15-070) are ongoing. Here, we review the role of the Bcl-2 family in apoptotic pathways and those agents that are known and/or designed to inhibit the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family of proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
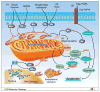
Fig. 1
The apoptotic pathway to cell death from the perspective of the Bcl-2 family of proteins.1, The intrinsic pathway is initiated by various signals, principally extracellular stimuli. 2, The extrinsic pathway is activated by Fas ligand or TRAIL, subsequently activating caspase-8. Caspase-8 transforms Bid into truncated Bid. In addition, caspase-8 initiates a cascade of caspase activation. 3, BH3-only proteins (Bim, Bid, Bad, Noxa, Puma) engage with anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins to relieve their inhibition of Bax and Bak to activate them. 4, Next, Bax and Bak are oligomerized and activated, leading to mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. 5, Once mitochondrial membranes are permeabilized, cytochrome c and/or Smac/DIABLO is released into the cytoplasm, wherein they combine with an adaptor molecule, apoptosis protease-activating factor 1, and an inactive initiator caspase, procaspase-9, within a multiprotein complex called the apoptosome. Smac/DIABLO inhibits inhibitors of apoptosis proteins to activate caspase-9. 6, Caspase-9 activates caspase-3, which is the initiation step for the cascade of caspase activation. Intrinsic and extrinsic pathways converge on caspase-3. Bcl-2 family proteins are also found on the endoplasmic reticulum and the perinuclear membrane in hematopoietic cells, but they are predominantly localized to mitochondria.
Similar articles
- Mcl-1 Phosphorylation defines ABT-737 resistance that can be overcome by increased NOXA expression in leukemic B cells.
Mazumder S, Choudhary GS, Al-Harbi S, Almasan A. Mazumder S, et al. Cancer Res. 2012 Jun 15;72(12):3069-79. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-4106. Epub 2012 Apr 23. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22525702 Free PMC article. - B cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) homology domain 3 (BH3) mimetics demonstrate differential activities dependent upon the functional repertoire of pro- and anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins.
Renault TT, Elkholi R, Bharti A, Chipuk JE. Renault TT, et al. J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 19;289(38):26481-26491. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.569632. Epub 2014 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25096574 Free PMC article. - Targeting ERK1/2-bim signaling cascades by BH3-mimetic ABT-737 as an alternative therapeutic strategy for oral cancer.
Shin JA, Kim LH, Lee SJ, Jeong JH, Jung JY, Lee HN, Hong IS, Cho SD. Shin JA, et al. Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 3;6(34):35667-83. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5523. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26447615 Free PMC article. - Mimicking the BH3 domain to kill cancer cells.
Ni Chonghaile T, Letai A. Ni Chonghaile T, et al. Oncogene. 2008 Dec;27 Suppl 1(0 1):S149-57. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.52. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 19641500 Free PMC article. Review. - Non-peptidic small molecule inhibitors against Bcl-2 for cancer therapy.
Azmi AS, Mohammad RM. Azmi AS, et al. J Cell Physiol. 2009 Jan;218(1):13-21. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21567. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18767026 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The copper chelator ATN-224 induces peroxynitrite-dependent cell death in hematological malignancies.
Lee K, Briehl MM, Mazar AP, Batinic-Haberle I, Reboucas JS, Glinsmann-Gibson B, Rimsza LM, Tome ME. Lee K, et al. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Jul;60:157-67. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23416365 Free PMC article. - Small cell and large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas of the pancreas are genetically similar and distinct from well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
Yachida S, Vakiani E, White CM, Zhong Y, Saunders T, Morgan R, de Wilde RF, Maitra A, Hicks J, Demarzo AM, Shi C, Sharma R, Laheru D, Edil BH, Wolfgang CL, Schulick RD, Hruban RH, Tang LH, Klimstra DS, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA. Yachida S, et al. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012 Feb;36(2):173-84. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182417d36. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22251937 Free PMC article. - Mcl-1 as a potential therapeutic target for human hepatocelluar carcinoma.
Yu Q, Liu ZY, Chen Q, Lin JS. Yu Q, et al. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016 Aug;36(4):494-500. doi: 10.1007/s11596-016-1614-7. Epub 2016 Jul 28. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27465322 - Interactions of pro-apoptotic BH3 proteins with anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins measured in live MCF-7 cells using FLIM FRET.
Liu Q, Leber B, Andrews DW. Liu Q, et al. Cell Cycle. 2012 Oct 1;11(19):3536-42. doi: 10.4161/cc.21462. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22895112 Free PMC article. - Pediatric relapsed or refractory leukemia: new pharmacotherapeutic developments and future directions.
August KJ, Narendran A, Neville KA. August KJ, et al. Drugs. 2013 Apr;73(5):439-61. doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0026-2. Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23568274 Review.
References
- Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ. Cell death: critical control points. Cell. 2004;116:205–19. - PubMed
- Strasser A, Harris AW, Bath ML, Cory S. Novel primitive lymphoid tumours induced in transgenic mice by cooperation between myc and bcl-2. Nature. 1990;348:331–3. - PubMed
- Green DR, Reed JC. Mitochondria and apoptosis [review] [59 refs] Science. 1998;281:1309–12. - PubMed
- Del Poeta G, Venditti A, Del Principe MI, et al. Amount of spontaneous apoptosis detected by Bax/Bcl-2 ratio predicts outcome in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Blood. 2003;101:2125–31. - PubMed
- Minn AJ, Rudin CM, Boise LH, Thompson CB. Expression of bcl-xL can confer a multidrug resistance phenotype. Blood. 1995;86:1903–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials