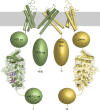Divide and conquer: high resolution structural information on TRP channel fragments - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Divide and conquer: high resolution structural information on TRP channel fragments
Rachelle Gaudet. J Gen Physiol. 2009 Mar.
No abstract available
Figures
Figure 1.
The ankyrin repeats of TRPV channels. Diagram shows the topology of TRPV channels with the relative position of the ankyrin repeats illustrated with the structure of the TRPV1 ARD. Only two of the four subunits are shown for clarity in yellow and green, respectively; the subunits in front and in back of the plane of the page are omitted. The transmembrane domains are illustrated using the homologous structure of the Shaker potassium channel (Long et al., 2005). The N- and C-terminal segments of unknown structure are depicted with shapes that approximate their relative size. ATP and ATP-interacting side chains are shown as sticks and colored according to atom type, and a transparent surface representation highlights the surface complementarity of the ATP and its binding site. The approximate size of those protein segments in numbers of amino acid (aa) residues is indicated for the green subunit. The transmembrane and ARDs of TRPV channels are each ∼250 amino acid residues. TRPV subunits typically are ∼800-residues long.
Figure 2.
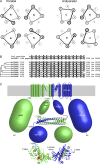
The coiled-coils of TRPM channels. (A) Helical wheel representation of parallel (left) and antiparallel (right) tetrameric coiled-coils. The “N” or “C” in each wheel indicates whether the N or C terminus, respectively, of the α-helix points toward the viewer. Darker lines are in front and lighter ones are in the back. In both coiled-coils, the a and d residues of the heptad repeats form the core, whereas the e and g residues form peripheral interactions. However, the details of the interactions are different. In a parallel coiled-coil, each layer of hydrophobic interactions consists of either four a or four d residues. In contrast, each antiparallel layer consists of two d and two a residues. (B) Sequence alignment of the predicted coiled-coil sequences of human TRPM channels. The sequence of the rat TRPM7 coiled-coil, for which the structure is available, is also included at the top. a and d position residues are shaded. The dendrogram was generated by ClustalW using an alignment of whole TRPM sequences. (C) Diagram of TRPM7 displaying the available structural information. Similarly to Fig. 1, only two of the four channel subunits are illustrated for clarity (green and blue, respectively), except for the coiled-coil structure where all four strands are shown. Note that the transmembrane domain would have fourfold rotational symmetry perpendicular to the membrane (gray shading), whereas the coiled-coil and α-kinase domains only have twofold symmetry. Shape sizes approximate the number of residues in each region, and the size (in number of amino acid residues [aa]) is indicated for the blue subunit. The approximate boundaries, in residue numbers, of different domains are also indicated.
Similar articles
- Hot on the trail of TRP channel structure.
Moiseenkova-Bell VY, Wensel TG. Moiseenkova-Bell VY, et al. J Gen Physiol. 2009 Mar;133(3):239-44. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200810123. J Gen Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19237588 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available. - Perspectives on TRP channel structure and the TRPA1 puzzle.
Latorre R. Latorre R. J Gen Physiol. 2009 Mar;133(3):227-9. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200910199. J Gen Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19237586 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - [Structural basis of multimodal responses by TRP channels].
Yamashita A. Yamashita A. Seikagaku. 2014 Aug;86(4):513-7. Seikagaku. 2014. PMID: 25255638 Review. Japanese. No abstract available. - TRP Channel: The structural era.
Li X, Fine M. Li X, et al. Cell Calcium. 2020 May;87:102191. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2020.102191. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Cell Calcium. 2020. PMID: 32199209 No abstract available. - Calciotropic and magnesiotropic TRP channels.
Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ. Hoenderop JG, et al. Physiology (Bethesda). 2008 Feb;23:32-40. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00039.2007. Physiology (Bethesda). 2008. PMID: 18268363 Review.
Cited by
- A Closer Look at Anandamide Interaction With TRPV1.
Muller C, Lynch DL, Hurst DP, Reggio PH. Muller C, et al. Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Jul 21;7:144. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00144. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32793630 Free PMC article. - The role of transient receptor potential cation channels in Ca2+ signaling.
Gees M, Colsoul B, Nilius B. Gees M, et al. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Oct;2(10):a003962. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003962. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20861159 Free PMC article. - Coarse architecture of the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) ion channel determined by fluorescence resonance energy transfer.
De-la-Rosa V, Rangel-Yescas GE, Ladrón-de-Guevara E, Rosenbaum T, Islas LD. De-la-Rosa V, et al. J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 11;288(41):29506-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.479618. Epub 2013 Aug 21. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23965996 Free PMC article. - In-Cell NMR: Analysis of Protein-Small Molecule Interactions, Metabolic Processes, and Protein Phosphorylation.
Kumar A, Kuhn LT, Balbach J. Kumar A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 17;20(2):378. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020378. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30658393 Free PMC article. Review. - High-resolution views of TRPV1 and their implications for the TRP channel superfamily.
Hellmich UA, Gaudet R. Hellmich UA, et al. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;223:991-1004. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-05161-1_11. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24961977 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bandell M., Story G.M., Hwang S.W., Viswanath V., Eid S.R., Petrus M.J., Earley T.J., Patapoutian A. 2004. Noxious cold ion channel TRPA1 is activated by pungent compounds and bradykinin.Neuron. 41:849–857 - PubMed
- Chubanov V., Waldegger S., Mederos y Schnitzler M., Vitzthum H., Sassen M.C., Seyberth H.W., Konrad M., Gudermann T. 2004. Disruption of TRPM6/TRPM7 complex formation by a mutation in the TRPM6 gene causes hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 101:2894–2899 - PMC - PubMed
- Gaudet R. 2006. Structural insights into the function of TRP channels. TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades. Liedtke W., Heller S., CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL: 349–359
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources