The DEXD/H-box RNA helicase DDX19 is regulated by an {alpha}-helical switch - PubMed (original) (raw)
The DEXD/H-box RNA helicase DDX19 is regulated by an {alpha}-helical switch
Ruairi Collins et al. J Biol Chem. 2009.
Abstract
DEXD/H-box RNA helicases couple ATP hydrolysis to RNA remodeling by an unknown mechanism. We used x-ray crystallography and biochemical analysis of the human DEXD/H-box protein DDX19 to investigate its regulatory mechanism. The crystal structures of DDX19, in its RNA-bound prehydrolysis and free posthydrolysis state, reveal an alpha-helix that inserts between the conserved domains of the free protein to negatively regulate ATPase activity. This finding was corroborated by biochemical data that confirm an autoregulatory function of the N-terminal region of the protein. This is the first study describing crystal structures of a DEXD/H-box protein in its open and closed cleft conformations.
Figures
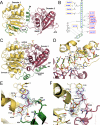
FIGURE 1.
Structure of human DDX19. A, overview of DDX19 with ADP bound and the N-terminal flanking helix in the central cleft. The Arg429 side chain that acts as an arginine finger is presented as_sticks. B_, schematic representation of the cleft-inserted helix with the two conserved domains of the protein, shown in the same view as in_panel A_. Residues that are conserved in DDX25 are shown in blue. C, overview of the DDX19-RNA complex, with Mg-ADPNP bound in the central cleft. The Arg429 side chain is presented as sticks. D, detail of the RNA binding site of the DDX19-RNA complex. E, detail of the nucleotide binding site in the open conformation, with the electron density (2_F_obs – _F_calc) for ADP rendered at 1.5 σ. F, detail of the nucleotide binding site in the RNA complex, with the electron density (2_F_obs –_F_calc) for Mg-ADPNP rendered at 1.5 σ. In all panels, the conserved domain-1 (yellow), the conserved domain-2 (red), and the N-terminal flanking sequence (green) are indicated.
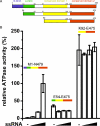
FIGURE 2.
Role of the N-terminal flanking sequence in the regulation of DDX19 ATPase activity. A, schematic diagram of the DDX19 protein constructs used in this study (not drawn to scale). N-term represents the N terminus. B, relative ATPase activities of DDX19 protein constructs in the presence of between 0 and 0.5 mg/ml ssRNA.
Similar articles
- Structural and functional analysis of the interaction between the nucleoporin Nup214 and the DEAD-box helicase Ddx19.
Napetschnig J, Kassube SA, Debler EW, Wong RW, Blobel G, Hoelz A. Napetschnig J, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Mar 3;106(9):3089-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813267106. Epub 2009 Feb 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19208808 Free PMC article. - Structure of the C-terminus of the mRNA export factor Dbp5 reveals the interaction surface for the ATPase activator Gle1.
Dossani ZY, Weirich CS, Erzberger JP, Berger JM, Weis K. Dossani ZY, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Sep 22;106(38):16251-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902251106. Epub 2009 Sep 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19805289 Free PMC article. - Comparative structural analysis of human DEAD-box RNA helicases.
Schütz P, Karlberg T, van den Berg S, Collins R, Lehtiö L, Högbom M, Holmberg-Schiavone L, Tempel W, Park HW, Hammarström M, Moche M, Thorsell AG, Schüler H. Schütz P, et al. PLoS One. 2010 Sep 30;5(9):e12791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012791. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20941364 Free PMC article. - From unwinding to clamping - the DEAD box RNA helicase family.
Linder P, Jankowsky E. Linder P, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jul 22;12(8):505-16. doi: 10.1038/nrm3154. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21779027 Review. - DEAD-box proteins as RNA helicases and chaperones.
Jarmoskaite I, Russell R. Jarmoskaite I, et al. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Jan-Feb;2(1):135-52. doi: 10.1002/wrna.50. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21297876 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Superfamily 2 helicases.
Byrd AK, Raney KD. Byrd AK, et al. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jun 1;17(6):2070-88. doi: 10.2741/4038. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22652765 Free PMC article. Review. - The Thermus thermophilus DEAD box helicase Hera contains a modified RNA recognition motif domain loosely connected to the helicase core.
Rudolph MG, Klostermeier D. Rudolph MG, et al. RNA. 2009 Nov;15(11):1993-2001. doi: 10.1261/rna.1820009. Epub 2009 Aug 26. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19710183 Free PMC article. - The DEAD-box helicase eIF4A: paradigm or the odd one out?
Andreou AZ, Klostermeier D. Andreou AZ, et al. RNA Biol. 2013 Jan;10(1):19-32. doi: 10.4161/rna.21966. Epub 2012 Sep 20. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 22995829 Free PMC article. Review. - Functions and regulation of the Brr2 RNA helicase during splicing.
Absmeier E, Santos KF, Wahl MC. Absmeier E, et al. Cell Cycle. 2016 Dec 16;15(24):3362-3377. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1249549. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27792457 Free PMC article. Review. - DDX RNA helicases: key players in cellular homeostasis and innate antiviral immunity.
Tapescu I, Cherry S. Tapescu I, et al. J Virol. 2024 Oct 22;98(10):e0004024. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00040-24. Epub 2024 Aug 30. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39212449 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Lorsch, J. R., and Herschlag, D. (1998) Biochemistry 37 2194–2206 - PubMed
- Jankowsky, E., Gross, C. H., Shuman, S., and Pyle, A. M. (2001) Science 291 121–125 - PubMed
- Tran, E. J., Zhou, Y., Corbett, A. H., and Wente, S. R. (2007) Mol. Cell 28 850–859 - PubMed
- Cordin, O., Banroques, J., Tanner, N. K., and Linder, P. (2006) Gene (Amst.) 367 17–37 - PubMed
- Jankowsky, E., and Fairman, M. E. (2007) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 17 316–324 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases