Stronger inflammatory/cytotoxic T-cell response in women identified by microarray analysis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Stronger inflammatory/cytotoxic T-cell response in women identified by microarray analysis
A Hewagama et al. Genes Immun. 2009 Jul.
Abstract
Women develop chronic inflammatory autoimmune diseases more often than men. The mechanisms causing the increased susceptibility are incompletely understood. Chronic immune stimulation characterizes many autoimmune disorders. We hypothesized that repeated stimulation may cause a different T-cell response in women than in men. Microarrays were used to compare gene expression in T cells from healthy men and women with and without repeated stimulation. Four days after a single stimulation, only 25% of differentially expressed, gender-biased genes were expressed at higher levels in women. In contrast, after restimulation, 72% were more highly expressed in women. Immune response genes were significantly over-represented among the genes upregulated in women and among the immune response genes, the inflammatory/cytotoxic effector genes interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), lymphotoxin beta (LTbeta), granzyme A (GZMA), interleukin-12 receptor beta2 (IL12Rbeta2), and granulysin (GNLY) were among those overexpressed to the highest degree. In contrast, IL17A was the only effector gene more highly expressed in men. Estrogen response elements were identified in the promoters of half the overexpressed immune genes in women, and in <10% of the male-biased genes. The differential expression of inflammatory/cytotoxic effector molecules in restimulated female T cells may contribute to the differences in autoimmune diseases between women and men.
Figures
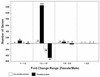
FIGURE 1. Expression profile of T cell genes differentially expressed between men and women
Bars shown greater than zero represent the numbers of genes expressed at higher levels in women than men, while the negative values represent the numbers of genes expressed more highly in men. Error bars represent the FDR of 4%.
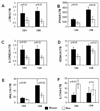
FIGURE 2. Expression levels of pro-inflammatory transcripts in restimulated T cells from men and women
PBMC from 10 racially matched male-female pairs were stimulated with PHA, cultured 4 days, then restimulated for 6 hours with PMA + ionomycin. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were isolated and expression levels of (A) LTB, (B) IFNG, (C) IL12RB2, (D) GZMA, (E) GNLY and (F) IL17A were measured by qRT- PCR relative to β-actin. Results are presented as the mean±SEM of the 10 determinations per group. Dark bars represent transcript levels in the women, and light bars transcript levels in the men.
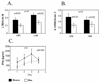
FIGURE 3. LTB, IL12RB2 and IFN-γ protein levels in restimulated T cells from men and women
(A) LTB and (B) IL12RB2 were measured by immunoblotting in the same restimulated CD4+ and CD8+ cells shown in figure 2. Results again are presented as the mean±SEM of the 10 determinations per group. (C) IFN-γ release by similarly restimulated T cells from 4 additional racially matched male-female pairs was measured by ELISA on the days indicated. Results again represent the mean±SEM of the 4 determinations per group.
Similar articles
- Lesional CD4+ IFN-γ+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis.
Maehara T, Mattoo H, Ohta M, Mahajan VS, Moriyama M, Yamauchi M, Drijvers J, Nakamura S, Stone JH, Pillai SS. Maehara T, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Feb;76(2):377-385. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209139. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 27358392 Free PMC article. - Interleukin-12 amplifies the M. leprae hsp65-cytotoxic response in the presence of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma generating CD56+ effector cells: interleukin-4 downregulates this effect.
Aleman M, De La Barrera S, Fink S, Finiasz M, Farina MH, Pizzariello G, Sasiain MD. Aleman M, et al. Scand J Immunol. 2000 Mar;51(3):262-70. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.2000.00675.x. Scand J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10736095 - Increased prevalence of peripheral blood granulysin-producing cytotoxic T lymphocytes in preeclampsia.
Molvarec A, Shiozaki A, Ito M, Toldi G, Stenczer B, Szarka A, Nakashima A, Vásárhelyi B, Rigó J Jr, Saito S. Molvarec A, et al. J Reprod Immunol. 2011 Sep;91(1-2):56-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2011.03.012. Epub 2011 Jul 18. J Reprod Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21763002 Clinical Trial. - Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) reveal increased induction capacity of intracellular interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in peripheral CD8+ lymphocytes co-cultured with intestinal epithelial cells.
Bisping G, Lügering N, Lütke-Brintrup S, Pauels HG, Schürmann G, Domschke W, Kucharzik T. Bisping G, et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001 Jan;123(1):15-22. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01443.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11167992 Free PMC article. - Differential development of CD4 and CD8 cytotoxic T cells (CTL) in PBMC across the leprosy spectrum; IL-6 with IFN-gamma or IL-2 generate CTL in multibacillary patients.
de la Barrera S, Finiasz DM, Fink S, Valdez R, Bottasso O, Balina LM, Sasiain MC. de la Barrera S, et al. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1997 Mar;65(1):45-55. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1997. PMID: 9207753
Cited by
- Mechanisms underlying sex differences in autoimmunity.
Fairweather D, Beetler DJ, McCabe EJ, Lieberman SM. Fairweather D, et al. J Clin Invest. 2024 Sep 17;134(18):e180076. doi: 10.1172/JCI180076. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39286970 Free PMC article. Review. - Sex as a Biological Variable in Early-Phase Oncology Clinical Trials: Enhancing the Path to Personalised Medicine.
Sutherland L, Carter L. Sutherland L, et al. Heliyon. 2024 Jun 7;10(12):e32597. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32597. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39183838 Free PMC article. Review. - Predictors of mortality in severe pneumonia patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Xie K, Guan S, Kong X, Ji W, Du C, Jia M, Wang H. Xie K, et al. Syst Rev. 2024 Aug 5;13(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02621-1. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39103964 Free PMC article. Review. - Sex hormones in COVID-19 severity: The quest for evidence and influence mechanisms.
Xiao H, Wei J, Yuan L, Li J, Zhang C, Liu G, Liu X. Xiao H, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(12):e18490. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18490. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38923119 Free PMC article. Review. - Sex differences in donor T cell targeting of host splenocyte subpopulations in acute and chronic murine graft-vs.-host disease: implications for lupus-like autoimmunity.
Soloviova K, Via CS. Soloviova K, et al. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 10:2024.06.07.595177. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.07.595177. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38915570 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
- Li J, McMurray RW. Effects of estrogen receptor subtype-selective agonists on autoimmune disease in lupus-prone NZB/NZW F1 mouse model. Clin Immunol. 2007;123(2):219–226. - PubMed
- Huang JL, Yao TC, See LC. Prevalence of pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus and juvenile chronic arthritis in a Chinese population: a nation-wide prospective population-based study in Taiwan. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2004;22(6):776–780. - PubMed
- Uekert SJ, Akan G, Evans MD, Li Z, Roberg K, Tisler C, et al. Sex-related differences in immune development and the expression of atopy in early childhood. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;118(6):1375–1381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- AR42525/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025877/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025877-04/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- ES015214/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR056370/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES015214-03/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042525-14/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042525/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG25877/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES015214/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR056370-01/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials