Comparative effects of three popular diets on lipids, endothelial function, and C-reactive protein during weight maintenance - PubMed (original) (raw)
Randomized Controlled Trial
Comparative effects of three popular diets on lipids, endothelial function, and C-reactive protein during weight maintenance
Michael Miller et al. J Am Diet Assoc. 2009 Apr.
Abstract
Although popular diets focus on weight loss and their favorable biochemical and physiological effects, fewer investigations have evaluated the biological impact of these diets during weight maintenance. To study this issue, three popular diets-Atkins, South Beach, and Ornish-were tested in a randomized and counterbalanced crossover study between January and December 2006. Participants completed each of the three 4-week isocaloric dietary intervention phases followed by a 4-week washout period. They were weighed weekly and caloric adjustments made if weight change exceeded 1 kg. At the completion of each dietary phase, 3-day food records were analyzed, fasting blood sampled, and brachial artery reactivity testing performed. Eighteen adults completed all three isocaloric dietary phases. During the South Beach and Ornish maintenance phase, there were significant reductions in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (11.8%; P=0.01, 16.6%; P=0.0006, respectively) compared to prediet baseline. In addition, in contrast to the Atkins maintenance phase, significant reductions in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and apolipoprotein B levels were observed after the South Beach (P=0.003, P=0.05; repeated measures analyses of variance) and Ornish maintenance phases (P=0.0004, P=0.006, repeated measures analyses of variance). Brachial artery testing revealed an inverse correlation between flow-mediated vasodilatation and intake of saturated fat (r=-0.33; P=0.016). These data suggest that during weight maintenance, less favorable biological effects are observed during a simulated, high-fat Atkins diet when compared to the South Beach and Ornish diet. The findings support additional study in subjects with visceral obesity and the metabolic syndrome, in whom an increased risk of coronary disease at baseline may be accentuated with chronic consumption of a diet that exhibits unfavorable effects on lipids and endothelial function.
Figures
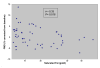
Figure 1
Inverse Correlation Between Saturated Fat Intake (gms/d) & Flow Mediated Vasodilation after correcting for baseline values
Comment in
- Saturated fat and vascular compliance.
Feinman R. Feinman R. J Am Diet Assoc. 2009 Sep;109(9):1524-5; author reply 1525, 1527. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2009.07.034. J Am Diet Assoc. 2009. PMID: 19699829 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Diets with high-fat cheese, high-fat meat, or carbohydrate on cardiovascular risk markers in overweight postmenopausal women: a randomized crossover trial.
Thorning TK, Raziani F, Bendsen NT, Astrup A, Tholstrup T, Raben A. Thorning TK, et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015 Sep;102(3):573-81. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.115.109116. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26178720 Clinical Trial. - Does the DASH diet lower blood pressure by altering peripheral vascular function?
Hodson L, Harnden KE, Roberts R, Dennis AL, Frayn KN. Hodson L, et al. J Hum Hypertens. 2010 May;24(5):312-9. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2009.65. Epub 2009 Aug 6. J Hum Hypertens. 2010. PMID: 19657359 Clinical Trial. - Comparison of the Atkins, Ornish, Weight Watchers, and Zone diets for weight loss and heart disease risk reduction: a randomized trial.
Dansinger ML, Gleason JA, Griffith JL, Selker HP, Schaefer EJ. Dansinger ML, et al. JAMA. 2005 Jan 5;293(1):43-53. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.1.43. JAMA. 2005. PMID: 15632335 Clinical Trial. - A systematic review of high-oleic vegetable oil substitutions for other fats and oils on cardiovascular disease risk factors: implications for novel high-oleic soybean oils.
Huth PJ, Fulgoni VL 3rd, Larson BT. Huth PJ, et al. Adv Nutr. 2015 Nov 13;6(6):674-93. doi: 10.3945/an.115.008979. Print 2015 Nov. Adv Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26567193 Free PMC article. Review. - Effects of carbohydrate-restricted diets on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in overweight and obese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Gjuladin-Hellon T, Davies IG, Penson P, Amiri Baghbadorani R. Gjuladin-Hellon T, et al. Nutr Rev. 2019 Mar 1;77(3):161-180. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuy049. Nutr Rev. 2019. PMID: 30544168
Cited by
- Differential Deleterious Impact of Highly Saturated Versus Monounsaturated Fat Intake on Vascular Function, Structure, and Mechanics in Mice.
Vega-Martín E, Gil-Ortega M, González-Blázquez R, Benedito S, Fernández-Felipe J, Ruiz-Gayo M, Del Olmo N, Chowen JA, Frago LM, Somoza B, Fernández-Alfonso MS. Vega-Martín E, et al. Nutrients. 2021 Mar 19;13(3):1003. doi: 10.3390/nu13031003. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33808927 Free PMC article. - Endotheliopathy of Obesity.
Cooke JP. Cooke JP. Circulation. 2020 Jul 28;142(4):380-383. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047574. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Circulation. 2020. PMID: 32718250 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Endothelium-gut communication: IGF-1Rs crosstalk with microbiota.
Bouman Chen Z, Kaur Malhi N. Bouman Chen Z, et al. EMBO Rep. 2021 May 5;22(5):e52896. doi: 10.15252/embr.202152896. Epub 2021 May 2. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 33938110 Free PMC article. - Fibrates, Hypertriglyceridemia, and CVD Risk: Where Do We Stand After the PROMINENT Trial for Triglyceride Lowering?
Chukwurah MI, Miller M. Chukwurah MI, et al. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023 Sep;25(9):987-992. doi: 10.1007/s11886-023-01926-2. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37505399 Review. - Endothelial function and weight loss: comparison of low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets.
Mohler ER 3rd, Sibley AA, Stein R, Davila-Roman V, Wyatt H, Badellino K, Rader DJ, Klein S, Foster GD. Mohler ER 3rd, et al. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013 Mar;21(3):504-9. doi: 10.1002/oby.20055. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013. PMID: 23404949 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Malik VS, Hu FB. Popular weight-loss diets: from evidence to practice. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007;4:34–41. - PubMed
- Brousseau ME, Schaefer EJ. Diet and coronary heart disease: clinical trials. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2000;2:487–493. - PubMed
- Dietschy JM. Dietary fatty acids and the regulation of plasma low-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations. J Nutr. 1998;128:444S–448S. - PubMed
- Keogh JB, Grieger JA, Noakes M, Clifton PM. Flow-mediated dilatation is impaired by a high-saturated fat diet but not by a high-carbohydrate diet. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:1274–1279. - PubMed
- Robinson SD, Harding SA, Cummins P, et al. Functional interplay between platelet activation and endothelial dysfunction in patients with coronary heart disease. Platelets. 2006;17:158–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials