Binding of SARS coronavirus to its receptor damages islets and causes acute diabetes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Binding of SARS coronavirus to its receptor damages islets and causes acute diabetes
Jin-Kui Yang et al. Acta Diabetol. 2010 Sep.
Abstract
Multiple organ damage in severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) patients is common; however, the pathogenesis remains controversial. This study was to determine whether the damage was correlated with expression of the SARS coronavirus receptor, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), in different organs, especially in the endocrine tissues of the pancreas, and to elucidate the pathogenesis of glucose intolerance in SARS patients. The effect of clinical variables on survival was estimated in 135 SARS patients who died, 385 hospitalized SARS patients who survived, and 19 patients with non-SARS pneumonia. A total of 39 SARS patients who had no previous diabetes and received no steroid treatment were compared to 39 matched healthy siblings during a 3-year follow-up period. The pattern of SARS coronavirus receptor-ACE2 proteins in different human organs was also studied. Significant elevations in oxygen saturation, serum creatinine, lactate dehydrogenase, creatine kinase MB isoenzyme, and fasting plasma glucose (FPG), but not in alanine transaminase were predictors for death. Abundant ACE2 immunostaining was found in lung, kidney, heart, and islets of pancreas, but not in hepatocytes. Twenty of the 39 followed-up patients were diabetic during hospitalization. After 3 years, only two of these patients had diabetes. Compared with their non-SARS siblings, these patients exhibited no significant differences in FPG, postprandial glucose (PPG), and insulin levels. The organ involvements of SARS correlated with organ expression of ACE2. The localization of ACE2 expression in the endocrine part of the pancreas suggests that SARS coronavirus enters islets using ACE2 as its receptor and damages islets causing acute diabetes.
Figures
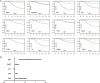
Fig. 1
a Probability of event free (no death) survival among SARS patients divided into two groups [yes (red line) and no (green line)] for old age (≥60 years), male gender, anemia (Hb <10 for men and <9 for women), thrombocytopenia (<80 × 109 per l), low level of CD4 (<200) or CD8 (<150) lymphocytes, clinically significant elevation of ALT (≥80 IU/l), AST (≥80 IU/l), LDH (≥250 IU/l), s-Cr (≥106 μmol/l for men and ≥97 μmol/l for women), hypoxia (SaO2 <93%), and hyperglycemia (FPG ≥7.0 mmol/l). b Multivariate baseline predictors of death including old age (≥60 years), elevated ALT (≥80 IU/l), elevated LDH (≥250 IU/l) and hyperglycemia (FPG ≥7.0 mmol/l) among the SARS patients, presented by hazard ratio and 95% CI
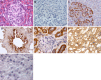
Fig. 2
Immunohistochemically specific pattern of staining for SARS-CoV receptor protein in different organs. Serial sections of the pancreas. a Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) stain shows the exocrine tissue of pancreas (red) with a pancreatic islet (in the middle). b Negative immunostaining control shows no non-specific staining especially caused by endogenous biotin. c Expression of ACE2 in pancreas as assessed by immunohistochemistry shows endocrine tissue is strongly positive compared with exocrine tissue. d Lung: marked ACE2 immunostaining was found in type I and type II alveolar epithelial cells, and capillary endothelium. e Kidney: ACE2 was very weakly present in glomerular visceral and parietal epithelium, but strongly present in the brush border and cytoplasm of proximal tubular cells, and in the cytoplasm of distal tubules and collecting ducts. f Heart: ACE2 was present in the myocytes, myocardium, border zone, endothelium of small-to-large arteries as well as sporadically within the smooth muscle of these vessels. g Liver: Küpffer cells, hepatocytes, and the endothelium of sinusoids were negative
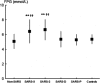
Fig. 3
Changes in FPG levels during the clinical course of SARS during follow-up. Non-SARS: FPG level in patients initially suspected of having SARS but later diagnosed with non-SARS pneumonia; SARS-0: the initial FPG level in SARS patients within 3 days after hospitalization; SARS-2: the initial FPG level after 2 weeks of hospitalization; SARS-D: the final FPG level before discharge; SARS-P: the FPG level from the follow-up study; Controls: the FPG level in the healthy siblings of SARS patients. **P < 0.01 versus non-SARS patients. †† P < 0.01 versus controls
Similar articles
- ACE2 receptor expression and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection depend on differentiation of human airway epithelia.
Jia HP, Look DC, Shi L, Hickey M, Pewe L, Netland J, Farzan M, Wohlford-Lenane C, Perlman S, McCray PB Jr. Jia HP, et al. J Virol. 2005 Dec;79(23):14614-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.23.14614-14621.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16282461 Free PMC article. - Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis.
Hamming I, Timens W, Bulthuis ML, Lely AT, Navis G, van Goor H. Hamming I, et al. J Pathol. 2004 Jun;203(2):631-7. doi: 10.1002/path.1570. J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15141377 Free PMC article. - Plasma glucose levels and diabetes are independent predictors for mortality and morbidity in patients with SARS.
Yang JK, Feng Y, Yuan MY, Yuan SY, Fu HJ, Wu BY, Sun GZ, Yang GR, Zhang XL, Wang L, Xu X, Xu XP, Chan JC. Yang JK, et al. Diabet Med. 2006 Jun;23(6):623-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2006.01861.x. Diabet Med. 2006. PMID: 16759303 - Receptor recognition and cross-species infections of SARS coronavirus.
Li F. Li F. Antiviral Res. 2013 Oct;100(1):246-54. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.08.014. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Antiviral Res. 2013. PMID: 23994189 Free PMC article. Review. - Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: a functional receptor for SARS coronavirus.
Kuhn JH, Li W, Choe H, Farzan M. Kuhn JH, et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Nov;61(21):2738-43. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4242-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15549175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Cushing's syndrome and COVID-19.
Attia A, Bertherat J. Attia A, et al. Pituitary. 2024 Nov 14. doi: 10.1007/s11102-024-01466-0. Online ahead of print. Pituitary. 2024. PMID: 39541074 Review. - Association of COVID-19 infection and the risk of new incident diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Zhou J, Wang Y, Xu R. Zhou J, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 26;15:1429848. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1429848. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39253580 Free PMC article. - Changing Spectrum of Invasive Fungal Infections of the Anterior Skull Base.
Bhuskute GS, Keshri AK, Seduchidambaram M, Dubey A, Hameed N, Chidambaram K, Muraleedharan M, Das KK, Mehrotra A, Srivastava A, Jaiswal A, Kumar R, Manogaran RS. Bhuskute GS, et al. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2023 Aug 29;85(5):458-464. doi: 10.1055/a-2148-2259. eCollection 2024 Oct. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2023. PMID: 39228884 Free PMC article. - Long-term outcome of patients with diabetic-range hyperglycemia first detected during admission for COVID-19: A single-center observational study.
Agarwal K, Kirti R, Shyama S, Kumar P, Biswas R, Ojha VS. Agarwal K, et al. J Family Med Prim Care. 2024 Aug;13(8):3374-3380. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_140_24. Epub 2024 Jul 26. J Family Med Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 39228533 Free PMC article. - Association Between COVID-19 and Diabetes Management Indices in Japanese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study.
Furumachi K, Kagatsume T, Higuchi A, Kozaru M, Kumagai E, Hosohata K. Furumachi K, et al. Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Aug 29;17:3759-3767. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S475917. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39224903 Free PMC article.
References
- Yang JK, Feng Y, Yuan MY, Yuan SY, Fu HJ, Wu BY, Sun GZ, Yang GR, Zhang XL, Wang L, Xu X, Xu XP, Chan JC. Plasma glucose levels and diabetes are independent predictors for mortality and morbidity in patients with SARS. Diabet Med. 2006;23:623–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2006.01861.x. - DOI - PubMed
- Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, Godbout K, Gosselin M, Stagliano N, Donovan M, Woolf B, Robison K, Jeyaseelan R, Breitbart RE, Acton S. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1–9. Circ Res. 2000;87:E1–E9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous